Abstract
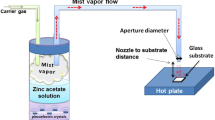
Ultrasonic Assisted SILAR method (UA-SILAR) was developed and highly oriented ZnO films were deposited on the glass substrate by this novel technique. The crystallinity and microstructure of as-deposited ZnO films were analyzed by means of XRD and SEM. Moreover, the underling deposition mechanism of ZnO films was discussed. Results show that obtained ZnO films exhibit an excellent crystallinity with the preferential orientation of (002) plane. The crystalline grain of films is about 40nm in size, which is supported by both the Sherrer equation and the SEM result. However, the ZnO film is composed of numerous clustered particulates in the size of 200 to 300nm, and each particulate is the compact aggregation of smaller ZnO crystalline grains. It is speculated that the excellent crystallinity of ZnO films may chiefly originate from the cavatition effect of the ultrasonic rinsing process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L Znaidi G J A A S Illia, S Benyahia, C Sanchez, A V Kanaev. Oriented ZnO Thin Films Synthesis by Sol-gel Process for Laser Application.Thin Solid Films, 2003, 428:257–262
T Saeed, P O Brien. Deposition and Characterization of ZnO Thin Films Grown by Chemical Bath Deposition.Thin Solid Films, 1995, 271:35–38
T P Niesen, M R De Guire. Deposition of Ceramic Thin Films at Low Temperatures From Aqueous Solutions.Solid State Ionics, 2002, 151:61–68
Y F Nicolau. Solution Deposition of Thin Solid Compound Films by a Successive Ionic-Layer Adsorption and Reaction Process.Applied Surface Science, 1985, 22/23:1061–1074.
M Ristov, Gj Sinadinovskil Grozdanov. Chemical Deposition of ZnO Films.Thin Solid Films, 1985, 123:63–67
A E Jimenez-Gonzailez, P K Nair. Photosensitive ZnO Thin Films Prepared by the Chemical Deposition Method SILAR.Semicon. Sci. Technol., 1995, 10:277–28
T Pauporté, D Lincot. Electrodeposition of Semiconductors for Optoelectronic Devices: Results on Zinc Oxide.Electrochimica Acta, 2000, 45(20):3345–3353
X D Gao, X M Li, W D Yu. Deposition of Polycrystalline ZnO Thin Films by Successive Ionic Layer Adsorption and Reaction Process (SILAR).Journal of Inorganic Materials, In Press (in Chinese)
Y R Ryu, S Zhu, J M Wrobel. Comparative Study of Textured and Epitaxial ZnO Films.Journal of Crystal Growth, 2000, 216:326–329
S Fujihara C Sasaki, T Kimura. Crystallization Behavior and Origin of C-axis Orientation in Sol-gel Derived ZnO: Li Thin Films on Glass Substrates.Applied Surface Science, 2001, 180:341–350
K S Suslick. Sonochemistry.Science, 1990, 247:1439–1445
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Financially supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China through 973-Project (No. 2002CB613306)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiangdong, G., Xiaomin, L. & Weidong, Y. Preparation and characterization of highly oriented ZnO film by ultrasonic assisted SILAR method. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 20, 23–26 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02835019
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02835019