Abstract
Introduction
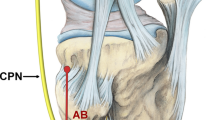
Injuries to the peroneal nerve are a common complication in operative treatment of proximal tibial or fibular fractures. To minimize the risk of iatrogenic injury to the nerve, detailed knowledge of the anatomy of the peroneal nerve is essential. Aim of this study was to present a detailed description of the position and branching of the peroneal nerve based on 3D-images to assist preparation for surgical approaches to the fibular head and the tibial plateau.
Methods
The common peroneal nerve, the deep and the superficial peroneal nerve were marked with a radiopaque thread in 18 formalin-embalmed specimens. Three-dimensional X-ray scans were then acquired from the knee and the proximal lower leg in full extension of the knee. In 3D-reconstructions of these scans, distances of the common peroneal nerve and its branches to clearly defined osseous landmarks were measured digitally. Furthermore, the height of the branching of the common peroneal nerve was measured in relation to the landmarks.
Results
The mean distance of the common peroneal nerve at the level of the tibial plateau to its posterior osseous limitation was 7.92 ± 2.42 mm, and 1.31 ± 2.63 mm to the lateral osseous limitation of the tibia. In a transversal plane, distance of the common peroneal nerve branching was 27.56 ± 3.98 mm relative to the level of the most proximal osseous extension of fibula and 11.77 ± 6.1 mm relative to the proximal extension of the tibial tuberosity. The deep peroneal nerve crossed the midline of the fibular shaft at a distance of 22.14 mm ± 4.35 distally to the most proximal extension of the fibula, the superficial peroneal nerve at a distance of 33.56 mm ± 6.68.
Conclusion
As the course of the peroneal nerve is highly variable in between individuals, surgical dissection for operative treatment of proximal posterolateral tibial or fibular fractures has to be done carefully. We defined an area were the peroneal nerve and its branches are unlikely to be found. However, specific safe zones should not be utilized due to the individual anatomic variation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johnson ME, Foster L, DeLee JC (2008) Neurologic and vascular injuries associated with knee ligament injuries. Am J Sports Med 36:2448–2462. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546508325669
Khan R, Birch R (2001) Latropathic injuries of peripheral nerves. J Bone Joint Surg Br 83:1145–1148
Kim DH, Murovic JA, Tiel RL, Kline DG (2004) Management and outcomes in 318 operative common peroneal nerve lesions at the Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center. Neurosurgery 54:1421–1428
Rozbruch SR, Fragomen AT, Ilizarov S (2006) Correction of tibial deformity with use of the Ilizarov-Taylor spatial frame. J Bone Jt Surg Ser A 88:156–174. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.F.00745
Dearden P, Lowery K, Sherman K et al (2015) Fibular head transfixion wire and its relationship to common peroneal nerve: cadaveric analysis. Strateg Trauma Limb Reconstr 10:73–78. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11751-015-0225-3
Frosch K-H, Balcarek P, Walde T, Stürmer KM (2010) A modified posterolateral approach for the treatment of tibial plateau fractures. Oper Orthop Traumatol 22:107–119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00064-010-3008-0
Levy BA, Vogt KJ, Herrera DA, Cole PA (2006) Maisonneuve fracture equivalent with proximal tibiofibular dislocation: a case report and literature review. J Bone Jt Surg Ser A 88:1111–1116
Van Seymortier P, Ryckaert A, Verdonk P et al (2008) Traumatic proximal tibiofibular dislocation. Am J Sports Med. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546507312162
Stufkens SA, van den Bekerom MPJ, Doornberg JN et al (2011) Evidence-based treatment of maisonneuve fractures. J Foot Ankle Surg 50:62–67. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jfas.2010.08.017
Stitgen SH, Cairns ER, Ebraheim N et al (1992) Anatomic considerations of pin placement in the proximal tibia and its relationship to the peroneal nerve. Clin Orthop Relat Res 278:134–137
Takeda A, Tsucbiya H, Mori Y et al (2001) Anatomical aspects of biopsy of the proximal fibula. Int Orthop 24:335–337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002640000185
Rubel IF, Schwarzbard I, Leonard A, Cece D (2004) Anatomic location of the peroneal nerve at the level of the proximal aspect of the tibia: Gerdy’s safe zone. J Bone Joint Surg Am 86–A:1625–1628
Hildebrand G, Tompkins M, Macalena J (2015) Fibular head as a landmark for identification of the common peroneal nerve: a cadaveric study. Arthrosc J Arthrosc Relat Surg 31:99–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arthro.2014.07.014
Ryan W, Mahony N, Delaney M et al (2003) Relationship of the common peroneal nerve and its branches to the head and neck of the fibula. Clin Anat 16:501–505. https://doi.org/10.1002/ca.10155
Reebye O (2004) Anatomical and clinical study of the common fibular nerve. Part 1: anatomical study. Surg Radiol Anat 26:365–370. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-004-0238-y
Moskovich R (1987) Proximal tibial transfixion for skeletal traction. Clin Orthop Relat Res 214:264–268
Niemeyer P, Stöhr A, Köhne M, Hochrein A (2017) Medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy. Oper Orthop Traumatol 29:294–305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00064-017-0509-5
Feucht MJ, Mehl J, Forkel P et al (2017) Distal femoral osteotomy using a lateral opening wedge technique. Oper Orthop Traumatol 29:320–329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00064-017-0503-y
Diermeier T, Imhoff AB, Beitzel K (2017) Flexion and extension osteotomy of the knee. Oper Orthop Traumatol 29:330–338. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00064-017-0499-3
Chiba K, Yonekura A, Miyamoto T et al (2017) Tibial condylar valgus osteotomy (TCVO) for osteoarthritis of the knee: 5-year clinical and radiological results. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-016-2609-3
Cuéllar A, Cuéllar R, Cuéllar A et al (2015) The effect of knee flexion angle on the neurovascular safety of all-inside lateral meniscus repair: a cadaveric study. Arthrosc J Arthrosc Relat Surg. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arthro.2015.04.100
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rausch, V., Hackl, M., Oppermann, J. et al. Peroneal nerve location at the fibular head: an anatomic study using 3D imaging. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 139, 921–926 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-019-03141-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-019-03141-7