Abstract
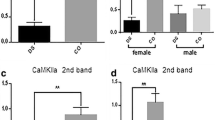
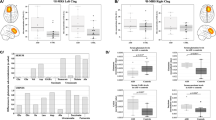
In this study, cortical receptor complex levels were determined in fetal Down syndrome (DS, trisomy 21) brain. Frontal cortices were obtained from individuals with DS (19th–22nd week of gestation) and controls. Membrane proteins were extracted, assayed on blue native gels and immunoblotted with brain receptor antibodies. Levels of a D1R-containing complex were markedly decreased in male and female cortices of DS individuals. Females with DS had significant reductions of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors α4 and α7, NMDA receptor GluN1 and AMPA receptor GluA1- and GluA3-containing receptor complexes. Levels of other brain receptor complexes (5-hydroxytryptamine 1A, GluA2 and GluR4 receptor-containing complexes) were comparable between the groups of females. Levels of GluA2- and GluA3-containing complexes were significantly increased in males. Decreased levels of D1R complexes in both sexes, along with the significant reduction of α4, α7-containing receptor complexes observed in females, may explain the brain deficits and impaired cognition observed in DS.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altafaj X, Ortiz-Abalia J, Fernandez M, Potier MC, Laffaire J, Andreu N, Dierssen M, Gonzalez-Garcia C, Cena V, Marti E, Fillat C (2008) Increased NR2A expression and prolonged decay of NMDA-induced calcium transient in cerebellum of TgDyrk1A mice, a mouse model of Down syndrome. Neurobiol Dis 32(3):377–384. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2008.07.024
Arai Y, Mizuguchi M, Takashima S (1996) Excessive glutamate receptor 1 immunoreactivity in adult Down syndrome brains. Pediatr Neurol 15(3):203–206 (S0887899496001671)
Arnsten AF, Cai JX, Murphy BL, Goldman-Rakic PS (1994) Dopamine D1 receptor mechanisms in the cognitive performance of young adult and aged monkeys. Psychopharmacology 116(2):143–151
Asher O, Tanya R, Shula P (2011) Adaptive and Behavioral Development in Children with Down Syndrome at School Age with Special Emphasis on Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). Prenatal Diagnosis and Screening for Down Syndrome. doi:10.5772/17455
Barch DM (2004) Pharmacological manipulation of human working memory. Psychopharmacology 174(1):126–135. doi:10.1007/s00213-003-1732-3
Bar-Peled O, Gross-Isseroff R, Ben-Hur H, Hoskins I, Groner Y, Biegon A (1991a) Fetal human brain exhibits a prenatal peak in the density of serotonin 5-HT1A receptors. Neurosci Lett 127(2):173–176
Bar-Peled O, Israeli M, Ben-Hur H, Hoskins I, Groner Y, Biegon A (1991b) Developmental pattern of muscarinic receptors in normal and Down’s syndrome fetal brain–an autoradiographic study. Neurosci Lett 133(2):154–158
Beaulieu JM, Gainetdinov RR (2011) The physiology, signaling, and pharmacology of dopamine receptors. Pharmacol Rev 63(1):182–217. doi:10.1124/pr.110.002642
Best TK, Siarey RJ, Galdzicki Z (2007) Ts65Dn, a mouse model of Down syndrome, exhibits increased GABAB-induced potassium current. J Neurophysiol 97(1):892–900. doi:10.1152/jn.00626.2006
Braudeau J, Delatour B, Duchon A, Pereira PL, Dauphinot L, de Chaumont F, Olivo-Marin JC, Dodd RH, Herault Y, Potier MC (2011) Specific targeting of the GABA-A receptor alpha5 subtype by a selective inverse agonist restores cognitive deficits in Down syndrome mice. J Psychopharmacol 25(8):1030–1042. doi:10.1177/0269881111405366
Bushnell PJ, Levin ED (1993) Effects of dopaminergic drugs on working and reference memory in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 45(4):765–776
