Summary
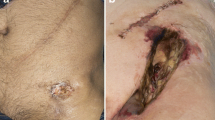
In conjunction with methods of improving blood flow and local surgical measures, antibacterial therapy is an essential component of the management of infected ischaemic lesions. Concentrations of active drug at the site of infection can be increased by intra-arterial administration, which produces higher tissue levels than intravenous administration. 35 patients with polyinfected ischaemic lesions were given ceftizoxime 2g once daily by intra-arterial infusion, with an additional 2 g/day by intravenous infusion, to maintain adequate concentrations of the drug over 24 hours. After an average treatment period of 9.2 days, infection was controlled in 25 patients (71%), and a further 6 patients whose infection did not improve satisfactorily subsequently underwent successful vascular reconstruction. Limb preservation was therefore achieved in a total of 31 patients (88%). There were no signs of local intolerance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amendt K, Hild R. Pharmacokinetics of mezlocillin after intra-arterial or intravenous injection in patients with peripheral arterial occlusive disease (PAOD). Journal of Vascular Diseases 19: 161–166, 1990
Gottlob R, Hugeneck J. Die intraarterielle Infusion. I. Kinetische Untersuchungen über den lokalen Blutspiegel. Wiener Medizinische Wochenschrift 18: 415–421, 1982
Hitzenberger G. Pharmakokinetik von Ceftizoxim. Wiener Medizinische Wochenschrift 15/16: 391–394, 1981
Klaus W. Pharmakologische Aspekte der Cephalosporin-Therapie. Forschritte der antimikrobiellen und antineoplastischen. Chemotherapie 8: 285–296, 1989
McNamara PJ, Trueb V, Stoeckel K. Protein binding of ceftriaxone in extravascular fluids. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 77: 401–404, 1988
Quintiliani R, Nightingale CH, Rossi JG. Cephalosporines: an overview. In Ristuccia AM, Cunha BA (Eds) Antimicrobial therapy, pp. 289–303, Raven Press, New York, 1984
Widmer LK, Hürlimann F. Erhöht die intraarterielle Zufuhr eines Pharmakons dessen Konzentration in den Akren? Zeitschrift Kreisl. Forschung 55: 410–417, 1966
Wise R. The clinical relevance of protein binding and tissue concentrations in antimicrobial therapy. Clinical Pharmacokinetics 11: 470–482, 1986
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mumme, A., Ernst, R., Kernen, M. et al. Intra-Arterial Treatment of Stage IV Arterial Occlusive Disease with Ceftizoxime. Drug Invest 4 (Suppl 1), 17–20 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03258339
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03258339