Abstract
Aims
Type 1 diabetes is increasing in children leading more T1D young adults to adult healthcare settings. This change is experienced as a tear and results in a disengagement from specialist services. This study reports on an implementation of an effective and pioneering program of transition in North Africa.
Methods
A total of 65 teenagers with T1D were recruited for a structured program of transition. They attend transitional meetings involving both pediatric and adult team and were, when ready, welcomed in specialized consultations for adolescents with a special « passport ». Here we study their characteristics before and after structured transition and the benefit of this program.
Results
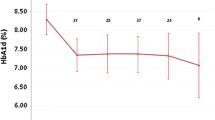
9 transition meetings took place (September 2012–December 2017). Mean age was 16.5 years. Mean age at onset of T1D was 7.5 years with average pediatric follow-up of 9 years.72% of young adults felt satisfied. After the transition meeting, 74% of patients wished to join directly adult unit. They were followed there for 28.4 ± 16.2 months. The glycaemic control improved significantly with a decrease in HbA1C of 0.93 ± 1.69% the first year of follow-up and the number of young adults achieving a HbA1C < 7.5% increased by 8%.
Conclusion
This program was beneficial for 75% of patients who demonstrated an improvement in their metabolic control the year following transition to adult care service. To our knowledge, this study is the first one in North Africa to report on the outcome of a structured transition program from pediatric to adult diabetes care.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Patterson CC, Dahlquist GG, Gyurus E et al (2009) Incidence trends for childhood type 1 diabetes in Europe during 1989–2003 and predicted new cases 2005–20: a multicentre prospective registration study. Lancet 373:2027–2033
Dabelea D (2009) The accelerating epidemic of childhood diabetes. Lancet 373(9680):1999–2000
Tuomilehto J (2013) The emerging global epidemic of type 1 diabetes. Curr Diabetes Rep 13(6):795–804
Hachicha M, Aloulou H, Yaich S et al (2012) Epidemiology of childhood T1D in Tunisia. Oral communication. In: Maghrebian Pediatric Congress. Hammamet, (Data not published)
Findley MK, Cha E, Wong E et al (2015) A systematic review of transitional care for emerging adults with diabetes. J Pediatr Nurs 30(5):e47–e62
Begley T (2013) Transition to adult care for young people with long-term conditions. Br J Nurs 22506:508–511
Blum RW, Garell D, Hodgman CH et al (1993) Transition from child-centered to adult health-care systems for adolescents with chronic conditions. A position paper of the society for adolescent medicine. J Adolesc Health 14:570–576
Bryden KS, Peveler RC, Stein A et al (2001) Clinical and psychological course of diabetes from adolescence to young adulthood: a longitudinal cohort study. Diabetes Care 24:1536–1540
Dovey-Pearce G, Christie D (2013) Transition in diabetes: young people move on- we should too. J Paediatr Child Health 23:174–179
Vanelli M, Caronna S, Adinolfi B et al (2004) Effectiveness of an uninterrupted procedure to transfer adolescents with type 1 diabetes from the paediatric to the adult clinic held in the same hospital: eight-year experience with the Parma protocol. Diabetes Nutr Metab 17:304–308
Cadario F, Prodam F, Bellone S et al (2009) Transition process of patients with type 1 diabetes (T1DM) from paediatric to the adult health care service: a hospital-based approach. Clin Endocrinol 71:346–350
VanWalleghem N, Macdonald CA, Dean HJ (2008) Evaluation of a systems navigator model for transition from pediatric to adult care for young adults with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 31:1529–1530
Vidal M, Jansa M, Anguita C et al (2004) Impact of a special therapeutic education programme in patients transferred from a paediatric to an adult diabetes unit. Eur Diabetes Nurs 1:23–27
Logan J, Peralta E, Brown K et al (2008) Smoothing the transition from paediatric to adult services in type 1 diabetes. J Diabetes Nurs 12:328–338
Holmes-Walker DJ, Llewellyn AC, Farrell K (2007) A transition care programme which improves diabetes control and reduces hospital admission rates in young adults with Type 1 diabetes aged 15–25 years. Diabet Med 24:764–769
Pyatak EA, Sequeira PA, Vigen CLP et al (2017) Clinical and psychosocial outcomes of a structured transition program among young adults with type 1 diabetes. J Adolesc Health 60(2):212–218
Sheehan AM, While AE, Coyne I (2015) The experiences and impact of transition from child to adult healthcare services for young people with type 1 diabetes: a systematic review. Diabet Med 32(4):440–458
Blum RW (2002) Introduction improving transition for adolescents with special health care needs from pediatric to adult-centered health care. Pediatrics 110:1301–1303
