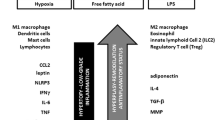
Abstract
Obesity is a pressing public health concern as it leads to a collection of abnormalities often termed the metabolic syndrome. Molecular studies are revealing novel pathways by which obesity-associated hormonal, nutrient, and tissue factors can stimulate the chronic low-grade inflammation that leads to insulin resistance. Signaling interactions between proinflammatory immune cells, particularly macrophages and lymphocytes, and insulin target cells in the liver and adipose tissue are key to this process and provide potential opportunities for the development of targeted therapies to improve insulin sensitivity and correct energy imbalance.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ATM:
-
Adipose tissue macrophage
- DIO:
-
Diet-induced obesity
- FFA:
-
Free fatty acid
- GPCR:
-
G protein-coupled receptor
- HFD:
-
High-fat diet
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- SAT:
-
Subcutaneous adipose tissue
- SFA:
-
Saturated fatty acid
- TNF:
-
Tumor necrosis factor
- VAT:
-
Visceral adipose tissue
- WAT:
-
White adipose tissue
References
Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, Curtin LR (2010) Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999–2008. JAMA 303(3):235–241. doi:2009.2014[pii].10.1001/jama.2009.2014
Moller DE, Kaufman KD (2005) Metabolic syndrome: a clinical and molecular perspective. Annu Rev Med 56:45–62. doi:10.1146/annurev.med.56.082103.104751
James PT, Leach R, Kalamara E, Shayeghi M (2001) The worldwide obesity epidemic. Obes Res 9(suppl 4):228S–233S. doi:10.1038/oby.2001.123
Johnson AR, Justin Milner J, Makowski L (2012) The inflammation highway: metabolism accelerates inflammatory traffic in obesity. Immunol Rev 249(1):218–238. doi:10.1111/j.1600-065X.2012.01151.x
Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Kit BK, Flegal KM (2012) Prevalence of obesity in the United States, 2009–2010, vol NCHS data brief, no 82. National Center for Health Statistics, Hyattsville, MD
Li P, Fan W, Xu J, Lu M, Yamamoto H, Auwerx J, Sears DD, Talukdar S, Oh D, Chen A, Bandyopadhyay G, Scadeng M, Ofrecio JM, Nalbandian S, Olefsky JM (2011) Adipocyte NCoR knockout decreases PPARgamma phosphorylation and enhances PPARgamma activity and insulin sensitivity. Cell 147(4):815–826. doi:S0092-8674(11)01220-7[pii].10.1016/j.cell.2011.09.050
Jacobi D, Stanya KJ, Lee CH (2012) Adipose tissue signaling by nuclear receptors in metabolic complications of obesity. Adipocyte 1(1):4–12. doi:10.4161/adip.19036
Hotamisligil GS, Shargill NS, Spiegelman BM (1993) Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha: direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science 259(5091):87–91
Xu H, Barnes GT, Yang Q, Tan G, Yang D, Chou CJ, Sole J, Nichols A, Ross JS, Tartaglia LA, Chen H (2003) Chronic inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development of obesity-related insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 112(12):1821–1830. doi:10.1172/JCI19451. 112/12/1821[pii]
Weisberg SP, McCann D, Desai M, Rosenbaum M, Leibel RL, Ferrante AW Jr (2003) Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J Clin Invest 112(12):1796–1808. doi:10.1172/JCI19246
Galic S, Oakhill JS, Steinberg GR (2010) Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. Mol Cell Endocrinol 316(2):129–139. doi:S0303-7207(09)00438-9[pii].10.1016/j.mce.2009.08.018
Despres JP, Lemieux I (2006) Abdominal obesity and metabolic syndrome. Nature 444(7121):881–887. doi:10.1038/nature05488
Kissebah AH, Vydelingum N, Murray R, Evans DJ, Hartz AJ, Kalkhoff RK, Adams PW (1982) Relation of body fat distribution to metabolic complications of obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 54(2):254–260
