Abstract
Purpose
We hypothesized that the ventilator-related causes of lung injury may be unified in a single variable: the mechanical power. We assessed whether the mechanical power measured by the pressure–volume loops can be computed from its components: tidal volume (TV)/driving pressure (∆P aw), flow, positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP), and respiratory rate (RR). If so, the relative contributions of each variable to the mechanical power can be estimated.
Methods
We computed the mechanical power by multiplying each component of the equation of motion by the variation of volume and RR:
where ∆V is the tidal volume, ELrs is the elastance of the respiratory system, I:E is the inspiratory-to-expiratory time ratio, and R aw is the airway resistance. In 30 patients with normal lungs and in 50 ARDS patients, mechanical power was computed via the power equation and measured from the dynamic pressure–volume curve at 5 and 15 cmH2O PEEP and 6, 8, 10, and 12 ml/kg TV. We then computed the effects of the individual component variables on the mechanical power.
Results
Computed and measured mechanical powers were similar at 5 and 15 cmH2O PEEP both in normal subjects and in ARDS patients (slopes = 0.96, 1.06, 1.01, 1.12 respectively, R 2 > 0.96 and p < 0.0001 for all). The mechanical power increases exponentially with TV, ∆P aw, and flow (exponent = 2) as well as with RR (exponent = 1.4) and linearly with PEEP.
Conclusions
The mechanical power equation may help estimate the contribution of the different ventilator-related causes of lung injury and of their variations. The equation can be easily implemented in every ventilator’s software.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
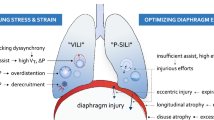
Ventilator/ventilation-induced lung injuries (VILI) result from the interaction between what the ventilator delivers to the lung parenchyma and how the lung parenchyma accepts it. Over the decades, our understanding of these two realities has progressively increased: from one side, different components of the ventilator load have been differently emphasized; on the other side, the conditions of the lung parenchyma dictating the response to a given ventilator load have been studied and clarified. The ventilator-generated causes of VILI include the pressures [1], volume [2], flow [3], and respiratory rate [4, 5]. On the other hand, the lung conditions favoring VILI primarily depend on the amount of edema, which leads to decreased lung dimensions [6], increased lung inhomogeneity, increased stress risers [7] and cyclic collapse and decollapse [8, 9]. We neglect here, for clarity, “extra-lung” factors such as perfusion, pH, gas tensions and temperature. Obviously, the ventilator and the lung causes of VILI may interact. Positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP), as an example, on one side increases the ventilator pressure load, and on the other side may decrease lung inhomogeneity and the intratidal lung collapse–decollapse. However, the distinction between the ventilator’s and the lung’s contribution to VILI may help to reach a better VILI-prevention strategy. In fact, it is worth considering that all the ventilator-related causes of VILI, although investigated separately, are components of a unique physical variable (i.e. the mechanical power), while most of the lung-related causes of VILI are primarily consequences of the amount of edema (i.e. the ARDS severity, at least in the early phases). If we consider the ventilatory setting, it is quite clear that tidal volume, pressures and flow are all components of the energy load, which, expressed per unit of time, is the mechanical power. In this paper, we would like to propose a simple model for the quantification of mechanical power at the bedside and to discuss its possible relevance in setting a “safe” mechanical ventilation.
Methods
Derivation of mechanical power equation
Equation of motion
According to the classical equation of motion [10] (with the addition of PEEP [11]), at any given time, the pressure (P) in the whole respiratory system is equal to:
Every component of the equation of motion is a pressure, in fact:
-
ELrs × ∆V = ∆P (pressure component due to the elastic recoil), being ELrs = (P plat − PEEP)/∆V (i.e. respiratory system elastance).
-
R aw × F = P peak − P plat (pressure component due to the motion), being R aw = (P peak − P plat)/F,
-
PEEP = P end-expiration it is not per se linked to motion, but it represents the baseline tension of the lung, as it is the pressure present in the respiratory system when ∆V and flow are equal to zero.
