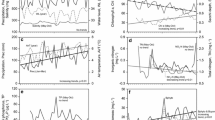
Abstract
Since the mid 1990s, the Atlantic and Gulf Coast regions have experienced a dramatic increase in the number of hurricane landfalls. In eastern North Carolina alone, eight hurricances have affected the coast in the past 9 years. These storms have exhibited individualistic hydrologic, nutrient, and sediment loading effects and represent a formidable challenge to nutrient management aimed at reducing eutrophication in the Pamlico Sound and its estuarine tributaries. Different rainfall amounts among hurricanes lead to variable freshwater and nutrient discharge and variable nutrient, organic matter, and sediment enrichment. These enrichments differentially affected physical and chemical properties (salinity, water residence time, transparency, stratification, dissolved oxygen), phytoplankton primary production, and phytoplankton community composition. Contrasting ecological responses were accompanied, by changes in nutrient and oxygen cycling, habitat, and higher trophic levels, including different direct effects on fish populations. Floodwaters from the two largest hurricances, Fran (1996) and Floyd (1999), exerted, multi-month to multi-annual effects on hydrology, nutrient loads, productivity, and biotic composition. Relatively low rainfall coastal hurricanes like Isabel (2003) and Ophelia (2005) caused strong vertical mixing and storm surges, but relatively minor hydrologic and nutrient effects. Both hydrologic loading and wind forcing are important drivers and must be integrated with nutrient loading in assessing short-term and long-term ecological effects of these storms. These climatic forcings cannot be managed but should be considered in the development of water quality management strategies for these and other large estuarine ecosystems faced with increasing frequencies and intensities of hurricane activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Adams, S. M., M. S. Greeley, J. M. Law, E. J. Noga, andJ. T. Zelikoff. 2003. Application of multiple sublethal stress indicators to assess the health of fish in Pamlico Sound following extensive flooding.Estuaries 26:1365–1382.
Anderson, J. B., A. B. Rodriguez, C. Fletcher, andD. Fitzgerald. 2001. Researchers focus attention on coastal response to climate change.Eos Transactions 82:513–520.
Bales, J. D. 2003. Effects of Hurricane Floyd inland flooding. September–October 1999, on tributaries to Pamlico Sound, North Carolina.Estuaries 26:1319–1328.
Borsuk, M. E., C. A. Stow, andK. H. Reckhow. 2003a. The confounding effect of flow on estuarine response to nitrogen loading.Journal of Environmental Engineering 130:605–614.
Borsuk, M. E., C. A. Stow, andK. H. Reckhow. 2003b. Integrated approach to TMDL development for the Neuse River estuary using a Bayesian probability network model (Neu-BERN).Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management 129:271–282.
Bowen, J. D. andJ. Hieronymus. 2000. Neuse River Estuary modeling and monitoring project stage 1: Predictions and uncertainty analysis of response to nutrient loading using a mechanistic eutrophication model. Water Resources Research Institute Report No. 325-D. University of North Carolina Water Resources Research Institute, Raleigh, North Carolina.
Burkholder, J., D. Eggleston, H. Glasgow, C. Brownie, R. Reed, G. Janowitz, M. Posey, G. Melia, C. Kinder, R. Corbett, D. Toms, J. Alphin, N. Deamer, andJ. Springer. 2004. Comparative impacts of two major hurricane seasons on the Neuse River and western Pamlico Sound ecosystems.Proceedings of the National Academy of Science USA 101:9291–9296.
Buzzelli, C. P., R. A. Luettich Jr.,S. P. Powers, C. H. Peterson, J. E. McNinch, J. L. Pinckney, andH. W. Paerl. 2002. Estimating the spatial extent of bottom-water hypoxia and habitat degradation in a shallow estuary.Marine Ecology Progress Series 230:103–112.
Buzzelli, C. P., J. R. Ramus, andH. W. Paerl. 2003. Ferry-based monitoring of surface water quality in North Carolina estuaries.Estuaries 26:975–984.
