Abstract
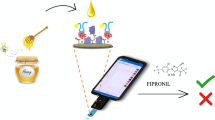
A new electrochemical magnetoimmunosensor (EMIS) has been developed for the screening of residues of sulfonamide antimicrobials in honey samples. The immunosensor is able to detect up to ten different sulfonamide congeners at levels below the action points established in some European countries (25 μg kg−1) after a hydrolysis step in which the sulfonamides are released from the corresponding conjugates formed in samples of this type. In spite of the complexity of the sample after the hydrolysis procedure, the EMIS could perform quantitative measurements, directly in these samples, without any additional sample cleanup or extraction step. For example, sulfapyridine, used as a reference, can be detected in hydrolyzed honey with a limit of detection (IC90) of 0.1 ± 0.03 μg kg−1. Considering that the use of antibiotics for bee treatment is prohibited in the European Union, the immunosensor presented here could be an excellent screening tool. Moreover, several samples can be processed in parallel, which facilitates the analysis, reducing the necessity to use more costly confirmatory methods for just screening. As a proof of concept, a set of blind honey samples (spiked and incurred) were analyzed and the results were compared with those obtained by high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry, demonstrating the potential of the EMIS as a screening tool.

ᅟ






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wegener HC (2003) Antibiotics in animal feed and their role in resistance development. Curr Opin Microbiol 6(5):439–445
Hiramatsu K, Cui L, Kuroda M, Ito T (2001) The emergence and evolution of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Trends Microbiol 9(10):486–493
Wang S, Hy Z, Wang L, Duan ZJ, Kennedy I (2006) Analysis of sulphonamide residues in edible animal products: a review. Food Addit Contam 23(4):362–384
Zotou A, Vasiliadou C (2006) Selective determination of sulfonamide residues in honey by SPE-RP-LC with UV detection. Chromatographia 64(5):307–311
Bogdanov S (2005) Contaminants of bee products. Apidologie 37:1–18
Sensderson JP, Naisbitt DJ, Park BK (2006) Role of bioacitvation in drug-induced hypersensitivity reactions. J AAPS 8:E55–E64
Heath JE, Littlefield NA (1984) Morphological effects of subchronic oral sulfamethazine administration on Fischer 344 rats and B6C3F1 mice. Toxicol Pathol 12(1):3–9
Food and Drug Regulations (1991)Table III, Division 15, Part B., Canada Gazette Part II, 125, 1478–1480
European Council (1990) Council Regulation (ECC) No 2377/99 of 26 June 1990 laying down a community procedure for the establishment of maximum residue limits of veterinary medicinal products in foodstuffs of animal origin. Off J Eur Communities L224:1
Reybroeck W, Daeseleire E, De Brabander HF, Herman L (2012) Antimicrobials in beekeeping. Vet Microbiol 158(1–2):1–11. doi:10.1016/j.vetmic.2012.01.012
Bernal J, Nozal MJ, Jiménez JJ, Martín MT, Sanz E (2009) A new and simple method to determine trace levels of sulfonamides in honey by high performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J Chromatogr A 1216(43):7275–7280. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2009.05.046
Sheridan R, Policastro B, Thomas S, Rice D (2008) Analysis and occurrence of 14 sulfonamide antibacterials and chloramphenicol in honey by solid-phase extraction followed by LC/MS/MS analysis. J Agric Food Chem 56(10):3509–3516
Maudens KE, Zhang G-F, Lambert WE (2004) Quantitative analysis of twelve sulfonamides in honey after acidic hydrolysis by high-performance liquid chromatography with post-column derivatization and fluorescence detection. J Chromatogr A 1047(1):85–92
Pang G-F, Cao Y-Z, Fan C-L, Zhang J-J, Li X-M, Li Z-Y, Jia G-Q (2003) Liquid chromatography–fluorescence detection for simultaneous analysis of sulfonamide residues in honey. Anal Bioanal Chem 376(4):534–54115
Sheth HB, Yaylayan VA, Low NH, Stiles ME, Sporns P (1990) Reaction of reducing sugars with sulfathiazole and importance of this reaction to sulfonamide residue analysis using chromatographic, colorimetric, microbiological, or ELISA methods. J Agric Food Chem 38(4):1125–1130