Cai JX, Arnsten AF (1997) Dose-dependent effects of the dopamine D1 receptor agonists A77636 or SKF81297 on spatial working memory in aged monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 283(1):183–189
Castellano C, Cabib S, Puglisi-Allegra S, Gasbarri A, Sulli A, Pacitti C, Introini-Collison IB, McGaugh JL (1999) Strain-dependent involvement of D1 and D2 dopamine receptors in muscarinic cholinergic influences on memory storage. Behav Brain Res 98(1):17–26 (S0166432898000461)
Clausen B, Schachtman TR, Mark LT, Reinholdt M, Christoffersen GR (2011) Impairments of exploration and memory after systemic or prelimbic D1-receptor antagonism in rats. Behav Brain Res 223(2):241–254. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2011.03.069
Cortes R, Probst A, Palacios JM (1988) Decreased densities of dopamine D1 receptors in the putamen and hippocampus in senile dementia of the Alzheimer type. Brain Res 475(1):164–167
Costa AC (2011) On the promise of pharmacotherapies targeted at cognitive and neurodegenerative components of Down syndrome. Dev Neurosci 33(5):414–427. doi:10.1159/000330861
de Lima MN, Presti-Torres J, Dornelles A, Scalco FS, Roesler R, Garcia VA, Schroder N (2011) Modulatory influence of dopamine receptors on consolidation of object recognition memory. Neurobiol Learn Mem 95(3):305–310. doi:10.1016/j.nlm.2010.12.007
Deutsch SI, Rosse RB, Mastropaolo J, Chilton M (2003) Progressive worsening of adaptive functions in Down syndrome may be mediated by the complexing of soluble Abeta peptides with the alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor: therapeutic implications. Clin Neuropharmacol 26(5):277–283
El-Ghundi M, Fletcher PJ, Drago J, Sibley DR, O’Dowd BF, George SR (1999) Spatial learning deficit in dopamine D(1) receptor knockout mice. Eur J Pharmacol 383(2):95–106 (S0014-2999(99)00573-7)
El-Ghundi M, O’Dowd BF, George SR (2001) Prolonged fear responses in mice lacking dopamine D1 receptor. Brain Res 892(1):86–93 (S0006-8993(00)03234-0)
El-Ghundi M, O’Dowd BF, George SR (2007) Insights into the role of dopamine receptor systems in learning and memory. Rev Neurosci 18(1):37–66
Engidawork E, Lubec G (2003) Molecular changes in fetal Down syndrome brain. J Neurochem 84(5):895–904 (1614)
Engidawork E, Gulesserian T, Balic N, Cairns N, Lubec G (2001) Changes in nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunits expression in brain of patients with Down syndrome and Alzheimer’s disease. J Neural Transm Suppl 61:211–222
Fenu S, Bassareo V, Di Chiara G (2001) A role for dopamine D1 receptors of the nucleus accumbens shell in conditioned taste aversion learning. J Neurosci 21:6897–6904
Ferretti V, Florian C, Costantini VJ, Roullet P, Rinaldi A, De Leonibus E, Oliverio A, Mele A (2005) Co-activation of glutamate and dopamine receptors within the nucleus accumbens is required for spatial memory consolidation in mice. Psychopharmacology 179(1):108–116. doi:10.1007/s00213-005-2144-3
Fodale V, Mafrica F, Caminiti V, Grasso G (2006) The cholinergic system in Down’s syndrome. J Intellect Disabil 10(3):261–274. doi:10.1177/1744629506067615
Gao C, Sun X, Wolf ME (2006) Activation of D1 dopamine receptors increases surface expression of AMPA receptors and facilitates their synaptic incorporation in cultured hippocampal neurons. J Neurochem 98(5):1664–1677. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03999.x
Gardiner KJ (2010) Molecular basis of pharmacotherapies for cognition in Down syndrome. Trends Pharmacol Sci 31(2):66–73. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2009.10.010