Energy per breath
In Fig. 1, we represent the energy that must be applied to the respiratory system in order to increase its volume (∆V) above its resting volume. For sake of clarity, we assume that the pressure–volume curve of the respiratory system (or of the lung) is linear in the range of volumes considered, i.e. up to the beginning of the total lung capacity (TLC) region.
a A graphical representation of the power equation. The graphic is composed of a large triangle (green plus azure), to which a parallelogram (Resistive, yellow) is added on the right. The left cathetus of the big triangle represents the total volume (i.e. TV + PEEP volume), while the upper cathetus represents the plateau pressure. The slope of the hypotenuse represents the compliance of the system, (in our case 1200 ml/30 cmH2O = 40 ml/cmH2O). The area of this large triangle is the total elastic energy present at plateau pressure and equals (1200 ml × 30 cmH2O)/2 × 0.000098 = 1764 J. This total elastic energy has two components: the smaller triangle (Elastic Static, green), which represents the energy delivered just once when PEEP is applied, and the larger rectangle trapezoid (Elastic Dynamic, azure), whose areas represent the elastic energy delivered at each tidal breath. Note that the rectangle trapezoid results from the sum of two components (both azure): a rectangle, whose area is TV × PEEP (third component of the power equation), and a triangle, whose area is TV × ∆P aw × 1/2, equal to ELrs × TV × 1/2 (first component of the power equation). The third component of the power equation is the area described by the Resistive parallelogram (yellow), whose area is equal to (P peak − P plat) × TV. b Dynamic pressure–volume loop obtained at 15 cmH2O PEEP, with the following measured parameters: P peak 32.8 cmH2O, P plat 29.2 cmH2O, TV 303 ml. The measured energy, i.e. the area of the trapezoid described by the inspiratory blue line, the peak pressure line (major base), the PEEP line (minor base) and the TV line (height) was 0.77 J, computed was 0.80 J. With the RR = 18 bpm, the measured power was then 13.9 J/min and the computed power was 14.4 J/min
-
Energy per breath at ZEEP. The energy (i.e. the area between the inflation line and the y axis) is the product of the absolute value of pressure (P) times the variation of volume (∆V), i.e. P × ∆V. Therefore, when the PEEP is zero, the energy applied to compensate the elastic recoil will be the area of the triangle, i.e. 1/2 × P plat × ∆V.
-
Energy per breath with PEEP. When PEEP is applied, the energy to reach the PEEP volume (∆V PEEP) would be equal to 1/2 × PEEP × ∆V PEEP, but it will be needed only once (as long as the PEEP will be maintained), since during the tidal ventilation the ∆V PEEP equals zero and consequently the term 1/2 × P × ∆V also equals zero. However, in the presence of PEEP, more energy is required to inflate the lung. Accordingly, the energy needed for the TV to reach the P plat is ∆P + PEEP (i.e. the P plat) multiplied by the volume displaced from the PEEP volume up to the plateau volume. This energy equals the area of the trapezoid having P plat and PEEP as bases and TV as height (see Fig. 1). For a more detailed discussion on the role of PEEP, see the Electronic Supplement, section E-1.
-
Energy per breath for gas motion. This energy is nearly equal to the area of the parallelogram on the right side of Fig. 1, in which one side is the (P peak − Pplat) and the other side is the ∆V. This representation is actually a simplification of the reality, since it may change during volume-controlled or pressure-controlled ventilation.
Accordingly, we can compute the energy per breath multiplying each pressure in the motion equation by the volume variation, as follows:
The first term of the Eq. (2), which is equal to ∆V × ∆P, has been divided by 2 (area of a triangle) in order to approximate the integral of their product (see Fig. 1a), while the second and the third terms do not require any correction, as they represent a parallel translation along the axis.
From Eq. (2):
Therefore:
In order to express the T insp as a function of respiratory rate (RR) and inspiratory-to-expiratory ratio (I:E), both readily available in every ventilator’s settings, the following derivation may be applied:
-
Premises:
-
T insp/T exp = I/E,
-
T insp + T exp = T tot,
-
T tot = 60/RR.
-
-
It follows that: T insp = T tot × (I:E/(1 + I:E))
-
Thus, substituting T insp in the Eq. (4):
If we express the volumes in liters and the pressures in cmH2O, their product multiplied by 0.098 will be expressed in Joules.
Mechanical power
According to Eq. (5), the mechanical power expressed in J/min will be:
From the above formula, it is possible to calculate the effects of changing whatever variable (tidal volume, driving pressure, respiratory rate, resistance) on the mechanical power applied to the respiratory system.
For a simplified version of Eq. (6) and for the computation of the mechanical power applied to the lung instead of to the whole respiratory system, see the Electronic Supplement, sections E-2 and E-3.
