Abstract
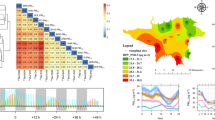
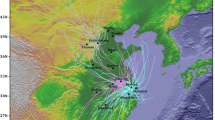
Air pollution potential (APP) is a measure of the meteorological conditions conducive to high air pollution levels, independent of source emissions. We propose the integrated concentration footprint (ICF) as a new indicator to quantify APP and present the climatology of the APP distribution in China. The HYSPLIT model was employed to calculate back trajectories and to derive ICF at grid points over China, for the period 2000–2012. The annual mean APP exhibited a distribution in reasonable agreement with topography and climate features. Seasonal characteristics of APP are also presented. Comparison of the seasonal variation in APP with that of air pollution data at selected cities produced diverse results. APP agreed well with air pollution variations in Urumqi, a city in northwestern China. However, in eastern China, APP peaked in summer, which is in contrast to observations, where the lowest air pollution levels occurred in this season. Two possible factors were considered to resolve this discrepancy, namely, the scarcity of pollutant sources over the sea surface and the wet removal of particulate matter. Adjusted APP exhibited an inland shift of its maximum in southeastern China and reduced values in summer, which were in more reasonable agreement with air pollution data. The correlations between adjusted APP values and air pollution levels were significantly improved in the southern coastal cities of Guangzhou and Shanghai, but could not adequately capture the observations for other inland cities. Although preliminary, the ICF provides a comprehensive measure of the meteorological background of China’s air pollution.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bowers JF, Bjorklund JR, Cheney CS, Schewe GJ (1980) Industrial Source Complex (ISC) dispersion model user’s guide. US Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Air Quality Planning and Standards
Byun D, Schere KL (2006) Review of the governing equations, computational algorithms, and other components of the Models-3 Community Multiscale Air Quality (CMAQ) modeling system. Appl Mech Rev 59:51–77. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2128636
Cai XH (2008) Footprint analysis in micrometeorology and its extended applications. Chin J Atmos Sci 32:123–132
Cai W, Li K, Liao H, Wang H, Wu L (2017) Weather conditions conducive to Beijing severe haze more frequent under climate change. Nat Clim Chang 7:257–262. https://doi.org/10.1038/NCLIMATE3249
Cai XH, Leclerc MY (2007) Forward-in-time and backward-in-time dispersion in the convective boundary layer: the concentration footprint. Bound-Layer Meteorol 123(2):201–218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-006-9141-x
Chan CK, Yao X (2008) Air pollution in mega cities in China. Atmos Environ 42(1):1–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.09.003
Chen XM, Zou Q, Zhou GB (2013) On impact of precipitation intensity of air pollutants in winter and spring in Chongqing downtown. J Southwest China Normal Univs 38:113–121
Draxler RR and Hess GD (1997) Description of the HYSPLIT_4 modeling system. Natl Ocean Atmos Administration Tech Memo Erl Arl 197–199
Editorial committee of Climatological Atlas of the People’s Republic of China (2002), Climatological Atlas of the People’s Republic of China (in Chinese), China Meteorological Press, Beijing
Feng X, Li Q, Zhu Y, Hou J, Jin L, Wang J (2015) Artificial neural networks forecasting of PM 2.5 pollution using air mass trajectory based geographic model and wavelet transformation. Atmos Environ 107:118–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.02.030
Finnigan J (2004) The footprint concept in complex terrain. Agric For Meteorol 127(3–4):117–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2004.07.008
Gassmann MI, Mazzeo NA (2000) Air pollution potential: regional study in Argentina. Environ Manag 25(4):375–382. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002679910029
Grell GA, Peckham SE, Schmitz R, McKeen SA, Frost G, Skamarock WC, Eder B (2005) Fully coupled “online” chemistry within the WRF model. Atmos Environ 39(37):6957–6975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2005.04.027
Gross E (1970) The national air pollution potential forecast program. National Meteorological Center Washington DC
