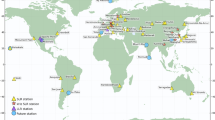
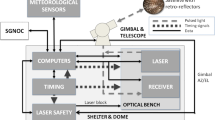
Abstract
Satellite Laser Ranging (SLR) began in the mid-1960s on satellites of opportunity with retro-reflectors intended as a part of intercomparison tests of satellite tracking techniques. Shortly thereafter, data from these satellites began to work their way into geodetic solutions and dedicated geodesy experiments. By early 1970s when future requirements for centimeter accuracy were envisioned, planning began for dedicated, spherical retro-reflector geodetic satellites. Built with high mass-to-area ratios, these satellites would have important applications in gravity field modeling, station geolocation and fiducial reference systems, Earth rotation, and fundamental physics. Early geodetic satellites were Starlette, launched in 1975 by Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales (CNES), and LAGEOS in 1976 by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). Recent geodetic satellites include LARES, launched in 2012, and LARES-2 under development, both by the Italian Space Agency (ASI). Today, a complex of these ‘geodetic satellites’ from low to high altitude Earth orbits supports many space geodesy requirements. This paper will discuss the evolution of the geodetic satellites from the early days, through current programs and out to future needs as we approach our goal for millimeter accuracy.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altamimi Z, Rebischung P, Metivier L, Xavier C (2016) ITRF2014: a new release of the International Terrestrial Reference Frame modeling nonlinear station motions. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 121:6109–6131. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016JB013098
Appleby GM (1998) Long-arc analyses of SLR observations of the Etalon geodetic satellites. J Geod 72(6):333–342. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001900050172
Appleby G, Rodrguez J, Altamimi Z (2016) Assessment of the accuracy of global geodetic satellite laser ranging observations and estimated impact on ITRF scale: estimation of systematic errors in LAGEOS observations 1993–2014. J Geod 90:1371. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-016-0929-2
Barlier F, Lefebvre M (2001) A new look at planet Earth: satellite geodesy and geoscience. In: Bleeker JAM, Geiss J, Huber MCE (eds) The century of space science. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 1623–1651. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-010-0320-9_66
Biancale R, Balmino G, Lemoine J-M, Marty J-C, Moynot C, Barlier F, Laurain O, Gegout P, Schwintzer P, Reigber C, Bode A, König R, Massmann F-H, Raimondo J-C, Schmidt R, ZhuS Yuan (2000) A new global Earth’s gravity field model from satellite orbit perturbations: GRIM5-S1. Geophys Res Lett 27(22):3611–3614. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000GL011721
Bloßfeld M, Müller H, Gerstl M, Štefka V, Bouman J, Göttl F, Horwath M (2015) Second-degree Stokes coefficients from multi-satellite SLR. J Geod 89(9):857–871. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-015-0819-z
Bloßfeld M, Gerstl M, Hugentobler U, Angermann D, Müller H (2014) Systematic effects in LOD from SLR observations. Adv Space Res 54:1049–1063. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2014.06.009
Bloßfeld M, Rudenko S, Kehm A, Panadina N, Müller H, Angermann D, Hugentobler U, Seitz M (2018) Consistent estimation of geodetic parameters from SLR satellite constellation measurements. J Geod 92:1003–1021
Bourda G (2008) Length-of-day and space-geodetic determination of the Earths variable gravity field. J Geod 82(4):295–305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-007-0180-y
Burmistrov V B, Parkhomenko N N, Pliev L F, Shargorodsky V D, Soyuzova N M, Vasiliev V P (1998) The westpac satellite: design features and first results of return signal analysis. In: Procedings of the 11 th international workshop on laser ranging, Deggendorf, Germany, 21–25 Sept, pp 297
Cazenave A, Daillet S (1981) Lunar tidal acceleration from Earth satellite orbit analyses. J Geophys Res 86(B6):1659–1663. https://doi.org/10.1029/JB086iB03p01659
Chao B, Eanes R (1995) Global gravitational changes due to atmospheric mass redistribution as observed by the Lageos nodal residual. Geophys J Int 122:755–764