Measurements of applied energy/power
We used data from a previous study, which included 30 patients with normal lungs (19 surgical and 11 medical control subjects) without ARDS and 50 ARDS patients (mild = 26, moderate = 16, severe = 8). The characteristics of the population are summarized in Table 1 (further details can be found in tables 1–3 of the original study) [12]. Each patient with and without ARDS was tested with four tidal volumes (6, 8, 10 and 12 ml/kg) and two PEEP levels (5 and 15 cmH2O). Flow and airway (P aw) pressures were recorded at 100 Hz and processed on a dedicated data acquisition system (Colligo; Elekton, Milan, Italy). The energy applied per breath has been measured using the dynamic pressure–volume curve recorded during tidal ventilation. The delivered energy per breath (airways + respiratory system) was defined as the area between the inspiratory limb of the airway pressure and the volume axis (see Fig. 1b). Note that pressure is expressed in absolute values (i.e. PEEP is included) while volumes are expressed as delta-volume above the EELV. The integral of the volume–pressure area, measured as liters × cmH2O, was then expressed in Joules (1 l × cmH2O = 0.000098 J). The mechanical power was obtained by multiplying the energy per breath by the respiratory rate.
Statistical methods
Univariable logistic regression was used for the assessment of the association between measured and computed mechanical power. In order to further assess the agreement between measured and computed mechanical power values, Bland–Altman analysis was used. Analysis was performed using SAS software, v.9.2 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA).
Results
Computed versus measured mechanical power
The regression between the mechanical power measured and computed in 30 patients mechanically ventilated for pathologies unrelated to the lung (i.e. “normal” lungs) are reported in Fig. 2a (5 cmH2O PEEP) and panel C (15 cmH2O PEEP). The mechanical powers were measured at 6, 8, 10, 12 ml/kg TV, accounting for 120 measurements for each PEEP level. The measured mechanical power (x axis) was strictly correlated with the one computed via the power equation, according to the following regressions: computed = 0.96 × measured + 0.16, R 2 = 0.98, p < 0.0001 (at 5 cmH2O PEEP) and computed = 1.05 × measured − 0.52, R 2 = 0.99, p < 0.0001 (at 15 cmH2O PEEP). The correspondent Bland–Altman analyses are reported in Fig. 2b, d. As shown, at PEEP 5 cmH2O, the mean of the differences was 0.196 J/min, the upper limit of agreement was 0.916 J/min, the lower limit of agreement was −0.525 J/min. At PEEP 15 cmH2O, the mean of the differences was −0.396 J/min, the upper limit of agreement was 0.560 J/min, and the lower limit of agreement was −1.353 J/min.
The regression between the mechanical power measured and computed in 50 ARDS patients are reported in Fig. 3a (5 cmH2O PEEP) and Fig. 3c (15 cmH2O PEEP). The mechanical powers were measured at 6, 8, 10, 12 ml/kg TV, accounting for 200 measurements for each PEEP level. The measured mechanical power (x axis) was strictly correlated with the one computed via the power equation, according to the following regressions: computed = 1.01 × measured − 0.48, R 2 = 0.96, p < 0.0001 (at 5 cmH2O PEEP) and computed = 1.12 × measured − 1.38, R 2 = 0.97, p < 0.0001 (at 15 cmH2O PEEP). The correspondent Bland–Altman analyses are reported in Fig. 3b, d. As shown, at PEEP 5 cmH2O the mean of the differences was 0.316 J/min, the upper limit of agreement was 1.471 J/min, the lower limit of agreement was −0.840 J/min. At PEEP 15 cmH2O, the mean of the differences was −0.840 J/min, the upper limit of agreement was 0.924 J/min, and the lower limit of agreement was −2.604 J/min.
Effects of ventilatory parameters on mechanical power
In Fig. 4, starting from a normal condition (ELrs 10 cmH2O/l, R aw 8 cmH2O/l/s), we show the changes of mechanical power as a function of the increase of one of its components (TV, ∆P aw, inspiratory flow, RR and PEEP) in 10 % steps, while the other components are maintained constant. As shown, the same percentage change of TV, driving pressure and inspiratory flow produce an identical exponential increase of mechanical power (exponent = 2), i.e. doubling the TV (as an example, from 6 to 12 ml/kg), produce a fourfold increase in mechanical power. For the same percentage increase of frequency, mechanical power increases exponentially, but with an exponent of 1.4, while an increase of PEEP causes a linear increase in mechanical power. The effects on mechanical power of changes in airway resistance and respiratory system elastance are reported in Fig. 5. The effects of different combinations of ventilator variables on the mechanical power may be seen on ad hoc computer program, which can be downloaded from the following link: http://www.ains.med.uni-goettingen.de/de/abteilung-anaesthesiologie/forschung/energy-calculator-software.