Chescheir, G. M., R. W. Skaggs, J. W. Gilliam, M. A. Breve, C. L. Munster, R. O. Evans, R. B. Leidy, andJ. E. Parsons. 1996. Effects of drainage and water table control on groundwater and surface water quality. Part II—Experimental results and simulation models. Water Resources Research Institute Report No. 301. University of North Carolina Water Resources Research Institute, Raleigh, North Carolina.
Christian, R. R., J. E. O'Neal, B. Peierls, L. Valdes, andH. W. Paerl. 2004. Episodic nutrient loading impacts on eutrophication of the southern Pamlico Sound: The effects of the 1999 hurricanes. Water Resources Research Institute Report No. 349. University of North Carolina Water Resources Research Institute, Raleigh, North Carolina.
Cifuentes, L. A. 1991. Spatial and temporal variations in terrestrially-derived organic matter from sediments of the Delaware Estuary.Estuaries 14:414–429.
Clesceri, E. J. 2003. Quantification of particulate organic matter sources in an eutrophic river estuary by stable carbon and nitrogen isotopes and photopigments (Neuse River Estuary, NC USA). Ph.D. Dissertation, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
Cooper, S. R., S. K. McGlothlin, M. Madritch, andD. L. Jones. 2004. Paleoecological evidence of human impacts on the Neuse and Pamlico Estuaries of North Carolina, USA.Estuaries 27:617–633.
Copeland, B. J. and J. Gray. 1991. Status and Trends Report of the Albemarle-Pamlico Estuary, J. Steel (ed.), Albemarle-Pamlico Estuarine Study. North Carolina Department of Environment, Health and Natural Resources, Report 90-01, Raleigh, North Carolina.
Curt, M. D., P. Aguado, G. Sánchez, M. Bigeriego, andJ. Fernández. 2004. Nitrogen isotope ratios of synthetic and organic sources of nitrate water contamination in Spain, 2004.Water Air and Soil Pollution 151:135–142.
Dodd, R. C., P. A. Cunningham, R. J. Curry, and S. J. Stichter. 1993. Watershed Planning in the Albemarle-Pamlico Estuarine System, Research Triangle Institute, North Carolina. Department of Environment, Health and Natural Resources, Report No. 93-01. Raleigh, North Carolina.
Eby, L. A. 2001. Response of a fish community to frequent and infrequent disturbances in an estuarine ecosystem. Ph.D. Dissertation, Duke University, Durham, North Carolina.
Eby, L. A. andL. B. Crowder. 2002. Hypoxia-based habitat compression in the Neuse River Estuary: Context-dependent shifts in behavioral avoidance thresholds.Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Science 59:952–965.
Eggleston, D. B. 1998. Population dynamics of the blue crab in North Carolina: Statistical analyses of fisheries survey data. North Carolina Department of Environmental Health and Natural Resources, Division of Marine Fisheries, Final Report for Contract M-6053, Raleigh, North Carolina.
Eggleston, D. B., J. Hightower, and E. Johnson. 2004. Population dynamics and stock assessment of the blue crab in North Carolina. Final Report to the North Carolina Sea Grant/Blue Crab Research Program for Project for Projects 99-FEG-10 and 00-FEG-11. Raleigh, North Carolina.
Emanuel, K. 2005. Increasing destructiveness of tropical cyclones over the past 30 years.Nature 436:686–688.
Fletcher, C., J. Anderson, K. Crook, G. Kaminsky, P. Larcombe, C. V. Murray-Wallace, F. Sansone, D. Scott, S. Riggs, A. Sallenger, I. Shennan, R. Theiler, andJ. F. Wehmiller. 2000. Coastal sedimentary research examines critical issues of national and global priority.EOS 81:181–186.
Giese, G. L., H. B. Wilder, and G. G. Parker. 1985. Hydrology of major estuaries and sounds of North Carolina, U.S. Geological Survey Water-Supply Paper 2221, Raleigh, North Carolina.
Goldenberg, S. B., C. W. Landsea, A. M. Mestas-Nuñez, andW. M. Gray. 2001. The recent increase in Atlantic hurricane activity: Causes and implications.Science 293:474–478.