Chen J, Wilson C (2008) Low degree gravity changes from GRACE, Earth rotation, geophysical models, and satellite laser ranging. J Geophys Res 113:B06402. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007JB005397
Chen J, Wilson C, Eanes R, Nerem R (1999) Geophysical interpretation of observed geocenter variations. J Geophys Res 104:2683–2690
Cheng M, Tapley BD (2001) Seasonal variations in low degree zonal harmonics of the Earth’s gravity field from satellite laser ranging observations. J Geophys Res 104(B2):2667–2681. https://doi.org/10.1029/1998JB900036
Cheng M, Ries J, Tapley B (2011) Variations of the Earth’s figure axis from satellite laser ranging and GRACE. J Geophys Res 116(B01):409
Cheng M, Tapley B, Ries J (2013) Deceleration in the Earth’s oblateness. J Geophys Res 118:740–747. https://doi.org/10.1002/jgrb.50058
Christodoulidis DC, Smith DE, Kolenkiewicz R, Klosko SM, Torrence MH, Dunn PJ (1985) Observing tectonic plate motions and deformations from satellite laser ranging. J Geophys Res 90(B11):9249–9263. https://doi.org/10.1029/JB090iB11p09249
Ciufolini I, Wheeler JA (1995) Gravitation and inertia. Princeton University Press, Princeton. ISBN: 0-691-03323-4
Ciufolini I, Pavlis EC, Chieppa F, Fernandes-Vieira E, Pérez-Mercader J (1998) Test of general relativity and measurement of the lense-thirring effect with two earth satellites. Science 279:2100–2103. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.279.5359.2100
Ciufolini I, Pavlis EC (2004) A confirmation of the general relativistic prediction of the Lense-Thirring effect. Nature 431(7011):958–960. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03007
Ciufolini I (2007) Dragging of inertial frames. Nature 449(7158):41–47. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06071
Ciufolini I, Paolozzi A, Pavlis E, König R, Ries J, Gurzadyan V, Penrose R, Sindoni G, Paris C, Khachatryan H, Mirzoyan S (2016) A test of general relativity using the LARES and LAGEOS satellites and a GRACE Earth gravity model: measurement of Earth’s dragging of inertial frames. Eur Phys J C 76:120. https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-016-3961-8
Ciufolini I, Paolozzi A, Pavlis EC, Sindoni G, Koenig R, Ries JC, Matzner R, Gurzadyan V, Penrose R, Rubincam D, Paris C (2017a) A new laser-ranged satellite for general relativity and space geodesy: I. An introduction to the LARES2 space experiment. Eur Phys J Plus 132(8):336. https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2017-11635-1
Ciufolini I, Pavlis EC, Sindoni G, Ries JC, Paolozzi A, Matzner R, Koenig R, Paris C (2017b) A new laser-ranged satellite for general relativity and space geodesy: II. Monte Carlo simulations and covariance analyses of the LARES 2 experiment. Eur Phys J Plus 132(8):337. https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2017-11636-0
Cox C, Chao B (2002) Detection of a large scale mass redistribution in the terrestrial system since 1998. Science 297:831–833
Degnan J (2016) Reducing the satellite contribution to range error. In: 20th International workshop on laser ranging, Potsdam, Germany, 2016. https://cddis.nasa.gov/lw20/docs/2016/papers/66-Degnan_paper.pdf
Devoti R, Luceri V, Sciaretta C, Bianco G, Di Donato G, Vermeersen LLA, Sadabini R (2001) The SLR secular gravity variations and their impact on the inference of mantle rheology and lithospheric thickness. Geophys Res Lett 28(5):855–858. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000GL011566
Dick G, Gendt G, Montag H, Nischan T, Sommerfeld W (1993) Results of ETALON data analysis. In: Montag H, Reigber C (eds) Geodesy and physics of the Earth: geodetic contributions to geodynamics. Springer, Berlin, pp 315–318. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-78149-0_73
Dickey J, Marcus S, de Viron O, Fukumori I (2002) Recent Earth’s oblateness variations: unraveling climate and postglacial rebound effects. Science 298:1975–1977. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1077777
Dow J, Agrotis L (1986) Polar motion and Earth rotation series from LAGEOS. Adv Space Res 6:17–21
Dunn P, Torrence M, Kolenkiewicz R, Smith D (1999) Earth scale defined by modern satellite ranging observations. Geophys Res Lett 26(10):1489–1492