Nedungadi TP, Clegg DJ (2009) Sexual dimorphism in body fat distribution and risk for cardiovascular diseases. J Cardiovasc Transl Res 2(3):321–327. doi:10.1007/s12265-009-9101-1
Ford ES, Li C, Zhao G, Pearson WS, Mokdad AH (2008) Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome among U.S. adolescents using the definition from the International Diabetes Federation. Diabetes Care 31(3):587–589. doi:10.2337/dc07-1030
Anderson GL, Neuhouser ML (2012) Obesity and the risk for premenopausal and postmenopausal breast cancer. Cancer Prev Res 5(4):515–521. doi:10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-12-0091
Vona-Davis L, Rose DP (2012) Type 2 diabetes and obesity metabolic interactions: common factors for breast cancer risk and novel approaches to prevention and therapy. Curr Diabetes Rev 8(2):116–130. doi:EPUB-CDR-20120117-002[pii]
Cleary MP, Grossmann ME (2009) Minireview: obesity and breast cancer: the estrogen connection. Endocrinology 150(6):2537–2542. doi:en.2009-0070[pii].10.1210/en.2009-0070
Siddle K (2012) Molecular basis of signaling specificity of insulin and IGF receptors: neglected corners and recent advances. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 3:34. doi:10.3389/fendo.2012.00034
Hirosumi J, Tuncman G, Chang L, Gorgun CZ, Uysal KT, Maeda K, Karin M, Hotamisligil GS (2002) A central role for JNK in obesity and insulin resistance. Nature 420(6913):333–336. doi:10.1038/nature01137
Yuan M, Konstantopoulos N, Lee J, Hansen L, Li ZW, Karin M, Shoelson SE (2001) Reversal of obesity- and diet-induced insulin resistance with salicylates or targeted disruption of Ikkbeta. Science 293(5535):1673–1677. doi:10.1126/science.1061620
Perseghin G, Petersen K, Shulman GI (2003) Cellular mechanism of insulin resistance: potential links with inflammation. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 27(suppl 3):S6–S11. doi:10.1038/sj.ijo.0802491
Mathis D, Shoelson SE (2011) Immunometabolism: an emerging frontier. Nat Rev Immunol 11(2):81. doi:10.1038/nri2922
Gregor MF, Hotamisligil GS (2011) Inflammatory mechanisms in obesity. Annu Rev Immunol 29:415–445. doi:10.1146/annurev-immunol-031210-101322
Liu G, Yang H (2012) Modulation of macrophage activation and programming in immunity. J Cell Physiol 228(3):502–512. doi:10.1002/jcp.24157
Nguyen MT, Favelyukis S, Nguyen AK, Reichart D, Scott PA, Jenn A, Liu-Bryan R, Glass CK, Neels JG, Olefsky JM (2007) A subpopulation of macrophages infiltrates hypertrophic adipose tissue and is activated by free fatty acids via toll-like receptors 2 and 4 and JNK-dependent pathways. J Biol Chem 282(48):35279–35292. doi:M706762200[pii].10.1074/jbc.M706762200
Lumeng CN, Bodzin JL, Saltiel AR (2007) Obesity induces a phenotypic switch in adipose tissue macrophage polarization. J Clin Invest 117(1):175–184. doi:10.1172/JCI29881
Osborn O, Olefsky JM (2012) The cellular and signaling networks linking the immune system and metabolism in disease. Nat Med 18(3):363–374. doi:10.1038/nm.2627. nm.2627[pii]
Patsouris D, Li PP, Thapar D, Chapman J, Olefsky JM, Neels JG (2008) Ablation of CD11c-positive cells normalizes insulin sensitivity in obese insulin resistant animals. Cell Metab 8(4):301–309. doi:S1550-4131(08)00282-9[pii].10.1016/j.cmet.2008.08.015
Solinas G, Vilcu C, Neels JG, Bandyopadhyay GK, Luo JL, Naugler W, Grivennikov S, Wynshaw-Boris A, Scadeng M, Olefsky JM, Karin M (2007) JNK1 in hematopoietically derived cells contributes to diet-induced inflammation and insulin resistance without affecting obesity. Cell Metab 6(5):386–397. doi:S1550-4131(07)00292-6[pii].10.1016/j.cmet.2007.09.011
