Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the stiffness of the surrounding tissue of breast lesions using the strain ratio assessment method by ultrasound (US) elastography.
Methods
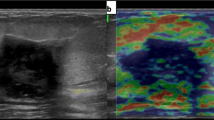
This was an institutional ethics committee approved prospective study. A total of 127 breast lesions in 118 women (mean age 48.23 ± 14.32, range 20–90) were examined with conventional and elastographic US. The strain ratio assessment method was utilized to semi-quantitatively evaluate the stiffness of the breast lesions and the surrounding tissue.
Results
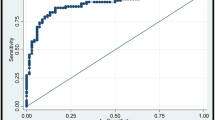
Fifty-five lesions were malignant and 72 were benign. The strain ratio of the surrounding tissue was significantly higher in malignant cases (1.49 ± 0.67) than in benign ones (1.17 ± 0.44) (P = 0.001), and yielded an Az value of 0.669 in the diagnosis of breast lesions. There was a significant high positive correlation between the strain ratio of the lesion and the strain ratio of the surrounding tissue in the malignant group (r = 0.740, P < 0.001), and a significant moderate positive correlation in the benign group (r = 0.595, P < 0.001).
Conclusion
The stiffness of the surrounding tissue of malignant breast lesions was higher than that of benign lesions. The strain ratio of the surrounding tissue and the lesions was significantly correlated, and has potential for breast lesion diagnosis.
Key Points
• Stiffness of the surrounding tissue of malignant breast lesions was increased.
• Stiffness of the surrounding tissue correlated with stiffness of breast lesions.
• Stiffness of the surrounding tissue has potential use in diagnosis of breast lesions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benson JR, Jatoi I (2012) The global breast cancer burden. Future Oncol 8:697–702
Kriege M, Brekelmans CT, Boetes C et al (2004) Efficacy of MRI and mammography for breast-cancer screening in women with a familial or genetic predisposition. N Engl J Med 351:427–437
Warner E, Plewes DB, Hill KA et al (2004) Surveillance of BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers with magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasound, mammography, and clinical breast examination. JAMA 292:1317–1325
Kolb TM, Lichy J, Newhouse JH (1998) Occult cancer in women with dense breasts: detection with screening US–diagnostic yield and tumor characteristics. Radiology 207:191–199
Schaefer FK, Waldmann A, Katalinic A et al (2010) Influence of additional breast ultrasound on cancer detection in a cohort study for quality assurance in breast diagnosis–analysis of 102,577 diagnostic procedures. Eur Radiol 20:1085–1092
Hooley RJ, Scoutt LM, Philpotts LE (2013) Breast ultrasonography: state of the art. Radiology 268:642–659
Itoh A, Ueno E, Tohno E et al (2006) Breast disease: clinical application of US elastography for diagnosis. Radiology 239:341–350
Ophir J, Cespedes I, Ponnekanti H, Yazdi Y, Li X (1991) Elastography: a quantitative method for imaging the elasticity of biological tissues. Ultrason Imaging 13:111–134
Ophir J, Garra B, Kallel F et al (2000) Elastographic imaging. Ultrasound Med Biol 26(Suppl 1):S23–29
Balleyguier C, Ciolovan L, Ammari S et al (2013) Breast elastography: the technical process and its applications. Diagn Interv Imaging 94:503–513
Goddi A, Bonardi M, Alessi S (2012) Breast elastography: a literature review. J Ultrasound 15:192–198
Nightingale K, McAleavey S, Trahey G (2003) Shear-wave generation using acoustic radiation force: in vivo and ex vivo results. Ultrasound Med Biol 29:1715–1723
Nightingale KR, Zhai L, Dahl JJ, Frinkley KD, Palmeri ML (2006) Shear wave velocity estimation using acoustic radiation force impulsive excitation in liver in vivo. Proc 2006 I.E. Ultrasonics Symposium 1156–1160.
