Abstract
Purpose
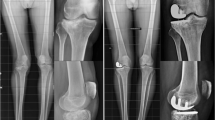
Proximal tibial fractures are typically treated with osteosynthesis. In older patients, this method has been reported to be associated with a high complication rate, risk of post-traumatic osteoarthritis, and long partial or non-weight bearing during the recovery phase. To avoid these problems, primary total knee replacement (TKR) has become an increasingly common treatment option.
Methods
Twenty-two patients (mean age 74 years, SD 12) underwent primary TKR due to tibial plateau fracture. Follow-up data were available for a mean of 19 (SD 16) months. Trauma mechanism, fracture classification, type of prosthesis used, complications, and re-operations during the follow-up were recorded. The Knee Society Score (KSS), Oxford Knee Score (OKS), range of flexion, and patient satisfaction were evaluated.
Results
13/22 of the fractures were due to a low-energy trauma. At final follow-up, mean KSS was 160 (SD 39) and mean OKS 27 (SD 11) points. Mean flexion was 109° (SD 16°). 14/17 of the patients were satisfied or highly satisfied with their post-operative knee and 11/17 reported their knee to be same or better than pre-trauma. 2/22 of the patients had complications requiring revision surgery.
Conclusion
TKR as a primary definitive method seems to be a useful alternative to osteosynthesis, enabling immediate full weight bearing and rapid mobilization of patients. The risk of complications associated with primary TKR is higher than those reported after TKR due to primary osteoarthritis but lower than those reported after TKR due to secondary osteoarthritis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Somersalo A, Paloneva J, Kautiainen H et al (2014) Incidence of fractures requiring inpatient care. Acta Orthop 85:525–530. https://doi.org/10.3109/17453674.2014.908340
Gerich T, Bosch U, Schmidt E et al (2001) Knee joint prosthesis implantation after fractures of the head of the tibia. Intermediate term results of a cohort analysis. Unfallchirurg 104:414–419
Su EP, Westrich GH, Rana AJ et al (2004) Operative treatment of tibial plateau fractures in patients older than 55 years. Clin Orthop Relat Res:240–248
Frattini M, Vaienti E, Soncini G, Pogliacomi F (2009) Tibial plateau fractures in elderly patients. Musculoskelet Surg 93:109–114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12306-009-0038-y
Weiss NG, Parvizi J, Hanssen AD et al (2003) Total knee arthroplasty in post-traumatic arthrosis of the knee. J Arthroplast 18:23–26. https://doi.org/10.1054/arth.2003.50068
Ali AM, El-Shafie M, Willett KM (2002) Failure of fixation of tibial plateau fractures. J Orthop Trauma 16:323–329
Wasserstein D, Henry P, Paterson JM et al (2014) Risk of total knee arthroplasty after operatively treated tibial plateau fracture a matched-population-based cohort study. J Bone Jt Surg - Ser A 96:144–150. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.L.01691
Nourissat G, Hoffman E, Hémon C et al (2006) Total knee arthroplasty for recent severe fracture of the proximal tibial epiphysis in the elderly subject. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 92:242–247
Rademakers MV, Kerkhoffs GMMJ, Sierevelt IN et al (2007) Operative treatment of 109 tibial plateau fractures: five- to 27-year follow-up results. J Orthop Trauma 21:5–10. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOT.0b013e31802c5b51
Schenker ML, Mauck RL, Ahn J, Mehta S (2014) Pathogenesis and prevention of posttraumatic osteoarthritis after intra-articular fracture. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 22:20–28. https://doi.org/10.5435/JAAOS-22-01-20
Honkonen SE (1995) Degenerative arthritis after tibial plateau fractures. J Orthop Trauma 9:273–277
Shimizu T, Sawaguchi T, Sakagoshi D et al (2016) Geriatric tibial plateau fractures: clinical features and surgical outcomes. J Orthop Sci 21:68–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jos.2015.09.008
Roerdink WH, Oskam J, Vierhout PA (2001) Arthroscopically assisted osteosynthesis of tibial plateau fractures in patients older than 55 years. Arthroscopy 17:826–831
Parkkinen M, Madanat R, Lindahl J, Mäkinen TJ (2016) Risk factors for deep infection following plate fixation of proximal tibial fractures. J Bone Jt Surg 98:1292–1297. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.15.00894
Ryu SM, Choi CH, Yang HS et al (2019) Causes and treatment outcomes of revision surgery after open reduction and internal fixation of tibial plateau fractures. Int Orthop 43:1685–1694. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-018-4080-y
Vermeire J, Scheerlinck T (2010) Early primary total knee replacement for complex proximal tibia fractures in elderly and osteoarthritic patients. Acta Orthop Belg 76:785–793
Huang J-F, Shen J-J, Chen J-J, Tong P-J (2016) Primary total knee arthroplasty for elderly complex tibial plateau fractures. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc 50:702–705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aott.2015.03.001
Sarzaeem MM, Omidian MM, Kazemian G, Manafi A (2017) Acute primary total knee arthroplasty for proximal tibial fractures in elderly. Arch Bone Jt Surg 5:302–307. https://doi.org/10.22038/abjs.2017.8435
Boureau F, Benad K, Putman S et al (2015) Does primary total knee arthroplasty for acute knee joint fracture maintain autonomy in the elderly? A retrospective study of 21 cases. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 101:947–951. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otsr.2015.09.021