Heering W, Usleber E, Dietrich D, Märtlbauer E (1998) Immunochemical screening for antimicrobial drug residues in commercial honey. Analyst 123:2759–2762
Schawaiger I, Schuch R (2000) Bound sulfathiazole residues in honey—need of a hydrolysis step for the analytical determination of total sulfathiazole content in honey. Dtsch Lebensmitt Rundsch 96(3):93–98
Wang YH, Li L, Chen CH, Cheng SR, Lee MS, Yu PP, Chang-Chien GP (2012) Investigation of breaking efficiency of N-glycosidic bond between sulfonamide and honey. Chem Res Chin Univ 28(2):195–199
Adrian J, Fernández F, Muriano A, Obregón R, Ramón J, Tort N, Marco M-P (2010) Immunochemical analytical methods for monitoring the aquatic environments. In: Namiesni J, Szefer P (eds) Analytical methods in aquatic environments. IWA Publishing, London
Nesterenko I, Nokel M, Eremin S (2009) Immunochemical methods for the detection of sulfanylamide drugs. J Anal Chem 64(5):435–444
Fernández F, Hegnerová K, Piliarik M, Sanchez-Baeza F, Homola J, Marco MP (2010) A label-free and portable multichannel surface plasmon resonance immunosensor for on site analysis of antibiotics in milk samples. Biosens Bioelectron 26(4):1231–1238
Viswanathan S, Radecka H, Radecki J (2009) Electrochemical biosensors for food analysis. Monatsh Chem/Chem Mon 140(8):891–899
Adrián J, Fernández F, Muriano A, Obregon R, Ramón-Azcon J, Tort N, Marco MP (2009) Biosensors for pharmaceuticals and emerging contaminants based on novel micro and nanotechnology approaches. In: Barceló D, Hansen P-D (eds) Biosensors for environmental monitoring of aquatic systems. Handbook of environmental chemistry, part 5J. Springer, Berlin, pp 47–68
Adrian J, Pasche S, Voirin G, Adrian J, Pinacho DG, Font H, Sánchez-Baeza F, Marco MP, Diserens J-M, Granier B (2009) Wavelength-interrogated optical biosensor for multi-analyte screening of sulfonamide, fluoroquinolone, β-lactam and tetracycline antibiotics in milk. Trends Anal Chem 28(6):769–777
Bratov A, Abramova N, Pilar Marco M, Sanchez-Baeza F (2012) Three-dimensional interdigitated electrode array as a tool for surface reactions registration. Electroanalysis 24(1):69–75. doi:10.1002/elan.201100392
Fernandez F, Pinacho DG, Sanchez-Baeza F, Pilar Marco M (2011) Portable surface plasmon resonance immunosensor for the detection of fluoroquinolone antibiotic residues in milk. J Agric Food Chem 59(9):5036–5043. doi:10.1021/jf1048035
Fernandez F, Sanchez-Baeza F, Pilar Marco M (2012) Nanogold probe enhanced surface plasmon resonance immunosensor for improved detection of antibiotic residues. Biosens Bioelectron 34(1):151–158. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2012.01.036
Giroud F, Gorgy K, Gondran C, Cosnier S, Pinacho DG, Marco MP, Sanchez-Baeza FJ (2009) Impedimetric immunosensor based on a polypyrrole-antibiotic model film for the label-free picomolar detection of ciprofloxacin. Anal Chem 81(20):8405–8409. doi:10.1021/ac901290m
Muriano A, Anisha Thayil KN, Salvador JP, Loza-Alvarez P, Soria S, Galve R, Marco MP (2012) Two-photon fluorescent immunosensor for androgenic hormones using resonant grating waveguide structures. Sensors Actuators B Chem 174:394–401. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2012.08.006
Jornet D, González-Martínez MA, Puchades R, Maquieira A (2010) Antibiotic immunosensing: determination of sulfathiazole in water and honey. Talanta 81(4–5):1585–1592
Centi S, Stoica A, Laschi S, Mascini M (2010) Development of an electrochemical immunoassay based on the use of an eight-electrodes screen-printed array coupled with magnetic beads for the detection of antimicrobial sulfonamides in honey. Electroanalysis 22(16):1881–1888
Cai M, Zhu L, Ding Y, Wang J, Li J, Du X (2012) Determination of sulfamethoxazole in foods based on CeO2/chitosan nanocomposite-modified electrodes. Mater Sci Eng C 32(8):2623–2627. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2012.08.017