Bercoff J, Tanter M, Fink M (2004) Supersonic shear imaging: a new technique for soft tissue elasticity mapping. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control 51:396–409
Tan SM, Teh HS, Mancer JF, Poh WT (2008) Improving B mode ultrasound evaluation of breast lesions with real-time ultrasound elastography–a clinical approach. Breast 17:252–257
Thomas A, Kummel S, Fritzsche F et al (2006) Real-time sonoelastography performed in addition to B-mode ultrasound and mammography: improved differentiation of breast lesions? Acad Radiol 13:1496–1504
Zhi H, Ou B, Luo BM, Feng X, Wen YL, Yang HY (2007) Comparison of ultrasound elastography, mammography, and sonography in the diagnosis of solid breast lesions. J Ultrasound Med 26:807–815
Zhu QL, Jiang YX, Liu JB et al (2008) Real-time ultrasound elastography: its potential role in assessment of breast lesions. Ultrasound Med Biol 34:1232–1238
Parajuly SS, Lan PY, Yan L, Gang YZ, Lin L (2010) Breast elastography: a hospital-based preliminary study in China. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 11:809–814
Lee JH, Kim SH, Kang BJ et al (2011) Role and clinical usefulness of elastography in small breast masses. Acad Radiol 18:74–80
Mansour SM, Omar OS (2012) Elastography ultrasound and questionable breast lesions: does it count? Eur J Radiol 81:3234–3244
Zhi H, Xiao XY, Ou B et al (2012) Could ultrasonic elastography help the diagnosis of small (</ = 2 cm) breast cancer with the usage of sonographic BI-RADS classification? Eur J Radiol 81:3216–3221
Thomas A, Degenhardt F, Farrokh A, Wojcinski S, Slowinski T, Fischer T (2010) Significant differentiation of focal breast lesions: calculation of strain ratio in breast sonoelastography. Acad Radiol 17:558–563
Cho N, Moon WK, Kim HY, Chang JM, Park SH, Lyou CY (2010) Sonoelastographic strain index for differentiation of benign and malignant nonpalpable breast masses. J Ultrasound Med 29:1–7
Fischer T, Peisker U, Fiedor S et al (2012) Significant differentiation of focal breast lesions: raw data-based calculation of strain ratio. Ultraschall Med 33:372–379
Zhao QL, Ruan LT, Zhang H, Yin YM, Duan SX (2012) Diagnosis of solid breast lesions by elastography 5-point score and strain ratio method. Eur J Radiol 81:3245–3249
Parajuly SS, Lan PY, Yun MB, Gang YZ, Hua Z (2012) Diagnostic potential of strain ratio measurement and a 5 point scoring method for detection of breast cancer: Chinese experience. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 13:1447–1452
Zhi H, Xiao XY, Yang HY, Ou B, Wen YL, Luo BM (2010) Ultrasonic elastography in breast cancer diagnosis: strain ratio vs 5-point scale. Acad Radiol 17:1227–1233
Zhou J, Zhan W, Chang C et al (2013) Role of acoustic shear wave velocity measurement in characterization of breast lesions. J Ultrasound Med 32:285–294
Jin ZQ, Li XR, Zhou HL et al (2012) Acoustic radiation force impulse elastography of breast imaging reporting and data system category 4 breast lesions. Clin Breast Cancer 12:420–427
Bai M, Du L, Gu J, Li F, Jia X (2012) Virtual touch tissue quantification using acoustic radiation force impulse technology: initial clinical experience with solid breast masses. J Ultrasound Med 31:289–294
Meng W, Zhang G, Wu C, Wu G, Song Y, Lu Z (2011) Preliminary results of acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) ultrasound imaging of breast lesions. Ultrasound Med Biol 37:1436–1443
Chang JM, Moon WK, Cho N et al (2011) Clinical application of shear wave elastography (SWE) in the diagnosis of benign and malignant breast diseases. Breast Cancer Res Treat 129:89–97
Wang ZL, Li JL, Li M, Huang Y, Wan WB, Tang J (2013) Study of quantitative elastography with supersonic shear imaging in the diagnosis of breast tumours. Radiol Med 118:583–590
Evans A, Whelehan P, Thomson K et al (2010) Quantitative shear wave ultrasound elastography: initial experience in solid breast masses. Breast Cancer Res 12:R104
Chang JM, Won JK, Lee KB, Park IA, Yi A, Moon WK (2013) Comparison of shear-wave and strain ultrasound elastography in the differentiation of benign and malignant breast lesions. AJR Am J Roentgenol 201:W347–356
Yi A, Cho N, Chang JM, Koo HR, La Yun B, Moon WK (2012) Sonoelastography for 1,786 non-palpable breast masses: diagnostic value in the decision to biopsy. Eur Radiol 22:1033–1040
Adamietz BR, Meier-Meitinger M, Fasching P et al (2011) New diagnostic criteria in real-time elastography for the assessment of breast lesions. Ultraschall Med 32:67–73
Yerli H, Yilmaz T, Kaskati T, Gulay H (2011) Qualitative and semiquantitative evaluations of solid breast lesions by sonoelastography. J Ultrasound Med 30:179–186
Colleoni M, Rotmensz N, Maisonneuve P et al (2007) Prognostic role of the extent of peritumoral vascular invasion in operable breast cancer. Ann Oncol 18:1632–1640
de Mascarel I, Bonichon F, Durand M et al (1998) Obvious peritumoral emboli: an elusive prognostic factor reappraised. Multivariate analysis of 1320 node-negative breast cancers. Eur J Cancer 34:58–65
American College of Radiology (ACR) (2003) ACR BI-RADS – Ultrasound ACR Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System, Breast Imaging Atlas. American College of Radiology, Reston
American College of Radiology (ACR) (2003) ACR BI-RADS – Mammography ACR Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System, Breast Imaging Atlas. American College of Radiology, Reston