Harding, L. W., E. C. Itsweire, andW. E. Esais. 1994. Estimates of phytoplankton biomass in the Chesapeake Bay from aircraft remote sensing of chlorophyll concentrations, 1989–1992.Remote Sensing of the Environment 49:41–56.
Heaton, T. H. E. 1986. Isotopic studies of nitrogen pollution in the hydrosphere and atmosphere: A review.Chemical Geology 59: 87–102.
Hughes, T. P. andJ. H. Connell. 1999. Multiple stressors on coral reefs: A long-term perspective.Limnology and Oceanography 44: 932–940.
Kendall, C., S. R. Silva, andV. J. Kelly. 2001. Carbon and nitrogen isotopic compositions of particulate organic matter in four large river systems across the United States.Hydrological Processes 15:1301–1346.
Levine, J. F., J. H. Hawkins, M. J. Dykstra, E. J. Noga, D. W. Moye, andR. S. Cone. 1990a. Epidemiology of ulcerative mycosis in Atlantic menhaden in the Tar-Pamlico River Estuary, North Carolina.Journal of Aquatic Animal Health 2:162–171.
Levine, J. F., J. H. Hawkins, M. J. Dykstra, E. J. Noga, D. W. Moye, andR. S. Cone. 1990b. Species distribution of ulcerative lesions on finfish in the Tar-Pamlico River Estuary, North Carolina.Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 8:1–5.
Luettich, Jr.,R. A., S. D. Carr, J. V. Reynold-Fleming, C. W. Fulcher, andJ. E. McNinch. 2002. Semi-diurnal seiching in a shallow, micro-tidal lagoonal estuary.Continental Shelf Research 22:1669–1681.
Mackey, M. D., D. J. Mackey, H. W. Higgins, andS. Wright. 1996. CHEMTAX—A program for estimating class abundances from chemical markers: Application to HPLC measurements of phytoplankton.Marine Ecology Progress Series 144:265–283.
Mariotti, A., C. Lancelot, andG. Billen. 1984. Natural isotopic composition of nitrogen as a tracer of origin for suspended organic matter in the Scheldt estuary.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 48:549–555.
Matson, E. A. andM. M. Brinson. 1990. Stable carbon isotopes and the C:N ratio in the estuaries of the Pamlico and Neuse rivers, North Carolina.Limnology and Oceanography 35:1290–1300.
Mew, H. E., D. K. Hirth, D. Lewis, R. B. Daniels, and A. J. Keyworth. 2002. Methodology for compiling ground water recharge maps in the Piedmont and Coastal Plain provinces of North Carolina. North Carolina Department of Environment and Natural Resources, Ground Water Bulletin Number 25, Raleigh, North Carolina.
Millie, D. F., H. W. Paerl, andJ. Hurley. 1993. Microalgal pigment assessments using high performance liquid chromatography: A synopsis of organismal and ecological applications.Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Science 50:2513–2527.
Noga, E. J. 1987. Propagation in cell culture of the dinoflagellateAmyloodinium, an ectoparasite of marine fishes.Science 236: 1302–1304.
Odum, W. E., E. P. Odum, andH. T. Odum. 1995. Nature's pulsing paradigm.Estuaries 18:547–555.
Paerl, H. W. 2005. Ecological effects of a recent rise in Atlantic hurricane activity on North Carolina's Pamlico Sound System: Putting Hurricane Isabel in perspective, p. 3–18.In K. G. Sellner (ed.), Hurricane Isabel in Perspective. Chesapeake Research Consortium, CRC Publications 05-160, Edgewater, Maryland.
Paerl, H. W., J. D. Bales, L. W. Ausley, C. P. Buzzelli, L. B. Crowder, L. A. Eby, J. M. Fear, M. Go, B. L. Peierls, T. L. Richardson, andJ. S. Ramus. 2001. Ecosystem impacts of 3 sequential hurricanes (Dennis, Floyd and Irene) on the U.S.'s largest lagoonal estuary, Pamlico Sound, NC.Proceedings of the National Academy of Science USA 98:5655–5660
Paerl, H. W., M. A. Mallin, C. A. Donahue, M. Go, and B. L. Peierls. 1995. Nitrogen loading sources and eutrophication of the Neuse River Estuary, NC: Direct and indirect roles of atmospheric deposition. University of North Carolina Water Resources Research Institute, North Carolina State University, Water Resources Research Report No. 291. Raleigh, North Carolina.