Marathe PH, Gao HX, Close KL (2017) American diabetes association standards of medical care in diabetes 2017. J Diabetes 9:320–324
American Academy of Pediatrics, American Academy of Family Physicians, American College of Physicians, Transitions Clinical Report Authoring Group, Cooley WC, Sagerman PJ (2011) Supporting the health care transition from adolescence to adulthood in the medical home. Pediatrics 128 (1): 182–200
Allen D, Channon S, Lowes L et al (2011) Behind the scenes:the changing roles of parents in the transition from child to adult diabetes service. Diabet Med 28:994–1000
Visentin K, Koch T, Kralik D (2006) Adolescents with Type 1 diabetes: transition between diabetes services. J Clin Nurs 15:761–769
Kipps S, Bahu T, Ong K et al (2002) Current methods of transfer of young people with Type 1 diabetes to adult services. Diabet Med 19(8):649–654
Price CS, Corbett S, Lewis-Barned N et al (2011) Implementing a transition pathway in diabetes: a qualitative study of the experiences and suggestions of young people with diabetes. Child Care Health Dev 37:852–860
Busse FP, Hiermann P, Galler A et al (2007) Evaluation of patients’ opinion and metabolic control after transfer of young adults with type 1 diabetes from a pediatric diabetes clinic to adult care. Horm Res 67:132–138
Kime N (2013) Young people with type 1 diabetes and their transition to adult services. Br J Community Nurs 18(14):6–8
Sparud-Lundin C, Danielson E, Ohrn I (2007) Handling the transition of adolescents with diabetes: participant observations and interviews with care providers in paediatric and adult diabetes outpatient clinics. Int J Integr Care 7:e05
Garvey KC, Wolpert HA, Laffel LM, Rhodes ET, Wolfsdorf JI, Finkelstein JA (2013) Health care transition in young adults with type 1 diabetes: barriers to timely establishment of adult diabetes care. Endocr Pract 19:946–952
Hynes L, Byrne M, Dinneen SF et al (2016) Barriers and facilitators associated with attendance at hospital diabetes clinics among young adults (15–30 years) with type 1 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. Pediatr Diabetes 17(7):509–518
Nakhla M, Daneman D, To T et al (2009) Transition to adult care for youths with diabetes mellitus: findings from a Universal. Health Care Syst Pediatr 124(6):e1134–e1141
Mankaï A, Ben Hamouda H, Amri F et al (2007) Screening by anti-endomysium antibodies for celiac disease in Tunisian children with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Gastroenterol Clin Biol 31(5):462–466
Salardi S, Maltoni G, Zanfardino A et al For the Diabetes Study Group of the Italian Society of Pediatric Endocrinology and Diabetology (ISPED) (2017) Whole lipid profile and not only HDL cholesterol is impaired in children with coexisting type 1 diabetes and untreated celiac disease. Acta Diabetol 54:889–894
Specht BJ, Wadwa RP, Snell-Bergeon JK et al (2013) Estimated insulin sensitivity and cardiovascular disease risk factors in adolescents with and without type 1 diabetes. J Pediatr 162:297–301
Petitti DB, Klingensmith GJ, Bell RA et al (2009) Glycaemic control in youth with diabetes: the search for diabetes in youth study. J Pediatr 155:668–672
Rica I, Mingorance A, Gomez-Gila AL et al (2017) Achievement of metabolic control among children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes in Spain. Acta Diabetol 54:677–683
Rollo A, Salardi S, Ciavarella A et al (2014) Transition from pediatric to adult care. Eight years after the transition from pediatric to adult diabetes care: metabolic control, complications and associated diseases. J Endocrinol Invest 37(7):653–659
Lotstein DS, Seid M, Klingensmith G et al (2013) Transition from pediatric to adult care for youth diagnosed with type 1 diabetes in adolescence. Pediatrics 131(4):e1062–e1070
Helgeson VS, Reynolds KA, Snyder PR et al (2013) Characterizing the transition from paediatric to adult care among emerging adults with type 1 diabetes. Diabet Med 30(5):610–615
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Statement of Human and Animal Rights
Our study have been reviewed by the hospital's ethics committee and have therefore been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in an appropriate version of the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki.
Statement of Informed Consent
All the persons cited gave their consent prior to their inclusion in the study. Details that might disclose identity of the subjects under study have been omitted.
Additional information
Managed By Massimo Porta.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Essaddam, L., Kallali, W., Jemel, M. et al. Implementation of effective transition from pediatric to adult diabetes care: epidemiological and clinical characteristics—a pioneering experience in North Africa. Acta Diabetol 55, 1163–1169 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-018-1196-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-018-1196-x