Abstract
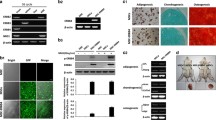
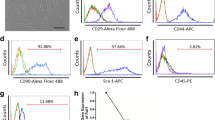
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are a promising source for cell-based treatment of myocardial infarction (MI), but existing strategies are restricted by low cell survival and engraftment. We examined whether SDF-1 transfection improve MSC viability and paracrine action in infarcted hearts. We found SDF-1-modified MSCs effectively expressed SDF-1 for at least 21days after exposure to hypoxia. The apoptosis of Ad-SDF-1-MSCs was 42% of that seen in Ad-EGFP-MSCs and 53% of untreated MSCs. In the infarcted hearts, the number of DAPI-labeling cells in the Ad-SDF-1-MSC group was 5-fold that in the Ad-EGFP-MSC group. Importantly, expression of antifibrotic factor, HGF, was detected in cultured MSCs, and HGF expression levels were higher in Ad-SDF-MSC-treated hearts, compared with Ad-EGFP-MSC or control hearts. Compared with the control group, Ad-SDF-MSC transplantation significantly decreased the expression of collagens I and III and matrix metalloproteinase 2 and 9, but heart function was improved in d-SDF-MSC-treated animals. In conclusion, SDF-1-modified MSCs enhanced the tolerance of engrafted MSCs to hypoxic injury in vitro and improved their viability in infarcted hearts, thus helping preserve the contractile function and attenuate left ventricle (LV) remodeling, and this may be at least partly mediated by enhanced paracrine signaling from MSCs via antifibrotic factors such as HGF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoki, M., Morishita, R., Taniyama, Y., Kida, I., Moriguchi, A., Matsumoto, K., Nakamura, T., Kaneda, Y., Higaki, J., and Ogihara, T. (2000). Angiogenesis induced by hepatocyte growth factor in non-infarcted myocardium and infarcted myocardium, up-regulation of essential transcription factor for angiogenesis, ets. Gene Ther. 7, 417–427.
Barkho, B.Z., Munoz, A.E., Li, X., Li, L., Cunningham, L.A., and Zhao, X. (2008). Endogenous matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-3 and MMP-9 promote the differentiation and migration of adult neural progenitor cells in response to chemokines. Stem Cells 26, 3139–3149.
Chen, M., Xie, H.Q., Deng, L., Li, X.Q., Wang, Y., Zhi, W., and Yang, Z.M. (2008). Stromal cell-derived factor-1 promotes bone marrow-derived cells differentiation to cardiomyocyte phenotypes in vitro. Cell Prolif. 41, 336–347.
Elmadbouh, I., Haider, HKh., Jiang, S., Idris, N.M., Lu, G., and Ashraf, M. (2007). Ex vivo delivered stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha promotes stem cell homing and induces angiomyogenesis in the infarcted myocardium. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 42, 792–803.
Fedak, P.W. (2008). Paracrine effects of cell transplantation, modifying ventricular remodeling in the failing heart. Semin. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 20, 87–93.
Gnecchi, M., He, H., Noiseux, N., Liang, O.D., Zhang, L., Morello, F., Mu, H., Melo, L.G., Pratt, R.E., Ingwall, J.S., et al. (2006). Evidence supporting paracrine hypothesis for Akt-modified mesenchymal stem cell-mediated cardiac protection and functional improvement. FASEB J. 20, 661–669.
Guo, J., Lin, G.S., Bao, C.Y., Hu, Z.M., and Hu, M.Y. (2007). Antiinflammation role for mesenchymal stem cells transplantation in myocardial infarction. Inflammation 30, 97–104.
Hiasa, K., Ishibashi, M., Ohtani, K., Inoue, S., Zhao, Q., Kitamoto, S., Sata, M., Ichiki, T., Takeshita, A., and Egashira, K. (2004). Gene transfer of stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha enhances ischemic vasculogenesis and angiogenesis via vascular endothelial growth factor/endothelial nitric oxide synthase-related pathway, nextgeneration chemokine therapy for therapeutic neovascularization. Circulation 109, 2454–2461.