Eanes RJ, Schutz BE, Tapley BD (1983) Earth and ocean tide effects on LAGEOS and Starlette. Proceedings ninth international symposium earth tides. E. Schweinzerbert’she Verlagbuchhandlong, Stiuggart, pp 236–249
Exertier P, Nicolas N, Berio P, Coulot D, Bonnefond P, Laurain O (2004) The Role of laser ranging for calibrating Jason-1: the Corsica tracking campaign. Mar Geod 27(1–2):333–340. https://doi.org/10.1080/01490410490476272
Förste C, Stubenvoll R, König R, Raimondo J-C, Barthelmes F, Kusche J, Dahle C, Neumayer H, Biancale R, Lemoine J-M, Bruinsma S (2009) Evaluation of EGM2008 by comparison with other recent global gravity field models. Newton’s Bull 4:26–37
Gaposchkin EM, Lambeck K (1971) Earth’s gravity field to the sixteenth degree and station coordinates from satellite and terrestrial data. J Geophys Res 76(29):4855–4883. https://doi.org/10.1029/JB076i020p04855
Gaposchkin EM (1979) Lageos orbital analysis in support of validation. Smithsonian astrophysics observatory (SAO), Grant NSG 5261, final report. https://ntrs.nasa.gov/archive/nasa/casi.ntrs.nasa.gov/19790015288.pdf
Gutierrez R, Wilson C (1987) Seasonal air and water redistribution effects on the Lageos and Starlette. Geophys Res Lett 14(9):929–932
He M, Tapley BD, Eanes RJ (1982) Earth rotation parameters deduced from Starlette laser ranging. Sci Sir Ser A Eng Trans 25(10):1090–1098. https://doi.org/10.1360/ya1982-25-10-1090
Henriksen SW (ed) (1977) National Geodetic Satellite Program, Part 1 and 2, NASA-SP-365-PT-1/2, 19780003602/78N11545. NASA, Washington, DC, United States
Kaula W M (1969) The terrestrial environment: solid—Earth and ocean physics, report of a study at Williamstown, Massachusetts, sponsored by NASA-Electronics Research Center and MIT Measurement Systems Laboratory
Krebs G (2017) Gunter’s space page. Etalon 1, 2. http://space.skyrocket.de/doc_sdat/etalon.htm
König R, Bode A, Chen Z, Reigber C (1997) Surface forces parameterization of GFZ-1 orbits and gravity field recovery. Adv Space Res 19(11):1677–1680. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0273-1177(97)00324-4
König R, Chen Z, Reigber C, Schwintzer P (1999) Improvement in global gravity field recovery using GFZ-1 satellite laser tracking data. J Geodesy 73(8):398–406. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001900050259
Kucharski D, Lim H, Kirchner G, Koidl F (2014) Spin parameters of low earth orbiting satellites Larets and Stella determined from satellite laser ranging data. Adv Space Res 53(1):90–96
Kucharski D, Kirchner G, Lim H, Koidl F (2011) Optical response of nanosatellite BLITS measured by the Graz 2 kHz SLR system. Adv Space Res 48(8):1335–1340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2011.06.016
Kucharski D, Otsubo T, Kirchner G, Bianco G (2012) Spin rate and spin axis orientation of LARES spectrally determined from satellite laser ranging data. Adv Space Res 50(11):473–477
Kucharski D, Kirchner G, Otsubo T, Koidl F (2015) A method to calculate zero-signature satellite laser ranging normal points for millimeter geodesy–a case study with Ajisai. Earth Planets Space 67:34. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40623-015-0204-4
Lejba P, Schillak S, Wnuck E (2007) Determination of orbits and SLR stations coordinates on the basis laser observations of the satellites Starlette and Stella. Adv Space Res 40(1):143–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2007.01.067
Lejba P, Schillak S (2011) Determination of station positions and velocities from laser ranging observations to Ajisai, Starlette and Stella satellites. Adv Space Res 47(4):654–662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2010.10.013
Lerch F, Klosko S, Patel G, Wagner C (1985) A gravity model for crustal dynamics (GEML2). J Geophys Res 90(B11):9301–9311. https://doi.org/10.1029/JB090iB11p09301
Luceri V, Pavlis E C, Kuzmicz-Cieslak M, Evans K, Pirri M, Bianco G (2019) The contribution of satellite laser ranging to the development of the ITRF2014. J Geod (submitted)
Minott P O, Zagwodzki T Q, Varghese T, Seldon M (1993) Prelaunch optical characterization of the laser geodynamic satellite (LAGEOS 2), NASA technical paper 3400
Moore P, Zhang Q, Alothman A (2005) Annual and semiannual variations of the Earth’s gravitational field from satellite laser ranging and CHAMP. J Geophys Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004JB003448
