Summary
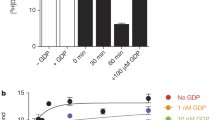
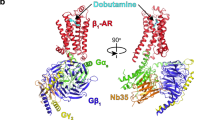
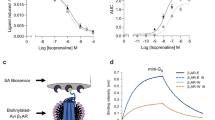
The [35S]GTPγS binding assay to measure G protein activation following agonist binding to G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) remains a powerful molecular technique to substantiate traditional pharmacological values of potency, efficacy, and affinity. The method described uses membrane preparations of the α2A-adrenergic receptor and purified G protein subunits expressed in Sf9 cells, reconstituted into a functional signaling system. This technology is generic and could be used with other GPCRs to demonstrate initial signaling events following receptor activation. Agonist-stimulated [35S]GTPγS binding is measured in a 96-well plate format using scintillation counting.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harrison, C., and Traynor, J.R. (2003) The [35S]GTPgammaS binding assay: approaches and applications in pharmacology. Life Sci. 74, 489–508.
Milligan, G. (2003) Principles: extending the utility of [35S]GTP gamma S binding assays. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 24, 87–90.
Niedernberg, A. Tunaru, S., Blaukat, A., Harris, B., and Kostenis, E. (2003) Comparative analysis of functional assays for characterization of agonist ligands at G protein-coupled receptors. J. Biomol. Screen. 8, 500–510.
Ferrer, M., Kolodin, G.D., Zuck, P., Peltier, R., Berry, K., Mandala, S.M., Rosen, H., Ota, H., Ozaki, S., Inglese, J., and Strulovici, B. (2003) A fully automated [35S]GTPgammaS scintillation proximity assay for the high-throughput screening of Gi-linked G protein-coupled receptors. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 1, 261–273.
Frang, H., Mukkala, V. M., Syysto, R., Ollikka, P., Hurskainen, P., Scheinin, M., and Hemmila, I. (2003) Nonradioactive GTP binding assay to monitor activation of g protein-coupled receptors. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 1, 275–280.
Hilf, G., Gierschik, P., and Jakobs, K.H. (1989) Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor-stimulated binding of guanosine 5'-O-(3-thiotriphosphate) to guanine-nucleotide-binding proteins in cardiac membranes. Eur. J. Biochem. 186, 725–731.
Barr, A.J., Brass, L.F., and Manning, D. R. (1997) Reconstitution of receptors and GTP-binding regulatory proteins (G proteins) in Sf9 cells. A direct evaluation of selectivity in receptor.G protein coupling. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 2223–2229.
Francken, B.J., Vanhauwe, J.F., Josson, K., Jurzak, M., Luyten, W.H., and Leysen, J. E. (2001) Reconstitution of human 5-hydroxytryptamine5A receptor--G protein coupling in E. coli and Sf9 cell membranes with membranes from Sf9 cells expressing mammalian G proteins. Receptors Channels 7, 303–318.
Leifert, W.R., Bailey, K., Cooper, T.H., Aloia, A.L., Glatz, R.V., and McMurchie, E.J. (2006) Measurement of heterotrimeric G protein and regulators of G protein signaling interactions by time-resolved fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Anal. Biochem. 355, 201–212.
Bradford, M.M. (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72, 248–254.
Wieland, T., Liedel, K., Kaldenberg-Stasch, S., Meyer zu Heringdorf, D., Schmidt, M., and Jakobs, K.H. (1995) Analysis of receptor-G protein interactions in permeabilized cells. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 351, 329–336.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Mrs. Sharon Burnard, Dr. Olgatina Bucco, and Dr. Amanda Aloia for their assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Humana Press, a part of Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Cooper, T., McMurchie, E.J., Leifert, W.R. (2009). [35S]GTPγS Binding in G Protein-Coupled Receptor Assays. In: Leifert, W. (eds) G Protein-Coupled Receptors in Drug Discovery. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 552. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60327-317-6_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60327-317-6_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, Totowa, NJ
Print ISBN: 978-1-60327-316-9
Online ISBN: 978-1-60327-317-6
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols