Abstract
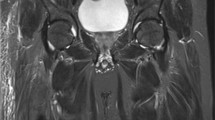
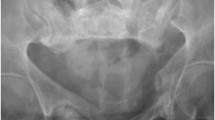
The purpose of our study was to evaluate magnetic resonance (MR) signal characteristics of acutely forming heterotopic ossification (HO) in paralyzed patients. Fourteen patients with spinal cord injury (female n=2, male n=12, mean age 38.3 years) and acute onset of radiographically proven HO had contrast-enhanced 1.5-T MRI within 13.4±18.3 days of clinical onset of symptoms. MR signal alterations of affected muscles, fascia, subcutaneous tissue, skin and adjacent bone were evaluated. A diffuse T2-hyperintense signal of multiple muscle groups was seen in all patients (bilateral in 12) involving quadriceps (n=13, 93%), adductors (n=13, 93%) and iliopsoas (n=12, 86%) with contrast enhancement in n=11 (79%), n=8 (57%) and n=8 (57%) patients. All patients had nonenhancing areas (mean size 2×3.5×5.8 cm) within diffusely enhancing muscles. HO formation occurred around these nonenhancing areas in four patients with computed tomography follow-up. Other MR findings included fascial edema (n=14, 100%), fascial enhancement (n=13, 93%), subcutaneous edema (n=13, 93%), subcutaneous enhancement (n=12, 86%), bone marrow edema (n=5, 36%), and joint effusion (n=12, 86%). MRI reveals mostly bilateral edema and enhancement of muscles, fascia and subcutaneous tissue during acute onset of HO. HO develops in the periphery of well-defined areas of no enhancement.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hernandez AM, Forner JV, de la Fuente T, Gonzalez C, Miro R (1978) The para-articular ossifications in our paraplegics and tetraplegics: a survey of 704 patients. Paraplegia 16:272–275
Blane CE, Perkash I (1981) True heterotopic bone in the paralyzed patient. Skelet Radiol 7:21–25
Prakash V, Lin MS, Perkash I (1978) Detection of heterotopic calcification with 99 mTc-pyrophosphate in spinal cord injury patients. Clin Nucl Med 3:167–169
Garland DE (1991) A clinical perspective on common forms of acquired heterotopic ossification. Clin Ortop 13–29
Stover SL, Hataway CJ, Zeiger HE (1975) Heterotopic ossification in spinal cord-injured patients. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 56:199–204
Subbarao JV, Garrison SJ (1999) Heterotopic ossification: diagnosis and management, current concepts and controversies. J Spinal Cord Med 22:273–283
Orzel JA, Rudd TG (1985) Heterotopic bone formation: clinical, laboratory, and imaging correlation. J Nucl Med 26:125–132
Freed JH, Hahn H, Menter R, Dillon T (1982) The use of the three-phase bone scan in the early diagnosis of heterotopic ossification (HO) and in the evaluation of Didronel therapy. Paraplegia 20:208–216
Bravo-Payno P, Esclarin A, Arzoz T, Arroyo O, Labarta C (1992) Incidence and risk factors in the appearance of heterotopic ossification in spinal cord injury. Paraplegia 30:740–745
Wharton GW, Morgan TH (1970) Ankylosis in the paralyzed patient. J Bone Jt Surg [Am] 52:105–112
Wharton GW. (1975) Heterotopic ossification. Clin Ortop 112:142–149
Muheim G, Donath A, Rossier AB (1973) Serial scintigrams in the course of ectopic bone formation in paraplegic patients. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med 118:865–869
Cassar-Pullicino VN, McClelland M, Badwan DA, McCall IW, Pringle RG, el Masry W (1993) Sonographic diagnosis of heterotopic bone formation in spinal injury patients. Paraplegia 31:40–50
Bodley R, Jamous A, Short D (1993) Ultrasound in the early diagnosis of heterotopic ossification in patients with spinal injuries. Paraplegia 31:500–506
Thomas EA, Cassar-Pullicino VN, McCall IW (1991) The role of ultrasound in the early diagnosis and management of heterotopic bone formation. Clin Radiol 43:190–196
Bressler EL, Marn CS, Gore RM, Hendrix RW (1987) Evaluation of ectopic bone by CT. Am J Roentgenol 148:931–935
Ledermann HP, Schweitzer ME, Morrison WB (2002) Pelvic heterotopic ossification: MR imaging characteristics. Radiology 222:189–195
Huang AB, Schweitzer ME, Hume E, Batte WG (1998) Osteomyelitis of the pelvis/hips in paralyzed patients: accuracy and clinical utility of MRI. J Comput Assist Tomogr 22:437–443
May DA, Disler DG, Jones EA, Balkissoon AA, Manaster BJ (2000) Abnormal signal intensity in skeletal muscle at MR imaging: patterns, pearls, and pitfalls. Radiographics 20 Spec No:S295–S315
Ditunno JF, Little JW, Tessler A, Burns AS (2004) Spinal shock revisited: a four-phase model. Spinal Cord 42:383–395
Snoecx M, De Muynck M, Van Laere M (1995) Association between muscle trauma and heterotopic ossification in spinal cord injured patients: reflections on their causal relationship and the diagnostic value of ultrasonography. Paraplegia 33:464–468
Silver JR (1969) Heterotopic ossification. A clinical study of its possible relationship to trauma. Paraplegia 7:220–230
Parikh J, Hyare H, Saifuddin A (2002) The imaging features of post-traumatic myositis ossificans, with emphasis on MRI. Clin Radiol 57:1058–1066
Shirkhoda A, Armin AR, Bis KG, Makris J, Irwin RB, Shetty AN (1995) MR imaging of myositis ossificans: variable patterns at different stages. J Magn Reson Imaging 5:287–292
Kransdorf MJ, Meis JM, Jelinek JS (1991) Myositis ossificans: MR appearance with radiologic–pathologic correlation. Am J Roentgenol 157:1243–1248
De Smet AA, Norris MA, Fisher DR (1992) Magnetic resonance imaging of myositis ossificans: analysis of seven cases. Skelet Radiol 21:503–507
Ehara S, Shiraishi H, Abe M, Mizutani H (1998) Reactive heterotopic ossification. Its patterns on MRI. Clin Imaging 22:292–296
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wick, L., Berger, M., Knecht, H. et al. Magnetic resonance signal alterations in the acute onset of heterotopic ossification in patients with spinal cord injury. Eur Radiol 15, 1867–1875 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-005-2769-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-005-2769-y