Summary
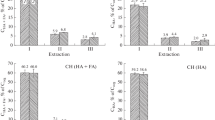
The extent of contamination of soil humic fractions by silica gel, sodium bicarbonate and sodium carbonate was investigated by infrared spectroscopy. Humic fractions were extracted with 0.1 N NaOH from a surface sample of a Davidson soil (Rhodic Paleudult, Reddish-brown Lateritic soil). After careful purification, the humic preparations were characterized by scanning with the Beckman IR-18A spectrophotometer using the micro KBr pellet technique. The spectra of the various humic fractions corresponded to the respective spectra reported in the literature. No indications were obtained for the presence of silica gel, sodium bicarbonate or sodium carbonate. Strong absorption at 1000 cm-1, as exhibited by non-purified humic acid, could be caused by Si-O vibrations. However, this band disappeared after washing humic acid with HCl-HF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailly J. R., Spectroscopie infra-rouge de quelques acides humiques. Plant and Soil 40, 285–302 (1974).
Clark F. E. and TanK. H., Identification of a polysaccharide ester linkage in humic acid. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1, 75–81 (1969).
Dubach P. and MehtaN. C., The chemistry of soil humic substances. Soils Fert. 26, 293–300 (1963).
GohK. M. and StevensonF. J., Comparison of infrared spectra of synthetic and natural humic and fulvic acids. Soil Sci. 112, 392–400 (1971).
Jambu P. and DupuisT., Electrophoretic and infrared absorption spectrographic study of hymatomelanic acids in hydromorphic calcic soils. Sci. Sol 1, 111–120 (1971).
Lowe L. E., Aspects of infrared spectra of humic acids in relation to method of preparation. Canad. J. Soil Sci. 49, 257–258 (1969).
Mortensen, J. L., Anderson, D. M. and White, J. L., Infrared spectrometry. In: Methods of Soil Analysis, Part I (C. A. Black, ed.) A.S.A. Monograph 9, 743–770 (1965).
Posner A. M., The humic acids extracted by various reagents from a soil. I. Yield, inorganic compounds and titration curves. J. Soil Sci. 17, 65–78 (1966).
Russell J. D. and AndersonH. A., Short communication. Comment on ‘spectroscopie infra-rouge de quelques acides humiques’ by J. R. Bailly. Plant and Soil 41, 695–696 (1974).
Schnitzer M. and KhanS. U., Humic substances in the environment. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, N.Y., 327 pp. (1972).
Schnitzer M., ShearerD. A. and WrightJ. R., A study in the infrared of high molecular weight organic matter extracted by various reagents from a podzolic B horizon. Soil Sci. 87, 252–257 (1959).
Stevenson F. J. and GohK. M., Infrared spectra of humic acids and related substances. Geochim. Cosmchim. Acta 35, 471–483 (1971).
Stevenson F. J. and GohK. M., Infrared spectra of humic and fulvic acids and their methylated derivatives: Evidence for non-specificity of analytical methods for oxygen-containing functional groups. Soil Sci. 113, 334–345 (1972).
TanK. H., Infrared absorption similarities between hymatomelanic acid and methylated humic acid. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 39, 70–73 (1975).
Theng B. K. G., WakeJ. R. H. and PosnerA. M., The infrared spectrum of humic acid. Soil Sci. 102, 70–72 (1966).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Contribution of the University of Georgia, College of Agric. Expt. Sta., College Sta., Athens, Georgia, USA.
Contribution of the University of Georgia, College of Agric. Expt. Sta., College Sta., Athens, Georgia, USA.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, K.H. Contamination of humic acid by silica gel and sodium bicarbonate. Plant Soil 44, 691–695 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011386
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011386