Summary
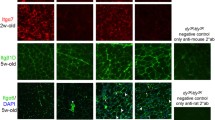
The laminin variant of adult skeletal muscle fibres and Schwann cells is known as merosin, and is composed of M-B1-B2 chains. Blood vessels and immature fibres express the A chain in association with B1 or S, and B2. The importance of merosin has recently been shown by its absence in one form of congenital muscular dystrophy and in the mutantdy/dy mouse, and by its partial deficiency in Fukuyama congenital muscular dystrophy. We have examined the immunocytochemical localization of the M, A, B1 and B2 laminin chains in human fetal muscle from 7 to 40 weeks' gestation to ascertain their developmental expression. The B1 and B2 chains were detected on muscle fibres at 7 weeks, but only traces of the A or M chain were seen. By 21 weeks maximal levels of all four subunits were observed on all fibres. This suggests that the basement membrane is still being assembled until this stage of development. Expression of the A chain on muscle fibres was not reduced until 34 weeks and low levels persisted at birth. The concomitant expression of the M and A chains at early stages may indicate a laminin variant, in addition to merosin, that is highly expressed in fetal muscle. Merosin was seen in intramuscular nerves at 11 weeks. B1 and B2 subunits were detected in blood vessels from 7 weeks' gestation and the A chain from 11 weeks. The capillary network, however, is not fully established in fetal muscle. Merosin is therefore detected early during human fetal muscle development, and this should be taken into account when assessing aborted fetuses at risk for congenital muscular dystrophy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arahata,K.,Hayashi,Y. K.,Koga,R.,Goto,K.,Lee,J. H.,Miyagoe,Y.,Ishii,H.,Tsukahara,T.,Takeda,S.,Woo,M.,Nonaka,I. &Atsuzaki,T. (1993) Laminin in animal models for muscular dystrophy. Defect of laminin M in skeletal and cardiac muscles and peripheral nerve of the homozygous dystrophicdy/dy mice.Proc. Japan Acad. 69, Ser B, 259–64.
Bradley,W. G. &Jenkison,M. (1974) Neural abnormalities in the dystrophic mouse.J. Neurol. Sci. 25, 249–55.
Burgeson,R. E.,Chiquet,M.,Deutzmann,R.,Ekblom,P.,Engel,J.,Kleinman,H.,Martin,G. R.,Meneguzzi,G.,Paulsson,M.,Sanes,J. et al. (1994) A new nomenclature for the laminins.Matrix Biol. 14, 209–11.
Clerk,A.,Strong,P. N. &Sewry,C. A. (1992) Characterisation of dystrophin during development of human skeletal muscle.Development 114, 395–402.
Clerk,A.,Morris,G. E.,Dubowitz,V.,Davies,K. E. &Sewry,C. A. (1993) Dystrophin-related protein, utrophin, in normal and dystrophic human fetal muscle.Histochem. J. 25, 554–61.
Ehrig,K.,Leivo,I.,Argraves,W. S.,Ruoslahti,E. &Engvall,E. (1990) Merosin, a tissue-specific basement membrane protein, is a laminin-like protein.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 3264–68.
Engvall,E. (1993) Laminin variants: Why, where and when?Kidney Internat. 43, 2–6.
Fukuyama,Y.,Osawa,M. &Suzuki,H. (1981) Congenital progressive muscular dystrophy of the Fukuyama type: clinical, genetic and pathological considerations.Brain Dev. 13, 1–29.
Hamilton,W. J. &Mossman,H. W. (1972)Human Embryology, 4th edn. Cambridge: Heffer & Sons.
Hayashi,Y. K.,Engvall,E.,Arikawa-Hirasawa,E.,Goto,K.,Koga,R.,Nonaka,Z.,Sugita,H. &Arahata,K. (1993) Abnormal expression of laminin subunits in muscular dystrophies.J. Neurol. Sci. 119, 53–64.
Hillaire,D.,Leclerc,A.,Fauré,S.,Topaloglu,H.,Chiannikulchai,N.,Guichenev,P.,Grinas,L.,Legos,P.,Philpot,J.,Evangelista,T. et al. (1994) Localisation of merosin-negative congenital muscular dystrophy to chromosome 6q2 by homozygosity mapping.Human. Mol. Genet. 3, 1657–61.
Hynes,R. O. &Lander,A. D. (1992) Contact and adhesive specificities in the associations, migrations, and targeting of cells and axons.Cell 68, 303–22.