Nastula J, Gross R (2015) Chandler wobble parameters from SLR and GRACE. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 120:4474–4483. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014JB01182
Otsubo T, Amagai J, Kunimori H (1999) The center-of-mass correction of the geodetic satellite AJISAI for single-photon laser ranging. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 37(4):2011–2018
Paolozzi A, Ciufolini I, Paris C, Sindoni G (2015) LARES: a new satellite specifically designed for testing general relativity. Int J Aerosp Eng 2015:9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/341384
Paolozzi A (2019) Studies on the materials of LARES 2 satellite. J Geod (submitted)
Pavlis E C (1994) High resolution earth orientation parameters from LAGEOS SLR data analysis at GSFC. In: IERS technical note 16, 1994
Pavlis E C (1999) Fortnightly resolution geocenter series: a combined analysis of LAGEOS 1 and 2 SLR data (1993–96). In: IERS technical note 25, Observatoire de Paris, April 1999
Pavlis EC (2002) Dynamical determination of origin and scale in the earth system from satellite laser ranging, in vistas for geodesy in the new millennium. In: Adam J, Schwarz K-P (eds) Proceedings of the 2001 international association of geodesy scientific assembly, Budapest, Hungary, 2–7 Sept 2001, pp 36–41. Springer-Verlag, New York. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-04709-5_7
Pavlis E C, Kuźmicz-Cieślak M (2009) Geocenter motion: causes and modeling approaches. In: Schillak S (ed) Proceedings of 16th international laser workshop, pp 16–26. Space Research Center, Polish Academy of Sciences, Warszawa, Poland
Pearlman M, Degnan J, Bosworth J (2002) The international laser ranging service. Adv Space Res 30(2):135–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0273-1177(02)00277-6
Peltier WR (1983) Constraint on deep mantle viscosity from LAGEOS acceleration data. Nature 304:434–436
Reigber C, Balmino G, Mller H, Bosch W, Moynot B (1985) GRIM gravity model improvement using LAGEOS (GRIM31). J Geophys Res 90(B11):9285–9299. https://doi.org/10.1029/JB090iB11p09285
Ries JC, Eanes RJ, Shum CK, Watkins MM (1992) Progress in the determination of the gravitational coefficient of the Earth. Geophys Res Lett 19(6):529–531. https://doi.org/10.1029/92GL00259
Rubincam DP (1987) LAGEOS orbit decay due to infrared radiation from Earth. J Geophys Res 92(B2):1287–1294. https://doi.org/10.1029/JB092iB02p01287
Rubincam D (1984) Postglacial rebound observed by LAGEOS and the effective viscosity of the lower mantle. J Geophys Res 89:1077–1088
Rubincam D (1990) Drag on the LAGEOS satellite. J Geophys Res 95:4881–4886
Rutkowska M, Jagoda M (2010) Estimation of the elastic earth parameters using the SLR LAGEOS 1 and LAGEOS 2 data. Acta Geophys 58:705. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11600-009-0062-1
Rutkowska M, Jagoda M (2012) Estimation of the elastic earth parameters using slr data for the low satellites STARLETTE and STELLA. Acta Geophys 60(4):1213–1223. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11600-012-0045-5
Schutz B E, Cheng M K, Shum C K, Eanes R J, Tapley B D (1989) Analysis of earth rotation solution from Starlette. J Geophys Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/JB094iB08p10167
Schutz BE, Cheng MK, Eanes RJ, Shum CK, Tapley BD (1993) Geodynamic results from starlette orbit analysis. In: Smith DE, Turcotte DL (eds) Contributions of space geodesy to geodynamics: Earth dynamics, vol 24. AGU, Washington, pp 175–190. https://doi.org/10.1029/GD024p0175
Sengoku A (1998) A plate motion study using Ajisai. Earth Planet Space 50:611. https://doi.org/10.1186/BF03352156
Smith DE, Kolenkiewicz R, Dunn PJ (1973a) A determination of the earth tidal amplitude and phase from the orbital perturbations of the Beacon Explorer C spacecraft. NASA GSFC No. 19730020633
Smith DE, Lerch FJ, Wagner C A (1973b) A gravitational field model for the Earth. Space research XIII. In: Proceedings of the fifteenth plenary meeting, Madrid, Spain, 10–24 May 1972, vol 1, pp 11–20, (A73-41325 21-13) Berlin, East Germany, Akademie-Verlag GmbH