Hogrefe C, Hao W, Civerolo K, Ku JY, Sistla G, Gaza RS, Sedefian L, Schere K, Gilliland A, Mathur R (2007) Daily simulation of ozone and fine particulates over New York State: findings and challenges. J Appl Meteorol Clim 46(7):961–979
Holzworth GC (1962) A study of air pollution potential for the western United States. J Appl Meteorol 1(3):366–382
Holzworth GC (1964) Estimates of mean maximum mixing depths in the contiguous United States. Mon Weather Rev 92(5):235–242
Holzworth GC (1967) Mixing depths, wind speeds and air pollution potential for selected locations in the United States. J Appl Meteorol 6(6):1039–1044. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0450(1967)006<1039:MDWSAA>2.0.CO;2
Hosler CR (1961) Low-level inversion frequency in the contiguous United States. Month Weather Rev 89(9):319–339
Huang Q, Cai X, Song Y, Zhu T (2017) Air stagnation in China (1985–2014): climatological mean features and trends. Atmos Chem Phys 17(12):7793–7805. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-17-7793-2017
Jacob DJ, Winner DA (2009) Effect of climate change on air quality. Atmos Environ 43(1):51–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2008.09.051
Ji D, Li L, Wang Y, Zhang J, Cheng M, Sun Y, Liu Z, Wang L, Tang G, Hu B, Chao N, Wen T, Miao H (2014) The heaviest particulate air-pollution episodes occurred in northern China in January, 2013: insights gained from observation. Atmos Environ 92:546–556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.04.048
Jorba O, Pérez C, Rocadenbosch F, Baldasano J (2004) Cluster analysis of 4-day back trajectories arriving in the Barcelona area, Spain, from 1997 to 2002. J Appl Meteorol 43:887–901. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0450(2004)043%3C0887:CAODBT%3E2.0.CO;2
Kormann R, Meixner FX (2001) An analytical footprint model for non-neutral stratification. Bound-Layer Meteorol 99(2):207–224. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018991015119
Lamb RG (1983) A regional scale (1000km) model of photochemical air pollution part 1. Theoretical formulation. US Environmental Protection Agency, EPA/600/3-33-035
Li X, Ding X, Gao H, Zhu Z (2011) Characteristics of air pollution index in typical cities of North China. J Arid Land Resour Environ 25:96–101
Meloni D, Di Sarra A, Biavati G, DeLuisi JJ, Monteleone F, Pace G, Piacentinod S, Sferlazzo DM (2007) Seasonal behavior of Saharan dust events at the Mediterranean island of Lampedusa in the period 1999–2005. Atmos Environ 41(14):3041–3056. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2006.12.001
Miller ME, Niemeyer LE (1963) Air pollution potential forecasts—a year’s experience. J Air Pollut Control Assoc 13:205–210
Niemeyer LE (1960) Forecasting air pollution potential. Mon Weather Rev 88(3):88–96
Ohara T, Akimoto H, Kurokawa J, Horii N, Yamaji K, Yan X, Hayasaka T (2007) An Asian emission inventory of anthropogenic emission sources for the period 1980–2020. Atmos Chem Phys 7(16):6843–6902. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-7-4419-2007
Pack DH (1964) Meteorology of air pollution. Science 146(3648):1119–1128
Pan YX, Jiang WM (1982) Atmospheric maximum mixing depth of the mainland of China. China Environ Sci 5:51–56
Pasquill F, Smith FB (1983) Atmospheric diffusion, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York
Perez P, Reyes J (2006) An integrated neural network model for PM10 forecasting. Atmos Environ 40(16):2845–2851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2006.01.010
Qu WJ, Arimoto R, Zhang XY, Zhao CH, Wang YQ, Sheng LF, Fu G (2010) Spatial distribution and interannual variation of surface PM10 concentrations over eighty-six Chinese cities. Atmos Chem Phys 10(12):5641–5662. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-10-5641-2010
Rannik Ü, Aubinet M, Kurbanmuradov O, Sabelfeld KK, Markkanen T, Vesala T (2000) Footprint analysis for measurements over a heterogeneous forest. Bound-Layer Meteorol 97(1):137–166. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1002702810929
Rutllant J, Garreaud R (1995) Meteorological air pollution potential for Santiago, Chile: towards an objective episode forecasting. Environ Monit Assess 34(3):223–244
