Abstract
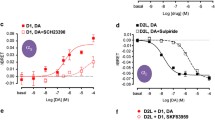
Agonist activity at recombinant human dopamine D4.4 receptors was compared in stably transfected CHO cells using two functional readouts: G protein activation by [35S]GTPγS binding and phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (pERK1/2). Results with a large series of agonists reveal markedly higher relative agonist efficacy in the pERK1/2 assay compared with [35S]GTPγS binding, while potencies were generally higher in the latter readout. Whereas efficacies were highly correlated when comparing both tests, potencies determined using the pERK1/2 assay were neither correlated with those for G protein activation nor with binding affinities. In order to examine if these differences may be attributable to distinct assay conditions (5 min incubation for pERK1/2 compared with binding equilibrium conditions for [35S]GTPγS), selected compounds were tested in a modified short-duration [35S]GTPγS binding assay. In these experiments, potencies were generally reduced; however, compounds exhibiting comparably high potency in the pERK1/2 assay were not affected by this duration-dependent potency shift. We conclude that assay parameters such as signal amplification and incubation time have to be considered with respect to the appropriate choice of experimental approaches that best reflect agonist activity at dopamine D4 receptors in vivo.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azzi M, Charest PG, Angers S, Rousseau G, Kohout T, Bouvier M, Pineyro G (2003) β-arrestin-mediated activation of MAPK by inverse agonists reveals distinct active conformations for G protein-coupled receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:11406–11411
Baker JG, Hall IP, Hill SJ (2003) Agonist and inverse agonist actions of β-blockers at the human β2-adrenoceptor provide evidence for agonist-directed signaling. Mol Pharmacol 64:1357–1369
Bardin L, Newman-Tancredi A, Depoortere R (2006) Effects of novel antipsychotics with preferential activity at D2–like and 5-HT1A receptors, in comparison with typical and atypical reference antipsychotics, in rodent models of cognition and memory deficits. 19th European Congress of NeuroPsychopharmacology, Paris, 16–20 September, 2006, P.3.d.005
Belcheva MM, Coscia CJ (2002) Diversity of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathways to ERK/MAP kinase. Neurosignals 11:34–44
Bitner RS, Nikkel AL, Otte S, Martino B, Barlow EH, Bhatia P, Stewart AO, Brioni JD, Decker MW, Moreland RB (2006) Dopamine D4 receptor signaling in the rat paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus: evidence of natural coupling involving immediate early gene induction and mitogen activated protein kinase phosphorylation. Neuropharmacology 50:521–531
Brioni JD, Moreland RB (2006) Dopamine D4 receptors and the regulation of penile erection. Drug Discovery Today 3:599–604
Bruins Slot LA, De Vries L, Newman-Tancredi A, Cussac D (2006) Differential profile of antipsychotics at serotonin 5-HT1A and dopamine D2S receptors coupled to extracellular signal-regulated kinase. Eur J Pharmacol 534:63–70
Bruins Slot LA, Palmier C, Tardif S, Cussac D (2007) Action of novel antipsychotics at human dopamine D3 receptors coupled to G protein and ERK1/2 activation. Neuropharmacology 53:232–241
Chang FM, Kidd JR, Livak KJ, Pakstis AJ, Kidd KK (1996) The world-wide distribution of allele frequencies at the human dopamine D4 receptor locus. Hum Genet 98:91–101
Cohen BM, Ennulat DJ, Centorrino F, Matthysse S, Konieczna H, Chu HM, Cherkerzian S (1999) Polymorphisms of the dopamine D4 receptor and response to antipsychotic drugs. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 141:6–10
Coldwell MC, Boyfield I, Brown T, Hagan JJ, Middlemiss DN (1999) Comparison of the functional potencies of ropinirole and other dopamine receptor agonists at human D2(long), D3 and D4.4 receptors expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Br J Pharmacol 127:1696–1702
Contreras ML, Wolfe BB, Molinoff PB (1986) Kinetic analysis of the interactions of agonists and antagonists with beta adrenergic receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 239:136–143