The percent increase of mechanical power as a function of TV/∆P aw/inspiratory flow (diamonds, squares and triangles), RR (stars), PEEP (circles). The variations of mechanical power with TV, ∆P aw and inspiratory flow are exactly the same, lying on the same line (for clarity, we show the mechanical power variations at different percent variations of TV, ∆P aw and inspiratory flow, otherwise all points would have been overlapped). While the mechanical power increases by 37 % with a 20 % increase of TV/∆P aw/inspiratory flow, it increases by 27 % and by 5.7 % with a 20 % increase of respiratory rate and PEEP, respectively. All the computations were done by changing one variable at a time, while keeping all the others constant
The percent variations of mechanical power as a function of ELrs (circles) and R aw (squares). The variations of mechanical power with R aw are lower than those with ELrs. While the mechanical power increases by 8 % with a 20 % increase of ELrs, it increases by 6 % with a 20 % increase of R aw, respectively. All the computations were done by changing one variable at a time, while keeping all the others constant
Discussion
Considering the time factor together with at least some components of the mechanical power in the genesis of VILI is obviously not new [13–15]. What we found in this study is that the “power equation”, as derived from the classical equation of motion [10, 16] (to which PEEP has been added, while the inertial forces have been neglected), provides results very similar to those obtained experimentally through the pressure–volume curve analysis. The advantage of a mathematical description of the mechanical power is that it enables the quantification of the relative contribution of its different components (TV, RR, ∆P aw, PEEP, I:E, flow) and anticipate the effects of their changes.
Components of mechanical power
Respiratory system elastance
The first component of the power equation (i.e. the power associated with the tidal volume/driving pressure) assumes a linear pressure–volume curve. If the elastance increases near the total lung capacity, due to overdistension, the computed energy will be underestimated. In contrast, the energy computed will be overestimated if the elastance decreases, as an example, due to recruitment. It must be noted, however, that the two phenomena (overdistension and recruitment) may occur simultaneously in different lung regions, resulting in an unchanged total elastance. In addition, a 10–20 % of change in elastance (either increasing or decreasing) should correspond to a 5–10 % change (either increasing or decreasing) in computed mechanical power (see Fig. 5). An automated system measuring the derivative of the pressure–volume at each P–V pair would avoid any possible over- or underestimation.
Airway resistance
The second component of the equation of power is the energy associated to the gas movement. As shown in Fig. 1a, in our model we assumed that both the resistance and the flow are constant during inflation. Accordingly, the difference P peak − P plat immediately reaches its working level, which is then maintained until the end of inspiration. This assumption is obviously an oversimplification. Actually, during mechanical ventilation, the airway resistances do decrease when the end-expiratory lung volume (EELV) increases [17, 18]. Both in normal subjects and in ARDS patients, when the ventilation started from 15 cmH2O PEEP, we found that computed mechanical power was higher than the measured one. The systematic overestimation is evident in the Bland–Altman plots related to the ventilation at 15 cmH2O PEEP (Figs. 2, 3d). Also in this case, an automated system measuring the airway resistances and flow would increase the accuracy of the computed power estimated.
Positive end-expiratory pressure
The third component of the equation of power equals the energy needed to overcome, throughout the whole inspiratory phase, the fibers’ tension due to PEEP.
In the work-of-breathing computations implemented in the ventilators, the PEEP is not considered, as the P–V loop starts from point (0, 0), regardless of PEEP and of end-expiratory lung volume. However, although the PEEP does not contribute to the cyclic energy load associated with the ventilation, its presence increases the energy load delivered to the respiratory system by a factor equal to PEEP × ∆V (see also the Electronic Supplement, section E-1). This effect of PEEP has been often neglected, although an increase in PEEP of 10–20 % increases the mechanical power to a similar extent.
