Abstract
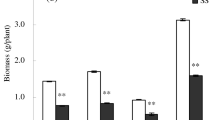
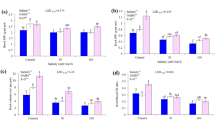
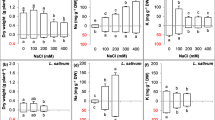
How many subcellular targets of the beneficial silicon effect do exist in salt-stressed rice? Here, we investigate the effects of silicon on the different components of salt stress, i.e., osmotic stress, sodium, and chloride toxicity. These components are separated by multivariate analysis of 18 variables measured in rice seedlings (Oryza sativa L.). Multivariate analysis can dissect vectors and extract targets as principal components, given the regressions between all variables are known. Consequently, the exploration of 153 correlations and 306 regression models between all variables is essential, and regression parameters for variables of shoot (silicon, sodium, chloride, carotenoids, chlorophylls a and b, and relative growth rate) and variables of shoot and root (hydrogen peroxide, ascorbate peroxidase (APX), catalase (CAT), fresh weight, dry weight, root-to-shoot ratio) are determined. The regression models [log (y) = y0 + a × log (x)] are confirmed by variance analysis of global goodness of fits (p < 0.0001). Thereby, logarithmic transformation yields linearization for multivariate analysis by Pearson’s correlation. Four principal components are extracted: two targets of osmotic stress, one target of sodium toxicity, and one target of chloride toxicity. Thereby, silicon improves salt tolerance by increasing APX and CAT activities and decreasing hydrogen peroxide, salt ion accumulation, photosynthetic pigment losses, and growth inhibition. Salt stress increases silicon uptake pointing to a physiological regulation of plant salt stress in the presence of silicon. This mechanism and its four components are promising targets for further agricultural application.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- APX (10):
-
Ascorbate peroxidase
- C-1, C-2, C-3, C-4:
-
Principal components determined by multivariate statistics
- CAR (8):
-
Carotenoids
- CAT (11):
-
Catalase
- CHLA (6), CHLB (7):
-
Chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b
- CL (13):
-
Shoot chloride
- DW (16):
-
Dry weight
- FW (15):
-
Fresh weight
- Na (12):
-
Shoot sodium
- PER (9):
-
Hydrogen peroxide
- RAPX (4), RCAT (5), RDW (2), RFW (1), RPER (3):
-
Parameters as before measured in roots instead of shoots
- RGR (18):
-
Relative growth rate of shoot
- RS (17):
-
Root-to-shoot ratio
- Si (14):
-
Shoot silicon
- u:
-
Unit of enzymatic activity of APX and CAT measured as described in the section “Materials and methods”
References
Adams TF, Wongchai C, Chaidee A, Pfeiffer W (2016) “Singing in the tube”—audiovisual assay of plant oil repellent activity against mosquitoes (Culex pipiens). Parasitol Res 115:225–239
Agarie S, Hanaoka N, Ueno O, Miyazaki A, Kubota F, Agata W, Kaufman PB (1998) Effects of silicon on tolerance to water deficit and heat stress in rice plants (Oryza sativa L.), monitored by electrolyte leakage. Plant Prod Sci 1:96–103
Al-aghabary K, Zhu Z, Shi Q (2005) Influence of silicon supply on chlorophyll content, chlorophyll fluorescence, and antioxidative enzyme activities in tomato plants under salt stress. J Plant Nutr 27:2101–2115
Albacete A, Ghanem ME, Dodd IC, Alfocea FP (2010) Principal component analysis of hormone profiling data suggests an important role for cytokinins in regulating leaf growth and senescence of salinized tomato. Plant Signal Behav 5:45–48
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Plant Physiol 24:1–15
Ashraf M, Rahmatullah AR, Afzal M, Tahir MA, Kanwal S, Maqsood MA (2009) Potassium and silicon improve yield and juice quality in sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.) under salt stress. J Agron Crop Sci 195:284–291
Barbier-Brygoo H, De Angeli A, Filleur S, Frachisse J-M, Gambale F, Thomine S, Wege S (2011) Anion channels/transporters in plants: from molecular bases to regulatory networks. Annu Rev Plant Biol 62:25–51