Crane JW, Shimizu K, Carrasco GA, Garcia F, Jia C, Sullivan NR, D’Souza DN, Zhang Y, Van de Kar LD, Muma NA, Battaglia G (2007) 5-HT1A receptors mediate (+)8-OH-DPAT-stimulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (MAP kinase) in vivo in rat hypothalamus: Time dependence and regional differences. Brain Res 1183:51–59
Cussac D, Duqueyroix D, Newman-Tancredi A, Millan MJ (2002) Stimulation by antipsychotic agents of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) coupled to cloned, human (h)serotonin (5-HT)1A receptors. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 162:168–177
Defea K (2007) β-arrestins and heterotrimeric G-proteins: collaborators and competitors in signal transduction. Br J Pharmacol 153(Suppl. 1):S298–S309
Depoortere R, Auclair AL, Bardin L, Bruins SL, Kleven MS, Colpaert F, Vacher B, Newman-Tancredi A (2007) F15063, a compound with D2/D3 antagonist, 5-HT1A agonist and D4 partial agonist properties. III. Activity in models of cognition and negative symptoms. Br J Pharmacol 151:266–277
Galandrin S, Bouvier M (2006) Distinct signaling profiles of β1 and β2 adrenergic receptor ligands toward adenylyl cyclase and mitogen-activated protein kinase reveals the pluridimensionality of efficacy. Mol Pharmacol 70:1575–1584
Gay EA, Urban JD, Nichols DE, Oxford GS, Mailman RB (2004) Functional selectivity of D2 receptor ligands in a Chinese hamster ovary hD2L cell line: evidence for induction of ligand-specific receptor states. Mol Pharmacol 66:97–105
Gazi L, Schoeffter P, Nunn C, Croskery K, Hoyer D, Feuerbach D (2000) Cloning, expression, functional coupling and pharmacological characterization of the rat dopamine D4 receptor. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 361:555–564
Gerhardt CC, Gros J, Strosberg AD, Issad T (1999) Stimulation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 pathway by human β3 adrenergic receptor: new pharmacological profile and mechanism of activation. Mol Pharmacol 55:255–262
Gilliland SL, Alper RH (2000) Characterization of dopaminergic compounds at hD2short, hD4.2 and hD4.7 receptors in agonist-stimulated [35S]GTPgammaS binding assays. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 361:498–504
Kenakin T (1996) The classification of seven transmembrane receptors in recombinant expression systems. Pharmacol Rev 48:413–463
Kenakin T (2007) Functional selectivity through protean and biased agonism: who steers the ship? Mol Pharmacol 72:1393–1401
Lahti RA, Mutin A, Cochrane EV, Tepper PG, Dijkstra D, Wikstrom H, Tamminga CA (1996) Affinities and intrinsic activities of dopamine receptor agonists for the hD21 and hD4.4 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 301:R11–R13
Leroy D, Missotten M, Waltzinger C, Martin T, Scheer A (2007) G protein-coupled receptor-mediated ERK1/2 phosphorylation: towards a generic sensor of GPCR activation. J Recept Signal Transduct Res 27:83–97
Martel JC, Leduc N, Ormiere AM, Faucillon V, Danty N, Culie C, Cussac D, Newman-Tancredi A (2007) WAY-100635 has high selectivity for serotonin 5-HT1A versus dopamine D4 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 574:15–19
Massotte D, Brillet K, Kieffer B, Milligan G (2002) Agonists activate Gi1α or Gi2α fused to the human mu opioid receptor differently. J Neurochem 81:1372–1382
Milligan G (2006) G-protein-coupled receptor heterodimers: pharmacology, function and relevance to drug discovery. Drug Discov Today 11:541–549
Moreland RB, Nakane M, Donnelly-Roberts DL, Miller LN, Chang R, Uchic ME, Terranova MA, Gubbins EJ, Helfrich RJ, Namovic MT, El Kouhen OF, Masters JN, Brioni JD (2004) Comparative pharmacology of human dopamine D2-like receptor stable cell lines coupled to calcium flux through Gαqo5. Biochem Pharmacol 68:761–772
Murphy LO, Blenis J (2006) MAPK signal specificity: the right place at the right time. Trends Biochem Sci 31:268–275
Neve KA, Seamans JK, Trantham-Davidson H (2004) Dopamine receptor signaling. J Recept Signal Transduct Res 24:165–205