Ghafari M, Falsafi SK, Hoeger H, Lubec G (2012a) Hippocampal levels of GluR1 and GluR2 complexes are modulated by training in the Multiple T-maze in C57BL/6J mice. Brain Struct Funct 217(2):353–362. doi:10.1007/s00429-011-0335-8
Ghafari M, Hoger H, Keihan Falsafi S, Russo-Schlaff N, Pollak A, Lubec G (2012b) Mass spectrometrical identification of hippocampal NMDA receptor subunits NR1, NR2A-D and five novel phosphorylation sites on NR2A and NR2B. J Proteome Res 11(3):1891–1896. doi:10.1021/pr201099u
Goldman-Rakic PS, Castner SA, Svensson TH, Siever LJ, Williams GV (2004) Targeting the dopamine D1 receptor in schizophrenia: insights for cognitive dysfunction. Psychopharmacology 174(1):3–16. doi:10.1007/s00213-004-1793-y
Granado N, Ortiz O, Suarez LM, Martin ED, Cena V, Solis JM, Moratalla R (2008) D1 but not D5 dopamine receptors are critical for LTP, spatial learning, and LTP-Induced arc and zif268 expression in the hippocampus. Cereb Cortex 18(1):1–12. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhm026
Granholm AC, Sanders LA, Crnic LS (2000) Loss of cholinergic phenotype in basal forebrain coincides with cognitive decline in a mouse model of Down’s syndrome. Exp Neurol 161(2):647–663. doi:10.1006/exnr.1999.7289
Hasbi A, O’Dowd BF, George SR (2011) Dopamine D1-D2 receptor heteromer signaling pathway in the brain: emerging physiological relevance. Mol Brain 4:26. doi:10.1186/1756-6606-4-26
Hersi AI, Rowe W, Gaudreau P, Quirion R (1995) Dopamine D1 receptor ligands modulate cognitive performance and hippocampal acetylcholine release in memory-impaired aged rats. Neuroscience 69(4):1067–1074 (030645229500319E)
Heston LL (1984) Down’s syndrome and Alzheimer’s dementia: defining an association. Psychiatr Dev 2(4):287–294
Hisahara S, Shimohama S (2011) Dopamine Receptors and Parkinson’s Disease. International Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. doi:10.1155/2011/403039
Horiguchi M, Hannaway KE, Adelekun AE, Huang M, Jayathilake K, Meltzer HY (2013) D(1) receptor agonists reverse the subchronic phencyclidine (PCP)-induced novel object recognition (NOR) deficit in female rats. Behav Brain Res 238:36–43. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2012.09.030
Hu JL, Liu G, Li YC, Gao WJ, Huang YQ (2010) Dopamine D1 receptor-mediated NMDA receptor insertion depends on Fyn but not Src kinase pathway in prefrontal cortical neurons. Mol Brain 3:20. doi:10.1186/1756-6606-3-20
Kang SU, Fuchs K, Sieghart W, Lubec G (2008) Gel-based mass spectrometric analysis of recombinant GABA(A) receptor subunits representing strongly hydrophobic transmembrane proteins. J Proteome Res 7(8):3498–3506. doi:10.1021/pr800236u
Kerr JN, Wickens JR (2001) Dopamine D-1/D-5 receptor activation is required for long-term potentiation in the rat neostriatum in vitro. J Neurophysiol 85(1):117–124
Kleschevnikov AM, Belichenko PV, Gall J, George L, Nosheny R, Maloney MT, Salehi A, Mobley WC (2012) Increased efficiency of the GABAA and GABAB receptor-mediated neurotransmission in the Ts65Dn mouse model of Down syndrome. Neurobiol Dis 45(2):683–691. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2011.10.009
Lauzon NM, Bechard M, Ahmad T, Laviolette SR (2013) Supra-normal stimulation of dopamine D1 receptors in the prelimbic cortex blocks behavioral expression of both aversive and rewarding associative memories through a cyclic-AMP-dependent signaling pathway. Neuropharmacology 67:104–114. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.10.029
Lebel M, Robinson P, Cyr M (2007) Canadian Association of Neurosciences Review: the role of dopamine receptor function in neurodegenerative diseases. Can J Neurol Sci 34(1):18–29