Paerl, H. W., J. L. Pinckney, J. Fear, andB. L. Peierls. 1998. Ecosystem response to internal and watershed organic matter loading: Consequences for hypoxia in the eutrophying Neuse River estuary, NC, USA.Marine Ecology Progress Series 166:17–25.
Paerl, H. W., L. M. Valdes, J. E. Adolf, B. L. Peierls, andL. W. Harding Jr. 2006a. Anthropogenic and climatic influences on the eutrophication of large estuarine ecosystems.Limnology and Oceanography 51:448–462.
Paerl, H. W., L. M. Valdes, M. F. Piehler, andM. E. Lebo. 2004. Solving problems resulting from solutions: The evolution of a dual nutrient management strategy for the eutrophying Neuse River Estuary, North Carolina, USA.Environmental Science and Technology 38:3068–3073.
Paerl, H. W., L. M. Valdes, M. F. Piehler, andC. A. Stow. 2006b. Assessing the effects of nutrient management in an estuary experiencing climatic change: The Neuse River Estuary, NC, USA.Environmental Management 37:422–436.
Paerl, H. W., L. M. Valdes, J. L. Pinckney, M. F. Piehler, J. Dyble, andP. H. Moisander. 2003. Phytoplankton photopigments as indicators of estuarine and coastal eutrophication.BioScience 53: 953–964.
Peierls, B. L., R. R. Christian, andH. W. Paerl. 2003. Water quality and phytoplankton as indicators of hurricane impacts on large estuarine ecosystems.Estuaries 26:1329–1343.
Peterson, B. J. andB. Fry. 1987. Stable isotopes in ecosystem studies.Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics 18:253–320.
Peterson, C. H. andR. Black. 1988. Density-dependent mortality caused by physical stress interacting with biotic history.American Naturalist 131:257–270.
Piehler, M. F., J. Dyble, P. H. Moisander, J. L. Pinckney, andH. W. Paerl. 2002a. Effects of modified nutrient concentrations and ratios on the structure and function of the native phytoplankton community in the Neuse River Estuary, North Carolina USA.Aquatic Ecology 36:371–385.
Piehler, M. F., S. P. Thompson, J. Dyble, P. H. Moisander, J. Fear, and H. W. Paerl. 2002b. Biologically mediated nitrogen cycling in the Neuse River Estuary. University of North Carolina Water Resources Research Institute Report #339. Raleigh, North Carolina.
Piehler, M. F., L. J. Twomey, N. S. Hall, andH. W. Paerl. 2004. Impacts of inorganic nutrient enrichment on the phytoplankton community structure and function in Pamlico Sound, NC USA.Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 61:197–209.
Pietrafesa, L. J., G. S. Janowitz, T.-Y. Chao, T. H. Weisberg, F. Askari, and E. Noble. 1996. The Physical Oceanography of Pamlico Sound. University of North Carolina Sea Grant Publication UNC-WP-86-5. Raleigh, North Carolina.
Pinckney, J. L., H. W. Paerl, M. B. Harrington, andK. E. Howe. 1998. Annual cycles of phytoplankton community structure and bloom dynamics in the Neuse River Estuary, NC (USA).Marine Biology 131:371–382.
Ramus, J., L. A. Eby, C. M. McClellan, andL. B. Crowder. 2003. Phytoplankton forcing by a record discharge event into a large lagoonal estuary.Estuaries 26:1344–1352.
Reckhow, K. H. 1999. Water quality prediction and probability network models.Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 56:1150–1158.
Riggs, S. R. 1999. Coupled inner shelf-shoreline sediment responses to small-scale Holocene sea-level fluctuations: North Carolina coastal zone, p. 165–167.In C. H. Fletcher and J. V. Matthews (eds.), The Non-steady State of the Inner Shelf and Shoreline: Coastal Change on the Time Scale of Decades to Millennia in the late Quaternary. University of Hawaii, Hawaii, Honolulu.