Beadle CL (1993) Growth analysis. In: Hall DO, Scurlock JMO, Bolhàr-Nordenkampf HR, Leegood RC, Long SP (eds) Photosynthesis and production in a changing environment: a field and laboratory manual. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 36–46
Beers RF, Sizer IW (1952) A spectrophotometric method for measuring the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide by catalase. J Biol Chem 195:133–140
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Brumós J, Colmenero-Flores JM, Conesa A, Izquierdo P, Sánchez G, Iglesias DJ, López-Climent MF, Gómez-Cadenas A, Talón M (2009) Membrane transporters and carbon metabolism implicated in chloride homeostasis differentiate salt stress responses in tolerant and sensitive Citrus rootstocks. Funct Integr Genomics 9:293–309
Caverzan A, Passaia G, Rosa SB, Ribeiro CW, Lazzarotto F, Margis-Pinheiro M (2012) Plant responses to stresses: role of ascorbate peroxidase in the antioxidant protection. Genet Mol Biol 35:1011–1019
Chew O, Whelan J, Millar AH (2003) Molecular definition of the ascorbate-glutathione cycle in Arabidopsis mitochondria reveals dual targeting of antioxidant defenses in plants. J Biol Chem 278:46869–46877
Chow W, Ball M, Anderson J (1990) Growth and photosynthetic responses of spinach to salinity: implications of K+ nutrition for salt tolerance. Aust J Plant Physiol 17:563–578
Curnow P, Senior L, Knight MJ, Thamatrakoln K, Hildebrand M, Booth PJ (2012) Expression, purification, and reconstitution of a diatom silicon transporter. Biochemistry 51:3776–3785
Currie HA, Perry CC (2007) Silica in plants: biological, biochemical and chemical studies. Ann Bot 100:1383–1389
Dai W, Zhang KQ, Duan BW, Sun CX, Zheng KL, Cai RYZ (2005) Rapid determination of silicon content in rice. Rice Sci 12:145–147
Elliott CL, Snyder GH (1991) Autoclave-induced digestion for the colorimetric determination of silicon in rice straw. J Agric Food Chem 39:1118–1119
Epstein E (1994) The anomaly of silicon in plant biology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:11–17
Epstein E (1999) Silicon. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 50:641–664
FAO, ITPS (2015) Status of the world’s soil resources (SWSR) – main report. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations and Intergovernmental Technical Panel on Soils, Rome
Farhangi-Abriz S, Torabian S (2018) Nano-silicon alters antioxidant activities of soybean seedling under salt toxicity. Protoplasma 255:953–962. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-017-1202-0
Fleck AT, Nye T, Repenning C, Stahl F, Zahn M, Schenk MK (2010) Silicon enhances suberization and lignification in roots of rice (Oryza sativa). J Exp Bot 62:2001–2011
Gong HJ, Randall DP, Flowers TJ (2006) Silicon deposition in the root reduces sodium uptake in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings by reducing bypass flow. Plant Cell Environ 29:1970–1979
Grégoire C, Rémus-Borel W, Vivancos J, Labbé C, Belzile F, Bélanger RR (2012) Discovery of a multigene family of aquaporin silicon transporters in the primitive plant Equisetum arvense. Plant J 72:320–330
Guerriero G, Hausman J-F, Legay S (2016) Silicon and the plant extracellular matrix. Front Plant Sci 7:463. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00463 eCollection 2016
HACH Company (1988) DR/2000 spectrophotometer procedures manual. Loveland, Colorado, pp 103–105
Haefele SM, Naklang K, Harnpichitvitaya D, Jearakongman S, Skulkhu E, Romyen P, Phasopa S, Tabtim S, Suriya-arunroj D, Khunthasuvon S, Kraisorakul D, Youngsuk P, Amarante ST, Wade LJ (2006) Factors affecting rice yield and fertilizer response in rainfed lowlands of northeast Thailand. Field Crops Res 98:39–51
Homblé F, Krammer E-M, Prévost M (2012) Plant VDAC: facts and speculations. Biochim Biophys Acta 1818:1486–1501
Isa M, Bai S, Yokoyama T, Ma JF, Ishibashi Y, Yuasa T, Iwaya-Inoue M (2010) Silicon enhances growth independent of silica deposition in a low-silica rice mutant, lsi1. Plant Soil 331:361–375