Arkan MC, Hevener AL, Greten FR, Maeda S, Li ZW, Long JM, Wynshaw-Boris A, Poli G, Olefsky J, Karin M (2005) IKK-beta links inflammation to obesity-induced insulin resistance. Nat Med 11(2):191–198. doi:nm1185[pii].10.1038/nm1185
Odegaard JI, Ricardo-Gonzalez RR, Goforth MH, Morel CR, Subramanian V, Mukundan L, Red Eagle A, Vats D, Brombacher F, Ferrante AW, Chawla A (2007) Macrophage-specific PPARgamma controls alternative activation and improves insulin resistance. Nature 447(7148):1116–1120. doi:nature05894[pii].10.1038/nature05894
Weisberg SP, Hunter D, Huber R, Lemieux J, Slaymaker S, Vaddi K, Charo I, Leibel RL, Ferrante AW Jr (2006) CCR2 modulates inflammatory and metabolic effects of high-fat feeding. J Clin Invest 116(1):115–124. doi:10.1172/JCI24335
Kanda H, Tateya S, Tamori Y, Kotani K, Hiasa K, Kitazawa R, Kitazawa S, Miyachi H, Maeda S, Egashira K, Kasuga M (2006) MCP-1 contributes to macrophage infiltration into adipose tissue, insulin resistance, and hepatic steatosis in obesity. J Clin Invest 116(6):1494–1505. doi:10.1172/JCI26498
Kosuri M, Bhatnagar A, Jala VR, Haribabu B (2011) Deficiency of the leukotriene B4 receptor, BLT-1, protects against systemic insulin resistance in diet-induced obesity. J Immunol 187(4):1942–1949.doi:doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1100196
Obstfeld AE, Sugaru E, Thearle M, Francisco AM, Gayet C, Ginsberg HN, Ables EV, Ferrante AW Jr (2010) C-C chemokine receptor 2 (CCR2) regulates the hepatic recruitment of myeloid cells that promote obesity-induced hepatic steatosis. Diabetes 59(4):916–925. doi:db09-1403[pii].10.2337/db09-1403
Kurihara T, Bravo R (1996) Cloning and functional expression of mCCR2, a murine receptor for the C-C chemokines JE and FIC. J Biol Chem 271(20):11603–11607
Charo IF, Myers SJ, Herman A, Franci C, Connolly AJ, Coughlin SR (1994) Molecular cloning and functional expression of two monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 receptors reveals alternative splicing of the carboxyl-terminal tails. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91(7):2752–2756
Inouye KE, Shi H, Howard JK, Daly CH, Lord GM, Rollins BJ, Flier JS (2007) Absence of CC chemokine ligand 2 does not limit obesity-associated infiltration of macrophages into adipose tissue. Diabetes 56(9):2242–2250. doi:db07-0425[pii].10.2337/db07-0425
Chen A, Mumick S, Zhang C, Lamb J, Dai H, Weingarth D, Mudgett J, Chen H, MacNeil DJ, Reitman ML, Qian S (2005) Diet induction of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and its impact on obesity. Obes Res 13(8):1311–1320. doi:10.1038/oby.2005.159
Samuelsson B, Dahlen SE, Lindgren JA, Rouzer CA, Serhan CN (1987) Leukotrienes and lipoxins: structures, biosynthesis, and biological effects. Science 237(4819):1171–1176
Haeggstrom JZ (2004) Leukotriene A4 hydrolase/aminopeptidase, the gatekeeper of chemotactic leukotriene B4 biosynthesis. J Biol Chem 279(49):50639–50642. doi:10.1074/jbc.R400027200. R400027200[pii]
Yokomizo T, Izumi T, Chang K, Takuwa Y, Shimizu T (1997) A G-protein-coupled receptor for leukotriene B4 that mediates chemotaxis. Nature 387(6633):620–624. doi:10.1038/42506
Xu J, Morinaga H, Oh D, Li P, Chen A, Talukdar S, Lazarowski E, Olefsky JM, Kim JJ (2012) GPR105 ablation prevents inflammation and improves insulin sensitivity in mice with diet-induced obesity. J Immunol 189(4):1992–1999. doi:jimmunol.1103207[pii].10.4049/jimmunol.1103207