Haufe T, Förch S, Müller P et al (2016) The role of a primary arthroplasty in the treatment of proximal tibia fractures in orthogeriatric patients. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/6047876
Schatzker J, McBroom R, Bruce D (1979) The tibial plateau fracture. The Toronto experience 1968--1975. Clin Orthop Relat Res 94–104
Kilian U (2003) Total knee replacement for primary treatment of intra-articular tibial head fractures in elderly patients. Unfallchirurg 106:1046–1050. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00113-003-0643-4
Malviya A, Reed MR, Partington PF (2011) Acute primary total knee arthroplasty for peri-articular knee fractures in patients over 65 years of age. Injury 42:1368–1371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2011.06.198
Nau T, Pflegerl E, Erhart J, Vecsei V (2003) Primary total knee arthroplasty for periarticular fractures. J Arthroplast 18:968–971. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0883-5403(03)00280-8
Schwarz N, Buchinger W, Mähring M et al (2008) Trauma hospital. Knee arthroplasty as primary therapy for proximal tibial fracture. Unfallchirurg 111:928–932. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00113-008-1426-8
Kini SG, Sathappan SS (2013) Role of navigated total knee arthroplasty for acute tibial fractures in the elderly. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 133:1149–1154. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-013-1792-8
Gaunder CL, Zhao Z, Henderson C et al (2018) Wound complications after open reduction and internal fixation of tibial plateau fractures in the elderly: a multicentre study. Int Orthop. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-018-3940-9
Lin S, Mauffrey C, Hammerberg EM et al (2014) Surgical site infection after open reduction and internal fixation of tibial plateau fractures. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 24:797–803. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-013-1252-8
Meulenkamp B, Martin R, Desy NM et al (2017) Incidence, risk factors, and location of articular malreductions of the tibial plateau. J Orthop Trauma 31:146–150. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOT.0000000000000735
Shao J, Chang H, Zhu Y et al (2017) Incidence and risk factors for surgical site infection after open reduction and internal fixation of tibial plateau fracture: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Surg 41:176–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2017.03.085
Volpin G, Dowd GS, Stein H, Bentley G (1990) Degenerative arthritis after intra-articular fractures of the knee. Long-term results. J Bone Joint Surg Br 72:634–638
Riou B, Rothmann C, Lecoules N et al (2007) Incidence and risk factors for venous thromboembolism in patients with nonsurgical isolated lower limb injuries. Am J Emerg Med 25:502–508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2006.09.012
Dittmer DK, Teasell R (1993) Complications of immobilization and bed rest. Part 1: Musculoskeletal and cardiovascular complications. Can Fam Physician 39:1428–32–11435–7
Mehin R, O’Brien P, Broekhuyse H et al (2012) Endstage arthritis following tibia plateau fractures: average 10-year follow-up. Can J Surg 55:7–94. https://doi.org/10.1503/cjs.003111
Oladeji L, Dreger T, Pratte E et al (2018) Total knee arthroplasty versus osteochondral allograft: prevalence and risk factors following tibial plateau fractures. J Knee Surg. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0038-1641593
Lunebourg A, Parratte S, Gay A et al (2015) Lower function, quality of life, and survival rate after total knee arthroplasty for posttraumatic arthritis than for primary arthritis. Acta Orthop 86:189–194. https://doi.org/10.3109/17453674.2014.979723
Civinini R, Carulli C, Matassi F et al (2009) Total knee arthroplasty after complex tibial plateau fractures. Musculoskelet Surg 93:143–147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12306-009-0033-3
Bala A, Penrose CT, Seyler TM et al (2015) Outcomes after total knee arthroplasty for post-traumatic arthritis. Knee 22:630–639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knee.2015.10.004
El-Galaly A, Haldrup S, Pedersen AB et al (2017) Increased risk of early and medium-term revision after post-fracture total knee arthroplasty. Acta Orthop 88:263–268. https://doi.org/10.1080/17453674.2017.1290479
Houdek MT, Watts CD, Shannon SF et al (2016) Posttraumatic total knee arthroplasty continues to have worse outcome than total knee arthroplasty for osteoarthritis. J Arthroplast 31:118–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2015.07.022
Softness KA, Murray RS, Evans BG (2017) Total knee arthroplasty and fractures of the tibial plateau. World J Orthop 8:107–114. https://doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v8.i2.107
Funding
This work received financial support from the Päivikki and Sakari Sohlberg Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study was approved by the ethical board of the Central Finland Health Care District 27.3.2017(6U/2017).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tapper, V., Toom, A., Pesola, M. et al. Knee joint replacement as primary treatment for proximal tibial fractures: analysis of clinical results of twenty-two patients with mean follow-up of nineteen months. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 44, 85–93 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-019-04415-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-019-04415-w