Schmid HP (1994) Source areas for scalars and scalar fluxes. Bound-Layer Meteorol 67(3):293–318. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00713146
Schmid HP (2002) Footprint modeling for vegetation atmosphere exchange studies: a review and perspective. Agric For Meteorol 113(1–4):159–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-1923(02)00107-7
Scott GM, Diab RD (2000) Forecasting air pollution potential: a synoptic climatological approach. J Air Waste Manage Assoc 50(10):1831–1842. https://doi.org/10.1080/10473289.2000.10464216
Shad R, Mesgari MS, Shad A (2009) Predicting air pollution using fuzzy genetic linear membership kriging in GIS. Comput Environ Urban Syst 33(6):472–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2009.10.004
Sogachev A, Leclerc MY (2011) On concentration footprints for a tall tower in the presence of a nocturnal low-level jet. Agric For Meteorol 151(6):755–764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2010.10.004
Stadlober E, Hörmann S, Pfeiler B (2008) Quality and performance of a PM10 daily forecasting model. Atmos Environ 42(6):1098–1109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.10.073
Streets DG, Fu JS, Jang CJ, Hao J, He K, Tang X, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Li Z, Zhang Q, Wang L, Wang B, Yu C, Wang L (2007) Air quality during the 2008 Beijing Olympic Games. Atmos Environ 41(26):480–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2006.08.046
Van der Wal JT, Janssen L (2000) Analysis of spatial and temporal variations of PM 10 concentrations in the Netherlands using Kalman filtering. Atmos Environ 34(22):3675–3687. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1352-2310(00)00085-6
Vesala T, Kljun N, Rannik Ü, Rinne J, Sogachev A, Markkanen T, Sabelfeld K, Foken T, Leclerc MY (2008) Flux and concentration footprint modelling: state of the art. Environ Pollut 152(3):653–666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2007.06.070
Viswanadham DV, Santosh KR (1989) Air pollution potential over south India. Bound-Layer Meteorol 48(3):299–313
Wang JXL, Angell JK (1999) Air stagnation climatology for the United States. NOAA/Air Resour Lab ATLAS 1
Xu DH, Zhu R (2000) Atmospheric advective and dispersion nonstatic box-model for prediction of the potential index of airborne pollutant. Q J Appl Meteorol 11:1–12
Zhang JK, Sun Y, Liu ZR, Ji DS, Hu B, Liu Q, Wang YS (2014) Characterization of submicron aerosols during a month of serious pollution in Beijing, 2013. Atmos Chem Phys 14(6):2887–2903. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-14-2887-2014
Zhang X, Wang C, Wang B (2011) Influence of meteorological condition on air quality over Shijiazhuang of Hebei Province. J Arid Meteorol 29:42–47
Zhang Y, Bocquet M, Mallet V, Seigneur C, Baklanov A (2012) Real-time air quality forecasting, part I: history, techniques, and current status. Atmos Environ 60:632–655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.06.031
Zhou XX, Ding YH, Wang PX (2008) Moisture transport in Asian summer monsoon region and its relationship with summer precipitation in China. Acta Meteor Sin 66:59–70
Zhu R, Xu D, Zhou C, Zhang Y, Zhou C, Kuang S (2002) Applications of CAPPS in the numerical prediction operational system of multi-city air pollution index. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science 2002:204–213
Zolghadri A, Cazaurang F (2006) Adaptive nonlinear state-space modelling for the prediction of daily mean PM 10 concentrations. Environ Model Softw 21(6):885–894. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2005.04.008
Zou Y, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Koo JH (2017) Arctic sea ice, Eurasia snow, and extreme winter haze in China. Sci Adv 3(3):e1602751. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1602751
Funding
This work was partially supported by the Clean Air Research Project in China (201509001, 201409001), National S&T Support Program (2014BAC06B02), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (41421064, 41575007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 271 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, M., Cai, X., Xu, C. et al. A climatological study of air pollution potential in China. Theor Appl Climatol 136, 627–638 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-018-2511-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-018-2511-8