Mechanical power and VILI
The VILI originates from the interaction between the mechanical power transferred to the ventilable lung parenchyma and the anatomo-pathological characteristics of the latter. Actually, TV/∆P aw, RR, flow, and PEEP are all components of a unique physical dimension, although each of them has been studied separately from the others and, likely, may contribute differently to the mechanical power. If the mechanical damage to the lung parenchyma is a function of the mechanical power, it is possible that different combinations of its components, resulting in a mechanical power greater than a given threshold, may produce similar damage, as recently suggested by animal experiments [5]. Obviously, as the mechanical power is influenced by the capacitive properties of the system, it should be standardized for a unit of lung gas volume or grams of lung tissue exposed to the ventilation.
Healthy lungs
Most of the literature on VILI in healthy lungs implies the use of different combinations of TV and PEEP, while the RR is usually set in order to maintain a given range of PaCO2. To induce injury in healthy lungs at “normal” frequency, TV greater than 30–40 ml/kg or even more, are required. These values, if referred to the lung size, correspond to a strain needed to reach the total lung capacity (2–3 times the FRC volume) [15]. To understand the relationship between mechanical power and healthy lungs in different species, we believe that two factors must be taken into account: the first are the lung dimensions and the second is the lung-specific elastance, which reflects the intrinsic elasticity of the lung parenchyma (12 cmH2O in humans, 6 cmH2O pigs and 4 cmH2O in rats) [19]. In heathy pigs weighing on average 21 kg, with an average FRC of 295 ml, we prospectively found a threshold value for VILI, as assessed by edema in CT scans, of 12 J/min [5], corresponding to approximately 40 mJ/min/ml.
Diseased lungs
The considerations about the lung dimensions and specific lung elastance also apply to the acutely diseased lung. The smaller the “baby lung”, the lower the mechanical power needed to induce damage should be, being the specific lung elastance similar to normal [20]. It is difficult for a mechanical power, such as to increase the “baby lung” near to its total capacity, would be applied in clinical practice. The diseased lung, however, is characterized by the presence of several interfaces between regions of different elasticity which may by doubling them concentrate the applied forces [7]. Indeed, the inhomogeneity of the lung, which dictates an inhomogeneous distribution of forces and obviously of mechanical power, is likely the main lung-dependent cause for the occurrence of VILI.
Limitations of the study
The energy delivered per breath is in part stored as elastic energy and in part dissipated, through various mechanism, into the lung. This fraction, represented by the hysteresis area of the P–V loop, is the one potentially harmful. However, as the hysteresis area is a near-constant fraction of the delivered energy (at least in the physiological range of tidal volumes) [21, 22], for simplicity we referred to the last one, which may be more easily computable and understandable.
The energy/power computation assumes a linear relationship between lung volume and elastance and resistance. As previously discussed, these linearities are likely lost at higher volume (15 cmH2O PEEP), leading to a possible over-/underestimation of mechanical power. However, if the mechanical power concept will prove to be useful, both elastance and resistance and could be automatically computed at each volume point on the P–V loop, overcoming the linearity bias.
To understand the relative weight of the different variables introduced in the equation of power, we investigated them individually, while keeping the other variables constant. This approach is obviously questionable, as increasing the TV—as an example—may be associated in normal practice with a decreased of respiratory rate, change of flow, etc. However, we provide an easy tool to compute whatever combination of variable is thought appropriate.
It must be stressed that the mechanical power is just one part of the problem. The other part is represented by the lung’s conditions. The same mechanical power may have different effects depending on dimensions of the lung, the presence of inhomogeneity, the extent of the stress risers, and the vessels’ filling state, all factors which condition an uneven distribution of the delivered energy. Therefore, to be clinically meaningful, the mechanical power must be normalized, at least to the lung volume [23].
Conclusions
The mechanical power analysis underlines concepts which may be of clinical relevance. First, it accounts for the extreme importance of TV/∆P aw in inducing VILI [24], as widely recognized in the scientific community. Secondly, it may account for the ambiguous effect of PEEP. In fact, the mechanical power increases linearly with PEEP, and may contribute to VILI. On the other hand, PEEP may decrease the lung-dependent causes of VILI (lung inhomogeneity and intratidal collapse–decollapse). The final effect (positive or negative) will depend on which of the two actions prevails and in which patients. Thirdly, the mechanical power underlines the usually neglected, but potentially relevant effect of respiratory rate, as the power increases exponentially when the RR increases. In summary, considering the mechanical power as a whole may provide better insights than considering its components separately.