Higashiyama, R., Inagaki, Y., Hong, Y.Y., Kushida, M., Nakao, S., Niioka, M., Watanabe, T., Okano, H., Matsuzaki, Y., Shiota, G., et al. (2007). Bone marrow-derived cells express matrix metal loproteinases and contribute to regression of liver fibrosis in mice. Hepatology 45, 213–222.
Hu, X., Yu, S.P., Fraser, J.L., Lu, Z., Ogle, M.E., Wang, J.A., and Wei, L. (2008). Transplantation of hypoxia-preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells improves infarcted heart function via enhanced survival of implanted cells and angiogenesis. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 135, 799–808.
Inagaki, Y., Higashiyama, R., and Okazaki, I. (2007). Treatment strategy for liver fibrosis through recruitment and differentiation of bone marrow stem/progenitor cells. Hepatol. Res. 37, 991–993.
Janowska-Wieczorek, A., Marquez, L.A., Dobrowsky, A., Ratajczak, M.Z., and Cabuhat, M.L. (2000). Differential MMP and TIMP production by human marrow and peripheral blood CD34(+) cells in response to chemokines. Exp. Hematol. 28, 1274–1285.
Kinnaird, T., Stabile, E., Burnett, M.S., Lee, C.W., Barr, S., and Fuchs, S. (2004). Marrow-derived stromal cells express genes encoding a broad spectrum of arteriogenic cytokines and promote in vitro and in vivo arteriogenesis through paracrine mechanisms. Circ. Res. 94, 678–685.
Koch, K.C., Schaefer, W.M., Liehn, E.A., Rammos, C., Mueller, D., Schroeder, J., Dimassi, T., Stopinski, T., and Weber, C. (2006). Effect of catheter-based transendocardial delivery of stromal cell-derived factor 1alpha on left ventricular function and perfusion in a porcine model of myocardial infarction. Basic Res. Cardiol. 101, 69–77.
Kollet, O., Shivtiel, S., Chen, Y.Q., Suriawinata, J., Thung, S.N., Dabeva, M.D., Kahn, J., Spiegel, A., Dar, A., Samira, S., et al. (2003). HGF, SDF-1, and MMP-9 are involved in stress-induced human CD34+ stem cell recruitment to the liver. J. Clin. Invest. 112, 160–169.
Kortesidis, A., Zannettino, A., Isenmann, S., Shi, S., Lapidot, T., and Gronthos, S. (2005). Stromal-derived factor-1 promotes the growth, survival, and development of human bone marrow stromal stem cells. Blood 105, 3793–3801.
Li, R.K., Mickle, D.A., Weisel, R.D., Rao, V., and Jia, Z.Q. (2001). Optimal time for cardiomyocyte transplantation to maximize myocardial function after left ventricular injury. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 72, 1957–1963.
Li, L., Zhang, Y., Li, Y., Yu, B., Xu, Y., Zhao, S., and Guan, Z. (2008). Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation attenuates cardiac fibrosis associated with isoproterenol-induced global heart failure. Transpl. Int. 21, 1181–1189.
Li, W., Ma, N., Ong, L.L., Nesselmann, C., Klopsch, C., Ladilov, Y., Furlani, D., Piechaczek, C., Moebius, J.M., Lützow, K., et al. (2008). Bcl-2 engineered MSCs inhibited apoptosis and improved heart function. Stem Cells 25, 2118–2127.
Liu, X.H., Bai, C.G., Xu, Z.Y., Huang, S.D., Yuan, Y., Gong, D.J., and Zhang, J.R. (2008). Therapeutic potential of angiogenin modified mesenchymal stem cells, angiogenin improves mesenchymal stem cells survival under hypoxia and enhances vasculogenesis in myocardial infarction. Microvasc. Res. 76, 23–30.
Mangi, A.A., Noiseux, N., Kong, D., He, H., Rezvani, M., Ingwall, J.S., and Dzau, V.J. (2003). Mesenchymal stem cells modified with Akt prevent remodeling and restore performance of infarcted hearts. Nat. Med. 9, 1195–1201.
Miyagawa, S., Sawa, Y., Fukuda, K., Hisaka, Y., Taketani, S., Memon, I.A., and Matsuda, H. (2006). Angiogenic gene cell therapy using suicide gene system regulates the effect of angiogenesis in infarcted rat heart. Transplantation 81, 902–907.