Leivo,I. &Engvall,E. (1988) Merosin, a protein specific for basement membranes of Schwann cells, striated muscle, and trophoblast, is expressed late in nerve and muscle development.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85, 1544–48.
Mercuri, E., Muntoni, F., Berardinelli, A., Pennock, J., Sewry, C. &Dubowitz, V. (1995) Somatosensory and visual evoked potentials in congenital muscular dystrophy: correlation with MRI changes and muscle merosin status.Neuropaediatrics 26 (in press).
Muntoni,F.,Sewry,C.,Wilson,L.,Tomé,F.,Angelini,C.,Trevisan,C.,Brambati,B. &Dubowitz,V. (1995) Prenatal diagnosis in congenital muscular dystrophy.Lancet 345, 591.
Philpot, J., Sewry, C., Pennock, J. &Dubowitz, V. (1995) Clinical phenotype in congenital muscular dystrophy: correlation with expression of merosin in skeletal muscle.Neuromusc. Disord. (in press).
Richards,A. J.,Al-Imara,L.,Carter,N.,Lloyd,J. C.,Leversha,M. A. &Pope,F. M. (1994) Localization of the gene (LAMA4) to chromosome 6q21 and isolation of a partial cDNA encoding a variant laminin A chain.Genomics 22, 237–39.
Sanes,J. R.,Engvall,E.,Butkowski,R. &Hunter,D. D. (1990) Molecular heterogeneity of basal laminae: isoforms of laminin and collagen IV at the neuromuscular junction.J. Cell Biol. 111, 1685–99.
Scammon,R. E. &Calkins,L. A. (1929)The Development and Growth of the External Dimensions of the Human Body in the Fetal Period. Minneapolis: University of Minneapolis Press.
Sewry, C. A., Philpot, J., Mahony, D., Wilson, L. A., Muntoni, F. &Dubowitz, V. (1995) Laminin subunits in congenital muscular dystrophy.Neuromusc. Disord. (in press).
Sunada,Y.,Bernier,S. M.,Kozak,C. A.,Yamada,Y. &Campbell,K. P. (1994) Deficiency of merosin in dystrophic dy mice and genetic linkage of laminin M chain.J. Biol. Chem. 269, 13729–32.
Toda,T.,Segawa,M.,Nomura,Y.,Nonaka,I.,Masuda,K.,Ishihara,T.,Suzuki,M.,Tomita,I.,Origichi,Y.,Ohno,K. et al. (1993) Localization of a gene for Fukuyama type congenital muscular dystrophy to chromosome 9q31–33.Nature Genet. 5, 283–86.
Tomé,F. M. S.,Evangelista,T.,Leclerc,A.,Sunada,Y.,Manole,E.,Estournet,B.,Barois,A. &Campbell,K. P. (1994a) Congenital muscular dystrophy with merosin deficiency.C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris,Life Sci. 317, 351–7.
Tomé,F. M. S.,Matsumura,K.,Chevallay,M.,Campbell,K. P. &Fardeau,M. (1994b) Expression of dystrophin-associated glycoproteins during human fetal muscle development: a preliminary immunocytochemical study.Neuromusc. Disord. 4, 343–8.
Troll,D. (1948) Age of foetuses determined from their increases.Acta Obstet. Gynec. Scand. 27, 327–37.
Voit,T.,Fardeau,M. &Tomé,F. M. S. (1994) Prenatal detection of merosin expression in human placenta.Neuropaediatrics 25, 332–3.
Vuolteenaho,R.,Nissinen,M.,Sainio,K.,Byers,M.,Eddy,R.,Hirvonen,H.,Shows,T. B.,Sariola,H.,Engvall,E. &Trggvason,K. (1994) Human laminin M chain (merosin): complete primary structure, chromosomal assignment and expression of the M and A chain in human fetal muscle.J. Cell Biol. 124, 381–94.
Xu,H.,Christmas,P.,Wu,X.,Wewer,U. M. &Engvall,E. (1994) Defective muscle basement membrane and lack of M-laminin in the dystrophicdy/dy mouse.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 5572–6.
Yurchenco,P. D. &O'Rear,J. J. (1994) Basal lamina assembly.Curr. Op. Cell Biol. 6, 674–81.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sewry, C.A., Chevallay, M. & Tomé, F.M.S. Expression of laminin subunits in human fetal skeletal muscle. Histochem J 27, 497–504 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02388749
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02388749