Oh DY, Talukdar S, Bae EJ, Imamura T, Morinaga H, Fan W, Li P, Lu WJ, Watkins SM, Olefsky JM (2010) GPR120 is an omega-3 fatty acid receptor mediating potent anti-inflammatory and insulin-sensitizing effects. Cell 142(5):687–698. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.07.041
Osborn O, da Oh Y, McNelis J, Sanchez-Alavez M, Talukdar S, Lu M, Li P, Thiede L, Morinaga H, Kim JJ, Heinrichsdorff J, Nalbandian S, Ofrecio JM, Scadeng M, Schenk S, Hadcock J, Bartfai T, Olefsky JM (2012) G protein-coupled receptor 21 deletion improves insulin sensitivity in diet-induced obese mice. J Clin Invest 122(7):2444–2453. doi:10.1172/JCI61953. 61953[pii]
Gardner J, Wu S, Ling L, Danao J, Li Y, Yeh WC, Tian H, Baribault H (2012) G-protein-coupled receptor GPR21 knockout mice display improved glucose tolerance and increased insulin response. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 418(1):1–5. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.11.117
Ichimura A, Hirasawa A, Poulain-Godefroy O, Bonnefond A, Hara T, Yengo L, Kimura I, Leloire A, Liu N, Iida K, Choquet H, Besnard P, Lecoeur C, Vivequin S, Ayukawa K, Takeuchi M, Ozawa K, Tauber M, Maffeis C, Morandi A, Buzzetti R, Elliott P, Pouta A, Jarvelin MR, Korner A, Kiess W, Pigeyre M, Caiazzo R, Van Hul W, Van Gaal L, Horber F, Balkau B, Levy-Marchal C, Rouskas K, Kouvatsi A, Hebebrand J, Hinney A, Scherag A, Pattou F, Meyre D, Koshimizu TA, Wolowczuk I, Tsujimoto G, Froguel P (2012) Dysfunction of lipid sensor GPR120 leads to obesity in both mouse and human. Nature 483(7389):350–354. doi:10.1038/nature10798
Elgazar-Carmon V, Rudich A, Hadad N, Levy R (2008) Neutrophils transiently infiltrate intra-abdominal fat early in the course of high-fat feeding. J Lipid Res 49(9):1894–1903. doi:M800132-JLR200[pii].10.1194/jlr.M800132-JLR200
Talukdar S, Oh DY, Bandyopadhyay G, Li D, Xu J, McNelis J, Lu M, Li P, Yan Q, Zhu Y, Ofrecio J, Lin M, Brenner MB, Olefsky JM (2012) Neutrophils mediate insulin resistance in mice fed a high-fat diet through secreted elastase. Nat Med 18(9):1407–1412. doi:10.1038/nm.2885. nm.2885[pii]
Pham CT (2006) Neutrophil serine proteases: specific regulators of inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 6(7):541–550. doi:nri1841[pii].10.1038/nri1841
Houghton AM (2010) The paradox of tumor-associated neutrophils: fueling tumor growth with cytotoxic substances. Cell Cycle 9(9):1732–1737. doi:11297[pii]
Houghton AM, Rzymkiewicz DM, Ji H, Gregory AD, Egea EE, Metz HE, Stolz DB, Land SR, Marconcini LA, Kliment CR, Jenkins KM, Beaulieu KA, Mouded M, Frank SJ, Wong KK, Shapiro SD (2010) Neutrophil elastase-mediated degradation of IRS-1 accelerates lung tumor growth. Nat Med 16(2):219–223. doi:nm.2084[pii].10.1038/nm.2084
Feuerer M, Herrero L, Cipolletta D, Naaz A, Wong J, Nayer A, Lee J, Goldfine AB, Benoist C, Shoelson S, Mathis D (2009) Lean, but not obese, fat is enriched for a unique population of regulatory T cells that affect metabolic parameters. Nat Med 15(8):930–939. doi:nm.2002[pii].10.1038/nm.2002
Winer S, Chan Y, Paltser G, Truong D, Tsui H, Bahrami J, Dorfman R, Wang Y, Zielenski J, Mastronardi F, Maezawa Y, Drucker DJ, Engleman E, Winer D, Dosch HM (2009) Normalization of obesity-associated insulin resistance through immunotherapy. Nat Med 15(8):921–929. doi:nm.2001[pii].10.1038/nm.2001
Cipolletta D, Feuerer M, Li A, Kamei N, Lee J, Shoelson SE, Benoist C, Mathis D (2012) PPAR-gamma is a major driver of the accumulation and phenotype of adipose tissue Treg cells. Nature 486(7404):549–553. doi:nature11132[pii].10.1038/nature11132
Strissel KJ, DeFuria J, Shaul ME, Bennett G, Greenberg AS, Obin MS (2010) T-cell recruitment and Th1 polarization in adipose tissue during diet-induced obesity in C57BL/6 mice. Obesity (Silver Spring) 18(10):1918–1925. doi:oby20101[pii].10.1038/oby.2010.1