Morita, H., Khanal, S., Rastogi, S., Suzuki, G., Imai, M., Todor, A., Sharov, V.G., Goldstein, S., O’Neill, T.P., and Sabbah, H.N. (2006). Selective matrix metalloproteinase inhibition attenuates progression of left ventricular dysfunction and remodeling in dogs with chronic heart failure. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 290, H2522–H2527.
Nakamura, T., Mizuno, S., Matsumoto, K., Sawa, Y., Matsuda, H., and Nakamura, T. (2000). Myocardial protection from ischemia/reperfusion injury by endogenous and exogenous HGF. J. Clin. Invest. 106, 1511–1519.
Novotny, N.M., Ray, R., Markel, T.A., Crisostomo, P.R., Wang, M., Wang, Y., and Meldrum, D.R. (2008). Stem cell therapy in myocardial repair and remodeling. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 207, 423–434.
Ohnishi, S., Sumiyoshi, H., Kitamura, S., and Nagaya, N. (2007). Mesenchymal stem cells attenuate cardiac fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis through paracrine actions. FEBS Lett. 581, 3961–3966.
Pasha, Z., Wang, Y., Sheikh, R., Zhang, D., Zhao, T., and Ashraf, M. (2008). Preconditioning enhances cell survival and differentiation of stem cells during transplantation in infarcted myocardium. Cardiovasc. Res. 77, 134–142.
Petit, I., Goichberg, P., Spiegel, A., Peled, A., Brodie, C., Seger, R., Nagler, A., Alon, R., and Lapidot, T. (2005). Atypical PKC-zeta regulates SDF-1-mediated migration and development of human CD34+ progenitor cells. J. Clin. Invest 115, 168–176.
Pittenger, M.F., Mackay, A.M., Beck, S.C., Jaiswal, R.K., Douglas, R., Mosca, J.D., Moorman, M.A., Simonetti, D.W., Craig, S., and Marshak, D.R. (1999). Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science 284, 143–173.
Pons, J., Huang, Y., Arakawa-Hoyt, J., Washko, D., Takagawa, J., Ye, J., Grossman, W., and Su, H. (2008). VEGF improves survival of mesenchymal stem cells in infarcted hearts. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 376, 419–422.
Reinhardt, D., Sigusch, H.H., Hensse, J., Tyagi, S.C., Körfer, R., and Figulla, H.R. (2002). Cardiac remodelling in end stage heart failure, upregulation of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) irrespective of the underlying disease, and evidence for a direct inhibitory effect of ACE inhibitors on MMP. Heart 88, 525–530.
Ruiz de Almodovar, C., Luttun, A., and Carmeliet, P. (2006). An SDF-1 trap for myeloid cells stimulates angiogenesis. Cell 124, 18–21.
Saxena, A., Fish, J.E., White, M.D., Yu, S., Smyth, J.W., Shaw, R.M., DiMaio, J.M., and Srivastava, D. (2008). Stromal cellderived factor-1alpha is cardioprotective after myocardial infarction. Circulation 117, 2224–2231.
Schober, A., Karshovska, E., Zernecke, A., and Weber, C. (2006). SDF-1alpha-mediated tissue repair by stem cells, a promising tool in cardiovascular medicine? Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 16, 103–108.
Schuh, A., Liehn, E.A., Sasse, A., Hristov, M., Sobota, R., Kelm, M., Merx, M.W., and Weber, C. (2008). Transplantation of endothelial progenitor cells improves neovascularization and left ventricular function after myocardial infarction in a rat model. Basic Res. Cardiol. 103, 69–77.
Schuleri, K.H., Boyle, A.J., and Hare, J.M. (2007). Mesenchymal stem cells for cardiac regenerative therapy. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 180, 195–218.
Shao, H., Tan, Y., Eton, D., Yang, Z., Uberti, M.G., Li, S., Schulick, A., and Yu, H. (2008). Statin and stromal cell derived factor-1 additively promote angiogenesis by enhancement of progenitor cells incorporation into new vessels. Stem Cells 26, 1376–1384.