Sadigh G, Carlos RC, Neal CH, Dwamena BA (2012) Accuracy of quantitative ultrasound elastography for differentiation of malignant and benign breast abnormalities: a meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat 134:923–931
De Muth JE (2006) Correlation. In: De Muth JE (ed) Basic statistics and pharmaceutical statistical applications. Chapman & Hall/CRC, Boca Raton, pp 311–342
Barr RG, Destounis S, Lackey LB II, Svensson WE, Balleyguier C, Smith C (2012) Evaluation of breast lesions using sonographic elasticity imaging: a multicenter trial. J Ultrasound Med 31:281–287
Regner DM, Hesley GK, Hangiandreou NJ et al (2006) Breast lesions: evaluation with US strain imaging–clinical experience of multiple observers. Radiology 238:425–437
Alhabshi SM, Rahmat K, Abdul Halim N et al (2013) Semi-quantitative and qualitative assessment of breast ultrasound elastography in differentiating between malignant and benign lesions. Ultrasound Med Biol 39:568–578
Raza S, Odulate A, Ong EM, Chikarmane S, Harston CW (2010) Using real-time tissue elastography for breast lesion evaluation: our initial experience. J Ultrasound Med 29:551–563
Navarro B, Ubeda B, Vallespi M, Wolf C, Casas L, Browne JL (2011) Role of elastography in the assessment of breast lesions: preliminary results. J Ultrasound Med 30:313–321
Houelleu Demay ML, Monghal C, Bertrand P, Vilde A, Brunereau L (2012) An assessment of the performance of elastography for the investigation of BI-RADS 4 and BI-RADS 5 breast lesions: correlations with pathological anatomy findings. Diagn Interv Imaging 93:757–766
Stachs A, Hartmann S, Stubert J et al (2013) Differentiating between malignant and benign breast masses: factors limiting sonoelastographic strain ratio. Ultraschall Med 34:131–136
Tozaki M, Fukuma E (2011) Pattern classification of shear wave elastography images for differential diagnosis between benign and malignant solid breast masses. Acta Radiol 52:1069–1075
Kim H, Youk JH, Gweon HM, Kim JA, Son EJ (2013) Diagnostic performance of qualitative shear-wave elastography according to different color map opacities for breast masses. Eur J Radiol 82:e326–331
Lee EJ, Jung HK, Ko KH, Lee JT, Yoon JH (2013) Diagnostic performances of shear wave elastography: which parameter to use in differential diagnosis of solid breast masses? Eur Radiol 23:1803–1811
Kumm TR, Szabunio MM (2010) Elastography for the characterization of breast lesions: initial clinical experience. Cancer Control 17:156–161
Youk JH, Gweon HM, Son EJ, Kim JA, Jeong J (2013) Shear-wave elastography of invasive breast cancer: correlation between quantitative mean elasticity value and immunohistochemical profile. Breast Cancer Res Treat 138:119–126
Chang JM, Park IA, Lee SH et al (2013) Stiffness of tumours measured by shear-wave elastography correlated with subtypes of breast cancer. Eur Radiol 23:2450–2458
Evans A, Whelehan P, Thomson K et al (2012) Invasive breast cancer: relationship between shear-wave elastographic findings and histologic prognostic factors. Radiology 263:673–677
Sadigh G, Carlos RC, Neal CH, Dwamena BA (2012) Ultrasonographic differentiation of malignant from benign breast lesions: a meta-analytic comparison of elasticity and BIRADS scoring. Breast Cancer Res Treat 133:23–35
Gong X, Xu Q, Xu Z, Xiong P, Yan W, Chen Y (2011) Real-time elastography for the differentiation of benign and malignant breast lesions: a meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat 130:11–18
Maskarinec G, Meng L, Ursin G (2001) Ethnic differences in mammographic densities. Int J Epidemiol 30:959–965
Golatta M, Schweitzer-Martin M, Harcos A et al (2013) Normal breast tissue stiffness measured by a new ultrasound technique: virtual touch tissue imaging quantification (VTIQ). Eur J Radiol 82:e676–679
Sadigh G, Carlos RC, Neal CH, Wojcinski S, Dwamena BA (2013) Impact of breast mass size on accuracy of ultrasound elastography vs. conventional B-mode ultrasound: a meta-analysis of individual participants. Eur Radiol 23:1006–1014
Garra BS, Cespedes EI, Ophir J et al (1997) Elastography of breast lesions: initial clinical results. Radiology 202:79–86
Wernicke M, Roitman P, Manfre D, Stern R (2011) Breast cancer and the stromal factor. The “prometastatic healing process” hypothesis. Medicina (B Aires) 71:15–21
Auvinen P, Tammi R, Parkkinen J et al (2000) Hyaluronan in peritumoral stroma and malignant cells associates with breast cancer spreading and predicts survival. Am J Pathol 156:529–536
Acknowledgements
The scientific guarantor of this publication is WeiWei Zhan. The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article. The authors state that this work has not received any funding. No complex statistical methods were necessary for this paper. Institutional review board approval was obtained. Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects (patients) in this study. No study subjects or cohorts have been previously reported. Methodology: Prospective, case-control study, performed at one institution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, J., Zhan, W., Dong, Y. et al. Stiffness of the surrounding tissue of breast lesions evaluated by ultrasound elastography. Eur Radiol 24, 1659–1667 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3152-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3152-7