Nishimura S, Manabe I, Nagasaki M, Eto K, Yamashita H, Ohsugi M, Otsu M, Hara K, Ueki K, Sugiura S, Yoshimura K, Kadowaki T, Nagai R (2009) CD8+ effector T cells contribute to macrophage recruitment and adipose tissue inflammation in obesity. Nat Med 15(8):914–920. doi:10.1038/nm.1964
Duffaut C, Galitzky J, Lafontan M, Bouloumie A (2009) Unexpected trafficking of immune cells within the adipose tissue during the onset of obesity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 384(4):482–485. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.05.002
Winer DA, Winer S, Shen L, Wadia PP, Yantha J, Paltser G, Tsui H, Wu P, Davidson MG, Alonso MN, Leong HX, Glassford A, Caimol M, Kenkel JA, Tedder TF, McLaughlin T, Miklos DB, Dosch HM, Engleman EG (2011) B cells promote insulin resistance through modulation of T cells and production of pathogenic IgG antibodies. Nat Med 17(5):610–617. doi:10.1038/nm.2353
Falorni A, Gambelunghe G, Forini F, Kassi G, Cosentino A, Candeloro P, Bolli GB, Brunetti P, Calcinaro F (2000) Autoantibody recognition of COOH-terminal epitopes of GAD65 marks the risk for insulin requirement in adult-onset diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85(1):309–316
Gomez-Tourino I, Camina-Darriba F, Otero-Romero I, Rodriguez MA, Hernandez-Fernandez A, Gonzalez-Fernandez A, Pena-Gonzalez E, Rodriguez J, Rodriguez-Segade S, Varela-Calvino R (2010) Autoantibodies to glial fibrillary acid protein and S100beta in diabetic patients. Diabet Med 27(2):246–248. doi:10.1111/j.1464-5491.2009.02911.x
Kotas ME, Lee HY, Gillum MP, Annicelli C, Guigni BA, Shulman GI, Medzhitov R (2011) Impact of CD1d deficiency on metabolism. PLoS One 6(9):e25478. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0025478.PONE-D-11-12529[pii]
Mantell BS, Stefanovic-Racic M, Yang X, Dedousis N, Sipula IJ, O’Doherty RM (2011) Mice lacking NKT cells but with a complete complement of CD8+ T-cells are not protected against the metabolic abnormalities of diet-induced obesity. PLoS One 6(6):e19831. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0019831.PONE-D-10-04900[pii]
Ji Y, Sun S, Xu A, Bhargava P, Yang L, Lam KS, Gao B, Lee CH, Kersten S, Qi L (2012) Activation of natural killer T cells promotes M2 macrophage polarization in adipose tissue and improves systemic glucose tolerance via interleukin-4 (IL-4)/STAT6 protein signaling axis in obesity. J Biol Chem 287(17):13561–13571. doi:M112.350066[pii].10.1074/jbc.M112.350066
Schipper HS, Rakhshandehroo M, van de Graaf SF, Venken K, Koppen A, Stienstra R, Prop S, Meerding J, Hamers N, Besra G, Boon L, Nieuwenhuis EE, Elewaut D, Prakken B, Kersten S, Boes M, Kalkhoven E (2012) Natural killer T cells in adipose tissue prevent insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 122(9):3343–3354. doi:10.1172/JCI62739.62739[pii]
Wu D, Molofsky AB, Liang HE, Ricardo-Gonzalez RR, Jouihan HA, Bando JK, Chawla A, Locksley RM (2011) Eosinophils sustain adipose alternatively activated macrophages associated with glucose homeostasis. Science 332(6026):243–247. doi:science.1201475[pii].10.1126/science.1201475
Zhang J, Shi GP (2012) Mast cells and metabolic syndrome. Biochim Biophys Acta 1822(1):14–20. doi:S0925-4439(10)00290-5[pii].10.1016/j.bbadis.2010.12.012
Liu J, Divoux A, Sun J, Zhang J, Clement K, Glickman JN, Sukhova GK, Wolters PJ, Du J, Gorgun CZ, Doria A, Libby P, Blumberg RS, Kahn BB, Hotamisligil GS, Shi GP (2009) Genetic deficiency and pharmacological stabilization of mast cells reduce diet-induced obesity and diabetes in mice. Nat Med 15(8):940–945. doi:nm.1994[pii].10.1038/nm.1994