Baniukevic J, Hakki Boyaci I, Goktug Bozkurt A, Tamer U, Ramanavicius A, Ramanaviciene A (2013) Magnetic gold nanoparticles in SERS-based sandwich immunoassay for antigen detection by well oriented antibodies. Biosens Bioelectron 43:281–288. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2012.12.014
Kuramitz H (2009) Magnetic microbead-based electrochemical immunoassays. Anal Bioanal Chem 394(1):61–69. doi:10.1007/s00216-009-2650-y
Orlov AV, Khodakova JA, Nikitin MP, Shepelyakovskaya AO, Brovko FA, Laman AG, Grishin EV, Nikitin PI (2013) Magnetic immunoassay for detection of staphylococcal toxins in complex media. Anal Chem 85(2):1154–1163. doi:10.1021/ac303075b
Pedrero M, Campuzano S, Pingarron JM (2012) Magnetic beads-based electrochemical sensors applied to the detection and quantification of bioterrorism/biohazard agents. Electroanalysis 24(3):470–482. doi:10.1002/elan.201100528
Xu J, Yin W, Zhang Y, Yi J, Meng M, Wang Y, Xue H, Zhang T, Xi R (2012) Establishment of magnetic beads-based enzyme immunoassay for detection of chloramphenicol in milk. Food Chem 134(4):2526–2531. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.04.083
Zacco E, Adrian J, Galve R, Marco M-P, Alegret S, Pividori MI (2007) Electrochemical magneto immunosensing of antibiotic residues in milk. Biosens Bioelectron 22(9–10):2184–2191
Adrian J, Font H, Diserens J-M, Sanchez-Baeza F, Marco MP (2009) Generation of broad specificity antibodies for sulfonamide antibiotics and development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for the analysis of milk samples. J Agric Food Chem 57(2):385–394. doi:10.1021/jf8027655
Font H, Adrian J, Galve R, Estevez MC, Castellari M, Gratacos-Cubarsí M, Sanchez-Baeza F, Marco MP (2008) Immunochemical assays for direct sulfonamide antibiotic detection in milk and hair samples using antibody derivatized magnetic nanoparticles. J Agric Food Chem 56(3):736–743. doi:10.1021/jf072550n
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1–2):248–254
Zacco E, Pividori MI, Alegret S, Galve R, Marco M-P (2006) Electrochemical magnetoimmunosensing strategy for the detection of pesticides residues. Anal Chem 78(6):1780–1788
Pividori MI, Merkoçi A, Alegret S (2003) Graphite-epoxy composites as a new transducing material for electrochemical genosensing. Biosens Bioelectron 19:473–484
Lermo A, Fabiano S, Hernández S, Galve R, Marco MP, Alegret S, Pividori MI (2009) Immunoassay for folic acid detection in vitamin-fortified milk based on electrochemical magneto sensors. Biosens Bioelectron 24(7):2057–2063
Adrian J, Pasche S, Diserens J-M, Sánchez-Baeza F, Gao H, Marco MP, Voirin G (2009) Waveguide interrogated optical immunosensor (WIOS) for detection of sulfonamide antibiotics in milk. Biosens Bioelectron 24(11):3340–3346
Adrian J, Pinacho D, Granier B, Diserens J-M, Sánchez-Baeza F, Marco MP (2008) A multianalyte ELISA for immunochemical screening of sulfonamide, fluoroquinolone and ß-lactam antibiotics in milk samples using class-selective bioreceptors. Anal Bioanal Chem 391(5):1703–1712
Acknowledgments
This work was performed in the frame of European project Conffidence (KBBE-211326). The AMR group (nowadays the Nb4D group) is a consolidated research group (Grup de Recerca) of the Generalitat de Catalunya and has support from the Departament d’Universitats, Recerca I Societat de la informació la Generalitat de Catalunya (expedient 2009 SGR 13432). CIBER-BBN is an initiative funded by the VI National R&D&I Plan 2008–2011, IniciativaIngenio 2010, Consolider Program, CIBER Actions and is financed by the Instituto de Salud Carlos III with assistance from the European Regional Development Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in the topical collection Rapid Detection in Food and Feed with guest editors Rudolf Krska and Michel Nielen.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muriano, A., Pinacho, DG., Chabottaux, V. et al. A portable electrochemical magnetoimmunosensor for detection of sulfonamide antimicrobials in honey. Anal Bioanal Chem 405, 7885–7895 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-013-7219-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-013-7219-0