Riggs, S. R. 2001. Anatomy of a flood, in facing our future, p. 29–45.In J. R. Maiolo, J. C. Whitehead, M. McGee, L. King, J. Johnson, and H. Stone (eds.), Hurricane Floyd and Recovery in the Coastal Plain. Coastal Carolina Press, Wilmington, North Carolina.
Riggs, S. R. and D. V. Ames. 2003. Drowning the North Carolina Coast: Sea-Level Rise and Estuarine Dynamics. North Carolina Sea Grant Pub. No. UNC-SG-03-04. Raleigh, North Carolina.
Roman, M. R., J. E. Adolf, J. Bichy, W. C. Boicourt, L. W. Harding Jr.,E. D. Houde, S. Jung, D. G. Kimmel, W. D. Miller, andX. Zhang. 2005. Chesapeake Bay plankton and fish abundance enhanced by Hurricane Isabel.Eos Transactions American Geophysical Union 86:261–265.
Ruzecki, E. P., J. H. Schubel, R. J. Huggett, A. M. Anderson, M. L. Wass, R. J. Marasco, andM. P. Lynch (eds.). 1976, The Effects of Tropical Storm Agnes on the Chesapeake Bay Estuarine System. Chesapeake Bay Research Consortium Publication No. 54, Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, Maryland.
Stanley, D. W. 1988. Historical trends in nutrient loading to the Neuse River Estuary, NC, p. 155–164.In W. Lyke and T. Hoban (eds.), Proceedings of the American Water Resources Association Symposium on Coastal Water Resources, AWRA Technical Publication Serial TPS-88-1. AWRA, Bethesda, Maryland.
Stow, C. A., M. E. Borsuk, andD. W. Stanley. 2001. Long-term changes in watershed nutrient inputs and riverine exports in the Neuse River, North Carolina.Water Research 35:1489–1499.
Tester, P. M., S. M. Varnam, M. E. Culver, D. L. Eslinger, R. P. Stumpf, R. N. Swift, J. K. Yungel, M. D. Black, andR. W. Litaker. 2003. Airborne detection of ecosystem responses to an extreme event: Phytoplankton displacement and abundance after hurricane induced flooding in the Albemarle-Pamlico Sound system.Estuaries 26:1353–1364.
Ulseth, A. J. andA. E. Hershey. 2005. Natural abundances of stable isotopes trace anthropogenic N and C in an urban stream.Journal of the North American Benthological Society 24:270–289.
Valdes, A. M., M. F. Piehler, J. L. Pinckney, K. E. Howe, K. Rossignol, andH. W. Paerl. 2006. Long-term temporal and spatial trends in phytoplankton biomass and class-level taxonomic composition in the hydrologically variable Neuse-Pamlico estuarine continuum, NC, USA.Limnology and Oceanography 51:1410–1420.
Wada, E. andA. Hattori. 1991. Nitrogen in the Sea: Forms, Abundances, and Rate Processes. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida.
Webster, P. J., G. J. Holland, J. A. Curry, andH. R. Chang. 2005. Changes in tropical cyclone number, duration, and intensity in a warming environment.Science 309:1844–1846.
Woodruff, D. L., R. P. Stumpf, J. A. Scope, andH. W. Paerl. 1999. Remote estimation of water clarity in Pamlico Sound, North Carolina.Remote Sensing of the Environment 68:41–52.
Sources of Unpublished Materials
North Carolina Department of Agriculture. 1997. North Carolina agricultural statistics [Online]. Available at www.agr.state.nc.us/stats (verified March 2, 2001).
North Carolina Department of Environment and Natural Resources (NC DENR) Division Marine Fisheries. unpublished data. 3441 Arendell Street, Morehead City, NC.
North Carolina Department of Environment and Natural Resources (NC DENR) Division of Water Quality. unpublished data. 4401 Reedy Creek Road Raleigh, NC 27607.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paerl, H.W., Valdes, L.M., Joyner, A.R. et al. Ecological response to hurricane events in the Pamlico Sound system, North Carolina, and implications for assessment and management in a regime of increased frequency. Estuaries and Coasts: J ERF 29, 1033–1045 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02798666
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02798666