Altintas MM, Azad A, Nayer B, Contreras G, Zaias J, Faul C, Reiser J, Nayer A (2011) Mast cells, macrophages, and crown-like structures distinguish subcutaneous from visceral fat in mice. J Lipid Res 52(3):480–488. doi:jlr.M011338[pii].10.1194/jlr.M011338
Divoux A, Moutel S, Poitou C, Lacasa D, Veyrie N, Aissat A, Arock M, Guerre-Millo M, Clement K (2012) Mast cells in human adipose tissue: link with morbid obesity, inflammatory status, and diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97(9):E1677–E1685. doi:10.1210/jc.2012-1532
Gao Z, Hwang D, Bataille F, Lefevre M, York D, Quon MJ, Ye J (2002) Serine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate 1 by inhibitor kappa B kinase complex. J Biol Chem 277(50):48115–48121. doi:10.1074/jbc.M209459200.M209459200[pii]
Gao Z, Zuberi A, Quon MJ, Dong Z, Ye J (2003) Aspirin inhibits serine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate 1 in tumor necrosis factor-treated cells through targeting multiple serine kinases. J Biol Chem 278(27):24944–24950. doi:10.1074/jbc.M300423200.M300423200[pii]
Ozes ON, Akca H, Mayo LD, Gustin JA, Maehama T, Dixon JE, Donner DB (2001) A phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/mTOR pathway mediates and PTEN antagonizes tumor necrosis factor inhibition of insulin signaling through insulin receptor substrate-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98(8):4640–4645. doi:10.1073/pnas.051042298.051042298[pii]
Nakamura T, Furuhashi M, Li P, Cao H, Tuncman G, Sonenberg N, Gorgun CZ, Hotamisligil GS (2010) Double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase links pathogen sensing with stress and metabolic homeostasis. Cell 140(3):338–348. doi:S0092-8674(10)00002-4[pii].10.1016/j.cell.2010.01.001
Tack CJ, Stienstra R, Joosten LA, Netea MG (2012) Inflammation links excess fat to insulin resistance: the role of the interleukin-1 family. Immunol Rev 249(1):239–252. doi:10.1111/j.1600-065X.2012.01145.x
Pradhan AD, Manson JE, Rifai N, Buring JE, Ridker PM (2001) C-reactive protein, interleukin 6, and risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus. JAMA 286(3):327–334
McGillicuddy FC, Harford KA, Reynolds CM, Oliver E, Claessens M, Mills KH, Roche HM (2011) Lack of interleukin-1 receptor I (IL-1RI) protects mice from high-fat diet-induced adipose tissue inflammation coincident with improved glucose homeostasis. Diabetes 60(6):1688–1698. doi:10.2337/db10-1278
Park E, Wong V, Guan X, Oprescu AI, Giacca A (2007) Salicylate prevents hepatic insulin resistance caused by short-term elevation of free fatty acids in vivo. J Endocrinol 195(2):323–331. doi:195/2/323[pii].10.1677/JOE-07-0005
Lee JY, Sohn KH, Rhee SH, Hwang D (2001) Saturated fatty acids, but not unsaturated fatty acids, induce the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 mediated through toll-like receptor 4. J Biol Chem 276(20):16683–16689. doi:10.1074/jbc.M011695200.M011695200[pii]
Senn JJ (2006) Toll-like receptor-2 is essential for the development of palmitate-induced insulin resistance in myotubes. J Biol Chem 281(37):26865–26875. doi:M513304200[pii].10.1074/jbc.M513304200
Shi H, Kokoeva MV, Inouye K, Tzameli I, Yin H, Flier JS (2006) TLR4 links innate immunity and fatty acid-induced insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 116(11):3015–3025. doi:10.1172/JCI28898
Saberi M, Woods NB, de Luca C, Schenk S, Lu JC, Bandyopadhyay G, Verma IM, Olefsky JM (2009) Hematopoietic cell-specific deletion of toll-like receptor 4 ameliorates hepatic and adipose tissue insulin resistance in high-fat-fed mice. Cell Metab 10(5):419–429. doi:S1550-4131(09)00294-0[pii].10.1016/j.cmet.2009.09.006