Smith DE, Christodoulidis DC, Kolenkiewicz R, Dunn PJ, Klosko SM, Torrence MH, Fricke S, Blackwell S (1985) A global geodetic reference frame from LAGEOS ranging (SL5.1AP). J Geophys Res 90(B11):9221–9233. https://doi.org/10.1029/JB090iB11p09221
Smith D, Kolenkiewicz R, Dunn P, Robbins J, Torrence M, Klosko S, Williamson R, Pavlis E, Douglas N, Fricke S (1990) Tectonic motion and deformation from satellite laser ranging to LAGEOS. J Geophys Res 95:22013–22041
Sokolov A, Sadovnikov M, Shargorodskiy V, Vasiliev V (2016) SC BLITS-M. In: Presented at the ILRS missions standing committee, October 2016, Potsdam, Germany
Sośnica K, Thaller D, Dach R, Jäggi A, Beutler G (2013) Impact of loading displacements on SLR-derived parameters and on the consistency between GNSS and SLR results. J Geod 87(8):751–769. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-013-0644-1
Sośnica K, Jäggi A, Thaller D, Dach R, Beutler G (2014) Contribution of Starlette Stella and AJISAI to the SLR-derived global reference frame. J Geod 88(8):789–804. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-014-0722-z
Sośnica K, Jäggi A, Meyer U, Thaller D, Beutler G, Arnold D, Dach R (2015) Time variable Earths gravity field from SLR satellites. J Geod 89(10):945–960. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-015-0825-1
Sośnica K, Bury G, Zajdel R (2018) Contribution of multi-GNSS constellation to SLR-derived terrestrial reference frame. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017GL076850J
Tapley B, Schutz B, Eanes R (1985) Station coordinates, baselines, and earth rotation from LAGEOS laser ranging: 1976–1984. J Geophys Res 90:9235–9248
Thaller D, Sośnica K, Steigenberger P, Roggenbuck O, Dach R (2015) Pre-combined GNSS-SLR Solutions: What Could be the Benefit for the ITRF? In: International association of geodesy symposia, Springer Berlin Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/1345_2015_215
Torrence M, Dunn P, Kolenkiewicz R (1995) Characteristics of the LAGEOS and ETALON Satellites Orbits. Adv Space Res 16(12):21–24
Vokrouhlicky D, Farinella P (1997) Thermal force effects on slowly rotating, spherical artificial satellitesII. Earth infrared heating. Planet Space Sci 45:419–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-0633(96)00147-X
Vokrouhlicky D, Farinella P (1998) The Yarkovsky seasonal effect on asteroidal fragments: a nonlinearized theory for the plane-parallel case. Astronom J 116(4):2032
Weiffenbach G C, Hoffman TE (1970) A passive stable satellite for earth-physics applications (cannonball a satellite for accurate laser ranging). Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory (SAO), special report no. 329,
Williamson RG, Marsh JG (1985) Starlette geodynamics: the Earth’s tidal response. J Geophys Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/JB090iB11p09346
Willis P, Deleflie F, Barlier F, Bar-Sever YE, Romans LJ (2005) Effects of thermosphere total density perturbations on LEO orbits during severe geomagnetic conditions (Oct-Nov 2003) using DORIS and SLR data. Adv Space Res 36(3):522–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2005.03.029
Yoder C, Williams J, Dickey J, Schutz B, Eanes R, Tapley B (1983) Secular variations of Earth’s gravitational harmonic \(J_{2}\) coefficient from Lageos and nontidal acceleration of Earth rotation. Nature 303:757–762
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the ILRS for providing the ground stations and the laser ranging data of all the satellites described in the paper. M.R. Pearlman and D. Arnold acknowledge the support of NASA Grant 80NSSC18K0220. F. Barlier and R. Biancale acknowledge the support of CNES and the Observatoire de la Cte dAzur/GEOAZUR. I. Ciufolini and A. Paolozzi acknowledge the Italian Space Agency for the support of the LARES and LARES 2 space missions under agreements No. 2017-23-H.0 and No. 2015-021-R.0. E. C. Pavlis acknowledges the support of NASA Grant NNX15AT34A.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Coauthor Mark Davis is deceased.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pearlman, M., Arnold, D., Davis, M. et al. Laser geodetic satellites: a high-accuracy scientific tool. J Geod 93, 2181–2194 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-019-01228-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-019-01228-y