Lejeune S, Dourmap N, Martres MP, Giros B, Dauge V, Naudon L (2013) The dopamine D1 receptor agonist SKF 38393 improves temporal order memory performance in maternally deprived rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem. doi:10.1016/j.nlm.2013.10.005
Maatta T, Tervo-Maatta T, Taanila A, Kaski M, Iivanainen M (2006) Mental health, behaviour and intellectual abilities of people with Down syndrome. Downs Syndr Res Pract 11(1):37–43
Manago F, Castellano C, Oliverio A, Mele A, De Leonibus E (2009) Role of dopamine receptors subtypes, D1-like and D2-like, within the nucleus accumbens subregions, core and shell, on memory consolidation in the one-trial inhibitory avoidance task. Learn Mem 16(1):46–52. doi:10.1101/lm.1177509
Martinez-Cue C, Martinez P, Rueda N, Vidal R, Garcia S, Vidal V, Corrales A, Montero JA, Pazos A, Florez J, Gasser R, Thomas AW, Honer M, Knoflach F, Trejo JL, Wettstein JG, Hernandez MC (2013) Reducing GABAA alpha5 receptor-mediated inhibition rescues functional and neuromorphological deficits in a mouse model of down syndrome. J Neurosci 33(9):3953–3966. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1203-12.2013
Mele A, Castellano C, Felici A, Cabib S, Caccia S, Oliverio A (1996) Dopamine-N-methyl-D-aspartate interactions in the modulation of locomotor activity and memory consolidation in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 308(1):1–12 (0014-2999(96)00266-X)
Nai Q, Li S, Wang SH, Liu J, Lee FJ, Frankland PW, Liu F (2010) Uncoupling the D1-N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor complex promotes NMDA-dependent long-term potentiation and working memory. Biol Psychiatry 67(3):246–254. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.08.011
Oka A, Takashima S (1999) The up-regulation of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGluR5) in Down’s syndrome brains. Acta Neuropathol 97(3):275–278
Pei L, Li S, Wang M, Diwan M, Anisman H, Fletcher PJ, Nobrega JN, Liu F (2010) Uncoupling the dopamine D1-D2 receptor complex exerts antidepressant-like effects. Nat Med 16(12):1393–1395. doi:10.1038/nm.2263
Pezze M, Bast T (2012) Dopaminergic modulation of hippocampus-dependent learning: blockade of hippocampal D1-class receptors during learning impairs 1-trial place memory at a 30-min retention delay. Neuropharmacology 63(4):710–718. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.05.036
Rinne JO, Rinne JK, Laakso K, Lonnberg P, Rinne UK (1985) Dopamine D-1 receptors in the parkinsonian brain. Brain Res 359(1–2):306–310 (0006-8993(85)91441-6)
Rios Valentim SJ, Gontijo AV, Peres MD, Rodrigues LC, Nakamura-Palacios EM (2009) D1 dopamine and NMDA receptors interactions in the medial prefrontal cortex: modulation of spatial working memory in rats. Behav Brain Res 204(1):124–128. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2009.05.026
Sawaguchi T (2000) The role of D1-dopamine receptors in working memory-guided movements mediated by frontal cortical areas. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 7(1):9–19 (S1353-8020(00)00044-4)
Schicknick H, Reichenbach N, Smalla KH, Scheich H, Gundelfinger ED, Tischmeyer W (2012) Dopamine modulates memory consolidation of discrimination learning in the auditory cortex. Eur J Neurosci 35(5):763–774. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2012.07994.x
Scott-McKean JJ, Costa AC (2011) Exaggerated NMDA mediated LTD in a mouse model of Down syndrome and pharmacological rescuing by memantine. Learn Mem 18(12):774–778. doi:10.1101/lm.024182.111