Himes RW, Smith CW (2010) Tlr2 is critical for diet-induced metabolic syndrome in a murine model. FASEB J 24(3):731–739. doi:fj.09-141929[pii].10.1096/fj.09-141929
Ehses JA, Meier DT, Wueest S, Rytka J, Boller S, Wielinga PY, Schraenen A, Lemaire K, Debray S, Van Lommel L, Pospisilik JA, Tschopp O, Schultze SM, Malipiero U, Esterbauer H, Ellingsgaard H, Rutti S, Schuit FC, Lutz TA, Boni-Schnetzler M, Konrad D, Donath MY (2010) Toll-like receptor 2-deficient mice are protected from insulin resistance and beta cell dysfunction induced by a high-fat diet. Diabetologia 53(8):1795–1806. doi:10.1007/s00125-010-1747-3
Schaeffler A, Gross P, Buettner R, Bollheimer C, Buechler C, Neumeier M, Kopp A, Schoelmerich J, Falk W (2009) Fatty acid-induced induction of toll-like receptor-4/nuclear factor-kappaB pathway in adipocytes links nutritional signalling with innate immunity. Immunology 126(2):233–245. doi:IMM2892[pii].10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.02892.x
Pal D, Dasgupta S, Kundu R, Maitra S, Das G, Mukhopadhyay S, Ray S, Majumdar SS, Bhattacharya S (2012) Fetuin-A acts as an endogenous ligand of TLR4 to promote lipid-induced insulin resistance. Nat Med 18:1279–1285. doi:10.1038/nm.2851
Mathews ST, Rakhade S, Zhou X, Parker GC, Coscina DV, Grunberger G (2006) Fetuin-null mice are protected against obesity and insulin resistance associated with aging. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 350(2):437–443. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.09.071
Heinrichsdorff J, Olefsky JM (2012) Fetuin-A: the missing link in lipid-induced inflammation. Nat Med 18(8):1182–1183. doi:10.1038/nm.2869
Wong SW, Kwon MJ, Choi AM, Kim HP, Nakahira K, Hwang DH (2009) Fatty acids modulate toll-like receptor 4 activation through regulation of receptor dimerization and recruitment into lipid rafts in a reactive oxygen species-dependent manner. J Biol Chem 284(40):27384–27392. doi:M109.044065[pii].10.1074/jbc.M109.044065
Holzer RG, Park EJ, Li N, Tran H, Chen M, Choi C, Solinas G, Karin M (2011) Saturated fatty acids induce c-Src clustering within membrane subdomains, leading to JNK activation. Cell 147(1):173–184. doi:S0092-8674(11)01004-X[pii].10.1016/j.cell.2011.08.034
Wen H, Gris D, Lei Y, Jha S, Zhang L, Huang MT, Brickey WJ, Ting JP (2011) Fatty acid-induced NLRP3-ASC inflammasome activation interferes with insulin signaling. Nat Immunol 12(5):408–415. doi:10.1038/ni.2022
Holland WL, Bikman BT, Wang LP, Yuguang G, Sargent KM, Bulchand S, Knotts TA, Shui G, Clegg DJ, Wenk MR, Pagliassotti MJ, Scherer PE, Summers SA (2011) Lipid-induced insulin resistance mediated by the proinflammatory receptor TLR4 requires saturated fatty acid-induced ceramide biosynthesis in mice. J Clin Invest 121(5):1858–1870. doi:10.1172/JCI43378
Stratford S, Hoehn KL, Liu F, Summers SA (2004) Regulation of insulin action by ceramide: dual mechanisms linking ceramide accumulation to the inhibition of Akt/protein kinase B. J Biol Chem 279(35):36608–36615. doi:10.1074/jbc.M406499200
Ussher JR, Koves TR, Cadete VJ, Zhang L, Jaswal JS, Swyrd SJ, Lopaschuk DG, Proctor SD, Keung W, Muoio DM, Lopaschuk GD (2010) Inhibition of de novo ceramide synthesis reverses diet-induced insulin resistance and enhances whole-body oxygen consumption. Diabetes 59(10):2453–2464. doi:10.2337/db09-1293
Frangioudakis G, Garrard J, Raddatz K, Nadler JL, Mitchell TW, Schmitz-Peiffer C (2010) Saturated- and n-6 polyunsaturated-fat diets each induce ceramide accumulation in mouse skeletal muscle: reversal and improvement of glucose tolerance by lipid metabolism inhibitors. Endocrinology 151(9):4187–4196. doi:10.1210/en.2010-0250