Jana S, Choudhuri MA (1982) Glycolate metabolism of three submersed aquatic angiosperms during ageing. Aquat Bot 12:345–354
Kafi M, Nabati J, Masoumi A, Mehrgerdi MZ (2011) Effect of salinity and silicon application on oxidative damage of sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench.]. Pak J Bot 43:2457–2462
Kronzucker HJ, Szczerba MW, Moazami-Goudarzi M, Britto DT (2006) The cytosolic Na+:K+ ratio does not explain salinity-induced growth impairment in barley: a dual-tracer study using 42K+ and 24Na+. Plant Cell Environ 29:2228–2237
Lanning FC (1963) Plant constituents, silicon in rice. J Agric Food Chem 11:435–437
Liang Y (1999) Effects of silicon on enzyme activity and sodium, potassium and calcium concentration in barley under salt stress. Plant Soil 209:217–224
Liang Y, Chen Q, Liu Q, Zhang W, Ding R (2003) Exogenous silicon (Si) increases antioxidant enzyme activity and reduces lipid peroxidation in roots of salt-stressed barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). J Plant Physiol 160:1157–1164
Liang YC, Zhang WH, Chen Q, Ding RX (2005) Effects of silicon on H+-ATPase and H+-PPase activity, fatty acid composition and fluidity of tonoplast vesicles from roots of salt-stressed barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Environ Exp Bot 53:29–37
Limpanavech P, Chaiyasuta S, Vongpromek R, Pichyangkura R, Khunwasi C, Chadchawan S, Lotrakul P, Bunjongrat R, Chaidee A, Bangyeekhun T (2008) Chitosan effects on floral production, gene expression, and anatomical changes in the Dendrobium orchid. Sci Hortic 116:65–72
Ma J, Nishimura K, Takahashi E (1989) Effect of silicon on growth of rice plant at different growth stages. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 35:347–356
Ma JF, Tamai K, Yamaji N, Mitani N, Konishi S, Katsuhara M, Ishiguro M, Murata Y, Yano M (2006) A silicon transporter in rice. Nature 440:688–691
Marino D, Dunand C, Puppo A, Pauly N (2012) A burst of plant NADPH oxidases. Trends Plant Sci 17:9–15
Matoh T, Kairusmee P, Takahashi E (1986) Salt-induced damage to rice plants and alleviation effect of silicate. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 32:295–304
Mitani N, Ma JF (2005) Uptake system of silicon in different plant species. J Exp Bot 56:1255–1261
Mitani N, Yamaji N, Ago Y, Iwasaki K, Ma JF (2011) Isolation and functional characterization of an influx silicon transporter in two pumpkin cultivars contrasting in silicon accumulation. Plant J 66:231–240
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:651–681
Munns R, James RA, Läuchli A (2006) Approaches to increasing the salt tolerance of wheat and other cereals. J Exp Bot 57:1025–1043
Nakano Y, Asada K (1981) Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol 22:867–880
Pfeiffer W, Höftberger M (2001) Oxidative burst in Chenopodium rubrum suspension cells. Physiol Plant 111:144–150
Ponte LF, Silva AL, Carvalho FE, Maia JM, Voigt EL, Silveira JA (2014) Salt-induced delay in cotyledonary globulin mobilization is abolished by induction of proteases and leaf growth sink strength at late seedling establishment in cashew. J Plant Physiol 171:1362–1371
Ratanopad S, Kainz W (2006) Using GIS and map data the analysis of the expansion of salinized soils. In: Nayak S, Pathan SK, Garg JK (eds) Proceedings of the ISPRS Commission IV symposium on “Geospatial databases for sustainable development”, Vol. 36, Part 4B, September 27–30, 2006. Archives of ISPRS, Goa, pp 916–921
Ren S, Weeda S, Li H, Whitehead B, Guo Y, Atalay A, Parry J (2012) Salt tolerance in soybean WF-7 is partially regulated by ABA and ROS signaling and involves withholding toxic Cl− ions from aerial tissues. Plant Cell Rep 31:1527–1533
Rios JJ, Martínez-Ballesta MC, Ruiz JM, Blasco B, Carvajal M (2017) Silicon-mediated improvement in plant salinity tolerance: the role of aquaporins. Front Plant Sci 8:948