Son, B.R., Marquez-Curtis, L.A., Kucia, M., Wysoczynski, M., Turner, A.R., Ratajczak, J., Ratajczak, M.Z., and Janowska-Wieczorek, A. (2006). Migration of bone marrow and cord blood mesenchymal stem cells in vitro is regulated by stromal-derived factor-1-CXCR4 and hepatocyte growth factor-c-met axes and involves matrix metalloproteinases. Stem Cells 24, 1254–1264.
Sun, L., Cui, M., Wang, Z., Feng, X., Mao, J., Chen, P., Kangtao, M., Chen, F., and Zhou, C. (2007). Mesenchymal stem cells modified with angiopoietin-1 improve remodeling in a rat model of acute myocardial infarction. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 357, 779–784.
Tang, J.M., Xie, Q.Y., Pan, G.D., Wang, J.N., and Wang, M.J. (2006). Mesenchymal stem cells participate in angiogenesis and improve heart function in rat model of myocardial ischemia with reperfusion. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 30, 353–361.
Tang, J., Wang, J., Yang, J., and Kong, X. (2008). Adenovirusmediated stromal cell-derived-factor-1alpha gene transfer induces cardiac preservation after infarction via angiogenesis of CD133+ stem cells and anti-apoptosis. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 7, 767–770.
Tang, J., Wang, J., Yang, J., Kong, X., Zheng, F., Guo, L., Zhang, L., and Huang, Y. (2009a). Mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing SDF-1 promote angiogenesis and improve heart function in experimental myocardial infarction in rats. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 36, 644–650.
Tang, J., Wang, J., Song, H., Huang, Y., Yang, J., Kong, X., Guo, L., Zheng, F., and Zhang, L. (2009b). Adenovirus-mediated stromal cell-derived factor-1 alpha gene transfer improves cardiac structure and function after experimental myocardial infarction through angiogenic and antifibrotic actions. Mol. Biol. Rep. [10.1007/s11033-009-9642-z]
Taniyama, Y., Morishita, R., Aoki, M., Hiraoka, K., Yamasaki, K., Hashiya, N., Matsumoto, K., Nakamura, T., Kaneda, Y., and Ogihara, T. (2002). Angiogenesis and antifibrotic action by hepatocyte growth factor in cardiomyopathy. Hypertension 40, 47–53.
Ueda, H., Nakamura, T., Matsumoto, K., Sawa, Y., Matsuda, H., and Nakamura, T. (2001). A potential cardioprotective role of hepatocyte growth factor in myocardial infarction in rats. Cardiovasc. Res. 51, 41–50.
Wang, Y., Ahmad, N., Wani, M.A., and Ashraf, M. (2004). Hepatocyte growth factor prevents ventricular remodeling and dysfunction in mice via Akt pathway and angiogenesis. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 37, 1041–1052.
Xu, X., Xu, Z., Xu, Y., and Cui, G. (2005). Effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on extracellular matrix after myocardial infarction in rats. Coron. Artery Dis. 16, 245–255.
Yamaguchi, J., Kusano, K.F., Masuo, O., Kawamoto, A., Silver, M., Murasawa, S., Bosch-Marce, M., Masuda, H., Losordo, D.W., Isner, J.M., et al. (2003). Stromal cell-derived factor-1 effects on ex vivo expanded endothelial progenitor cell recruitment for ischemic neovascularization. Circulation 107, 1322–1328.
Yang, Z.J., Ma, D.C., Wang, W., Xu, S.L., Zhang, Y.Q., Chen, B., Zhou, F., Zhu, T.B., Wang, L.S., Xu, Z.Q., et al. (2006). Experimental study of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells combined with hepatocyte growth factor transplantation via noninfarct-relative artery in acute myocardial infarction. Gene Ther. 13, 1564–1568.
Zhang, M., Mal, N., Kiedrowski, M., Chacko, M., Askari, A.T., and Popovic, Z.B. (2007). SDF-1 expression by mesenchymal stem cells results in trophic support of cardiac myocytes after myocardial infarction. FASEB J. 21, 3197–3207.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, J., Wang, J., Guo, L. et al. Mesenchymal stem cells modified with stromal cell-derived factor 1α improve cardiac remodeling via paracrine activation of hepatocyte growth factor in a rat model of myocardial infarction. Mol Cells 29, 9–19 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-010-0001-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-010-0001-7