References
Kumar A et al (1973) Pulmonary barotrauma during mechanical ventilation. Crit Care Med 1(4):181–186
Dreyfuss D et al (1988) High inflation pressure pulmonary edema. Respective effects of high airway pressure, high tidal volume, and positive end-expiratory pressure. Am Rev Respir Dis 137(5):1159–1164
Protti A et al. (2016) Role of strain rate in the pathogenesis of ventilator-induced lung edema. Crit Care Med 44(9):e838–e845. doi:10.1097/CCM.0000000000001718
Hotchkiss JR Jr et al (2000) Effects of decreased respiratory frequency on ventilator-induced lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 161(2 Pt 1):463–468
Cressoni M et al (2016) Mechanical power and development of ventilator-induced lung injury. Anesthesiology 124(5):1100–1108. doi:10.1097/ALN.0000000000001056
Gattinoni L et al (1987) Pressure-volume curve of total respiratory system in acute respiratory failure. Computed tomographic scan study. Am Rev Respir Dis 136(3):730–736
Cressoni M et al (2014) Lung inhomogeneity in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 189(2):149–158
Gattinoni L et al (1995) Effects of positive end-expiratory pressure on regional distribution of tidal volume and recruitment in adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 151(6):1807–1814
Tremblay L et al (1997) Injurious ventilatory strategies increase cytokines and c-fos m-RNA expression in an isolated rat lung model. J Clin Investig 99(5):944–952
Otis AB, Fenn WO, Rahn H (1950) Mechanics of breathing in man. J Appl Physiol 2(11):592–607
Marini JJ, Crooke PS 3rd (1993) A general mathematical model for respiratory dynamics relevant to the clinical setting. Am Rev Respir Dis 147(1):14–24
Chiumello D et al (2008) Lung stress and strain during mechanical ventilation for acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 178(4):346–355
Valenza F et al (2003) Positive end-expiratory pressure delays the progression of lung injury during ventilator strategies involving high airway pressure and lung overdistention. Crit Care Med 31(7):1993–1998
Brunner JX, Wysocki M (2009) Is there an optimal breath pattern to minimize stress and strain during mechanical ventilation? Intensive Care Med 35(8):1479–1483
Caironi P et al (2011) Time to generate ventilator-induced lung injury among mammals with healthy lungs: a unifying hypothesis. Intensive Care Med 37(12):1913–1920
Rodarte JR, Rehder K (1986) Dynamics of respiration. In: Macklem PT, Mead J (eds) Handbook of Physiology. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 131–144
Pelosi P et al (1995) Alterations of lung and chest wall mechanics in patients with acute lung injury: effects of positive end-expiratory pressure. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 152(2):531–537
Guerin C, Fournier G, Milic-Emili J (2001) Effects of PEEP on inspiratory resistance in mechanically ventilated COPD patients. Eur Respir J 18(3):491–498
Protti A et al (2015) Lung anatomy, energy load, and ventilator-induced lung injury. Intensive Care Med Exp 3(1):34
Gattinoni L, Pesenti A (2005) The concept of “baby lung”. Intensive Care Med 31(6):776–784
Bachofen H, Hildebrandt J (1971) Area analysis of pressure-volume hysteresis in mammalian lungs. J Appl Physiol 30(4):493–497
Fredberg JJ, Stamenovic D (1989) On the imperfect elasticity of lung tissue. J Appl Physiol 67(6):2408–2419
Gattinoni L et al (2016) The “baby lung” became an adult. Intensive Care Med 42(5):663–673
Amato MBP et al (2000) Ventilation with lower tidal volumes as compared with traditional tidal volumes for acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. The acute respiratory distress syndrome network. N Engl J Med 342(18):301–308
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Take-home message:
Each ventilatory variable found to be associated with lung injury is actually a contributor to the mechanical power delivered to the respiratory system. The equation we propose accurately reflects the measured mechanical power, which increases exponentially with TV, ∆P aw, flow (exponent = 2), and RR (exponent = 1.4) and linearly with PEEP.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gattinoni, L., Tonetti, T., Cressoni, M. et al. Ventilator-related causes of lung injury: the mechanical power. Intensive Care Med 42, 1567–1575 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-016-4505-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-016-4505-2