Robert N, d’Erfurth I, Marmagne A, Erhardt M, Allot M, Boivin K, Gissot L, Monachello D, Michaud M, Duchêne A-M, Barbier-Brygoo H, Maréchal-Drouard L, Ephritikhine G, Filleur S (2012) Voltage-dependent-anion-channels (VDACs) in Arabidopsis have a dual localization in the cell but show a distinct role in mitochondria. Plant Mol Biol 78:431–446
Romero-Aranda MR, Jurado O, Cuartero J (2006) Silicon alleviates the deleterious salt effect on tomato plant growth by improving plant water status. J Plant Physiol 163:847–855
Shi Y, Wang Y, Flowers TJ, Gong H (2013) Silicon decreases chloride transport in rice (Oryza sativa L.) in saline conditions. J Plant Physiol 170:847–853
Tateda C, Watanabe K, Kusano T, Takahashi Y (2011) Molecular and genetic characterization of the gene family encoding the voltage-dependent anion channel in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 62:4773–4785
Tavakkoli E, Rengasamy P, McDonald GK (2010) High concentrations of Na+ and Cl− ions in soil solution have simultaneous detrimental effects on growth of faba bean under salinity stress. J Exp Bot 61:4449–4459
Tavakkoli E, Fatehi F, Coventry S, Rengasamy P, McDonald GK (2011) Additive effects of Na+ and Cl− ions on barley growth under salinity stress. J Exp Bot 62:2189–2203
Vajrabhaya M, Vajrabhaya T (1991) Somaclonal variation for salt tolerance in rice. In: Bajaj YPS (ed) Rice. Springer, Berlin, pp 368–382
Van Bockhaven J, De Vleesschauwer D, Höfte M (2013) Towards establishing broad-spectrum disease resistance in plants: silicon leads the way. J Exp Bot 64:1281–1293
Wang X, Wei Z, Liu D, Zhao G (2011) Effects of NaCl and silicon on activities of antioxidative enzymes in roots, shoots and leaves of alfalfa. Afr J Biotechnol 10:545–549
Wang S, Liu P, Chen D, Yin L, Li H, Deng X (2015) Silicon enhanced salt tolerance by improving the root water uptake and decreasing the ion toxicity in cucumber. Front Plant Sci 6:759. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00759
Wellburn AR (1994) The spectral determination of chlorophylls a and b, as well as total carotenoids, using various solvents with spectrophotometers of different resolution. J Plant Physiol 144:307–313
Wijnhoud JD, Konboon Y, Lefroy RDB (2003) Nutrient budgets: sustainability assessment of rainfed lowland rice-based systems in northeast Thailand. Agric Ecosyst Environ 100:119–127
Wongchai C, Chaidee A, Pfeiffer W (2012) Multivariate analyses of salt stress and metabolite sensing in auto- and heterotroph Chenopodium cell suspensions. Plant Biol 14:129–141
Yeo AR, Flowers SA, Rao G, Welfare K, Senanayake N, Flowers TJ (1999) Silicon reduces sodium uptake in rice (Oryza sativa L.) in saline conditions and this is accounted for by a reduction in the transpirational bypass flow. Plant Cell Environ 22:559–565
Zhang J, Liu H, Zhao QZ, Du YX, Chang QX, Lu QL (2011) Effects of ATP production on silicon uptake by roots of rice seedlings. Plant Biosyst 145:866–872
Zhu JK (2001) Plant salt tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 6:66–71
Zhu Z, Wei G, Li J, Qian Q, Yu J (2004) Silicon alleviates salt stress and increases antioxidant enzymes activity in leaves of salt-stressed cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Plant Sci 167:527–533
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr. Aniela Sommer for the comments on the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Grant for New Scholar (co-funded by TRF and CHE, MRG5280200) and the Higher Education Research Promotion and National Research University Project of Thailand (FW656B).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Bhumi Nath Tripathi
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Table 1
(DOCX 29 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lekklar, C., Chadchawan, S., Boon-Long, P. et al. Salt stress in rice: multivariate analysis separates four components of beneficial silicon action. Protoplasma 256, 331–347 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-018-1293-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-018-1293-2