Abstract.
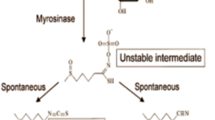
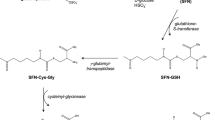
The consumption of cruciferous vegetables has long been associated with a reduced risk in the occurrence of cancer at various sites, including the prostate, lung, breast and colon. This protective effect is attributed to isothiocyanates present in these vegetables, and sulforaphane (SF), present in broccoli, is by far the most extensively studied to uncover the mechanisms behind this chemoprotection. The major mechanism by which SF protects cells was traditionally thought to be through Nrf2-mediated induction of phase 2 detoxification enzymes that elevate cell defense against oxidative damage and promote the removal of carcinogens. However, it is becoming clear that there are multiple mechanisms activated in response to SF, including suppression of cytochrome P450 enzymes, induction of apoptotic pathways, suppression of cell cycle progression, inhibition of angiogenesis and anti-inflammatory activity. Moreover, these mechanisms seem to have some degree of interaction to synergistically afford chemoprevention.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received: 10 November 2006; received after revision 15 January 2007; accepted 5 February 2007
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Juge, N., Mithen, R.F. & Traka, M. Molecular basis for chemoprevention by sulforaphane: a comprehensive review. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 64, 1105 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-007-6484-5
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-007-6484-5