Newman-Tancredi A, Audinot V, Chaput C, Verriele L, Millan MJ (1997) [35S]Guanosine-5′-O-(3-thio)triphosphate binding as a measure of efficacy at human recombinant dopamine D4.4 receptors: actions of antiparkinsonian and antipsychotic agents. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 282:181–191
Newman-Tancredi A, Heusler P, Martel JC, Ormiere AM, Leduc N, Cussac D (2008) Agonist and antagonist properties of antipsychotics at human dopamine D4.4 receptors: G-protein activation and K channel modulation in transfected cells. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 11:298–307
Oak JN, Oldenhof J, Van Tol HH (2000) The dopamine D4 receptor: one decade of research. Eur J Pharmacol 405:303–327
Oak JN, Lavine N, Van Tol HH (2001) Dopamine D4 and D2L receptor stimulation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway is dependent on trans-activation of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor. Mol Pharmacol 60:92–103
Oldenhof J, Vickery R, Anafi M, Oak J, Ray A, Schoots O, Pawson T, von Zastrow M, Van Tol HH (1998) SH3 binding domains in the dopamine D4 receptor. Biochemistry 37:15726–15736
Sato M, Horinouchi T, Hutchinson DS, Evans BA, Summers RJ (2007) Ligand-directed signaling at the β3-adrenoceptor produced by 3-(2-Ethylphenoxy)-1-[(1,S)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronapth-1-ylamino]-2S-2-propanol oxalate (SR59230A) relative to receptor agonists. Mol Pharmacol 72:1359–1368
Shoemaker JL, Ruckle MB, Mayeux PR, Prather PL (2005) Agonist-directed trafficking of response by endocannabinoids acting at CB2 receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 315:828–838
Stanasila L, Lim WK, Neubig RR, Pattus F (2000) Coupling efficacy and selectivity of the human µ-opioid receptor expressed as receptor-Gα fusion proteins in Escherichia coli. J Neurochem 75:1190–1199
Tarazi FI, Zhang K, Baldessarini RJ (2004) Dopamine D4 receptors: beyond schizophrenia. J Recept Signal Transduct Res 24:131–147
Urban JD, Clarke WP, von Zastrow M, Nichols DE, Kobilka B, Weinstein H, Javitch JA, Roth BL, Christopoulos A, Sexton PM, Miller KJ, Spedding M, Mailman RB (2007a) Functional selectivity and classical concepts of quantitative pharmacology. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 320:1–13
Urban JD, Vargas GA, von Zastrow M, Mailman RB (2007b) Aripiprazole has functionally selective actions at dopamine D2 receptor-mediated signaling pathways. Neuropsychopharmacology 32:67–77
Wedemeyer C, Goutman JD, Avale ME, Franchini LF, Rubinstein M, Calvo DJ (2007) Functional activation by central monoamines of human dopamine D4 receptor polymorphic variants coupled to GIRK channels in Xenopus oocytes. Eur J Pharmacol 562:165–173
Werry TD, Gregory KJ, Sexton PM, Christopoulos A (2005) Characterization of serotonin 5-HT2C receptor signaling to extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2. J Neurochem 93:1603–1615
Wong AH, Van Tol HH (2003) The dopamine D4 receptors and mechanisms of antipsychotic atypicality. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 27:1091–1099
Zawilska JB, Rosiak J, Berezinska M, Nowak JZ (2003) L-745,870 suppresses the nighttime serotonin N-acetyltransferase activity in chick retina: in vivo evidence for agonist activity at D4-dopamine receptors. J Neural Transm 110:219–227
Zhen X, Zhang J, Johnson GP, Friedman E (2001) D4 dopamine receptor differentially regulates Akt/nuclear factor-κB and extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathways in D4MN9D cells. Mol Pharmacol 60:857–864
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper is especially dedicated to the memory of our appreciated colleague and co-author, Dr. Liesbeth Bruins Slot, who left us much too soon the 4th of April, 2008.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heusler, P., Bruins Slot, L., Rauly-Lestienne, I. et al. Activation of G proteins and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 phosphorylation via human dopamine D4.4 receptors: differential pathway-dependent potencies of receptor agonists. Naunyn-Schmied Arch Pharmacol 379, 87–99 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-008-0333-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-008-0333-4