Seeman P, Niznik HB, Guan HC, Booth G, Ulpian C (1989) Link between D1 and D2 dopamine receptors is reduced in schizophrenia and Huntington diseased brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86(24):10156–10160
Siddiqui A, Lacroix T, Stasko MR, Scott-McKean JJ, Costa AC, Gardiner KJ (2008) Molecular responses of the Ts65Dn and Ts1Cje mouse models of Down syndrome to MK-801. Genes Brain Behav 7(7):810–820. doi:10.1111/j.1601-183X.2008.00428.x
Takahashi H, Kato M, Takano H, Arakawa R, Okumura M, Otsuka T, Kodaka F, Hayashi M, Okubo Y, Ito H, Suhara T (2008) Differential contributions of prefrontal and hippocampal dopamine D(1) and D(2) receptors in human cognitive functions. J Neurosci 28(46):12032–12038. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3446-08.2008
Tang TS, Chen X, Liu J, Bezprozvanny I (2007) Dopaminergic signaling and striatal neurodegeneration in Huntington’s disease. J Neurosci 27(30):7899–7910. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1396-07.2007
Unterberger U, Lubec G, Dierssen M, Stoltenburg-Didinger G, Farreras JC, Budka H (2003) The cerebral cortex in fetal Down syndrome. J Neural Transm Suppl 67:159–163
Wallace TL, Ballard TM, Pouzet B, Riedel WJ, Wettstein JG (2011) Drug targets for cognitive enhancement in neuropsychiatric disorders. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 99(2):130–145. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2011.03.022
Wang X, Zhao Y, Zhang X, Badie H, Zhou Y, Mu Y, Loo LS, Cai L, Thompson RC, Yang B, Chen Y, Johnson PF, Wu C, Bu G, Mobley WC, Zhang D, Gage FH, Ranscht B, Zhang YW, Lipton SA, Hong W, Xu H (2013) Loss of sorting nexin 27 contributes to excitatory synaptic dysfunction by modulating glutamate receptor recycling in Down’s syndrome. Nat Med 19(4):473–480. doi:10.1038/nm.3117
Welinder C, Ekblad L (2011) Coomassie staining as loading control in Western blot analysis. J Proteome Res 10(3):1416–1419. doi:10.1021/pr1011476
White NM, Packard MG, Seamans J (1993) Memory enhancement by post-training peripheral administration of low doses of dopamine agonists: possible autoreceptor effect. Behav Neural Biol 59(3):230–241
Yang SN (2000) Sustained enhancement of AMPA receptor- and NMDA receptor-mediated currents induced by dopamine D1/D5 receptor activation in the hippocampus: an essential role of postsynaptic Ca2+. Hippocampus 10(1):57–63. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-1063(2000)
Zarrindast MR, Sattari-Naeini M, Motamedi F (1992) Effect of D-1 or D-2 receptor stimulation on memory retrieval in mice. J Psychopharmacol 6(4):526–531. doi:10.1177/026988119200600409
Zarrindast MR, Ardjmand A, Ahmadi S, Rezayof A (2012) Activation of dopamine D1 receptors in the medial septum improves scopolamine-induced amnesia in the dorsal hippocampus. Behav Brain Res 229(1):68–73. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2011.12.033
Acknowledgments
The human biospecimens used in this project were provided by the Fetal Tissue Bank of the Vall d’Hebron University Hospital Biobank with appropriate ethics approval. The work was partially supported by the Verein zur Durchführung der wissenschaftlichen Forschung auf dem Gebiet der Neonatologie und Kinder intensiv Medizin.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
S. Keihan Falsafi, M. Dierssen and M. Ghafari contributed equally to the paper.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keihan Falsafi, S., Dierssen, M., Ghafari, M. et al. Reduced cortical neurotransmitter receptor complex levels in fetal Down syndrome brain. Amino Acids 48, 103–116 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-015-2062-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-015-2062-6