Dbaibo GS, El-Assaad W, Krikorian A, Liu B, Diab K, Idriss NZ, El-Sabban M, Driscoll TA, Perry DK, Hannun YA (2001) Ceramide generation by two distinct pathways in tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced cell death. FEBS Lett 503(1):7–12
Chavez JA, Summers SA (2012) A ceramide-centric view of insulin resistance. Cell Metab 15(5):585–594. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2012.04.002
Hotamisligil GS (2010) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the inflammatory basis of metabolic disease. Cell 140(6):900–917. doi:S0092-8674(10)00187-X[pii].10.1016/j.cell.2010.02.034
Engin F, Hotamisligil GS (2010) Restoring endoplasmic reticulum function by chemical chaperones: an emerging therapeutic approach for metabolic diseases. Diabetes Obes Metab 12(suppl 2):108–115. doi:10.1111/j.1463-1326.2010.01282.x
Hu P, Han Z, Couvillon AD, Kaufman RJ, Exton JH (2006) Autocrine tumor necrosis factor alpha links endoplasmic reticulum stress to the membrane death receptor pathway through IRE1alpha-mediated NF-kappaB activation and down-regulation of TRAF2 expression. Mol Cell Biol 26(8):3071–3084. doi:26/8/3071[pii].10.1128/MCB.26.8.3071-3084.2006
Urano F, Wang X, Bertolotti A, Zhang Y, Chung P, Harding HP, Ron D (2000) Coupling of stress in the ER to activation of JNK protein kinases by transmembrane protein kinase IRE1. Science 287(5453):664–666. doi:8218[pii]
Lee AH, Scapa EF, Cohen DE, Glimcher LH (2008) Regulation of hepatic lipogenesis by the transcription factor XBP1. Science 320(5882):1492–1496. doi:10.1126/science.1158042
Yamamoto K, Takahara K, Oyadomari S, Okada T, Sato T, Harada A, Mori K (2010) Induction of liver steatosis and lipid droplet formation in ATF6alpha-knockout mice burdened with pharmacological endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol Biol Cell 21(17):2975–2986. doi:10.1091/mbc.E09-02-0133
Zhang K, Wang S, Malhotra J, Hassler JR, Back SH, Wang G, Chang L, Xu W, Miao H, Leonardi R, Chen YE, Jackowski S, Kaufman RJ (2011) The unfolded protein response transducer IRE1alpha prevents ER stress-induced hepatic steatosis. EMBO J 30(7):1357–1375. doi:10.1038/emboj.2011.52
Ni M, Lee AS (2007) ER chaperones in mammalian development and human diseases. FEBS Lett 581(19):3641–3651. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2007.04.045
Ozcan U, Yilmaz E, Ozcan L, Furuhashi M, Vaillancourt E, Smith RO, Gorgun CZ, Hotamisligil GS (2006) Chemical chaperones reduce ER stress and restore glucose homeostasis in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes. Science 313(5790):1137–1140. doi:10.1126/science.1128294
Kammoun HL, Chabanon H, Hainault I, Luquet S, Magnan C, Koike T, Ferre P, Foufelle F (2009) GRP78 expression inhibits insulin and ER stress-induced SREBP-1c activation and reduces hepatic steatosis in mice. J Clin Invest 119(5):1201–1215. doi:10.1172/JCI37007
Ozcan U, Cao Q, Yilmaz E, Lee AH, Iwakoshi NN, Ozdelen E, Tuncman G, Gorgun C, Glimcher LH, Hotamisligil GS (2004) Endoplasmic reticulum stress links obesity, insulin action, and type 2 diabetes. Science 306(5695):457–461. doi:306/5695/457[pii].10.1126/science.1103160
Ye J, Gao Z, Yin J, He Q (2007) Hypoxia is a potential risk factor for chronic inflammation and adiponectin reduction in adipose tissue of ob/ob and dietary obese mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 293(4):E1118–E1128. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00435.2007
Pasarica M, Sereda OR, Redman LM, Albarado DC, Hymel DT, Roan LE, Rood JC, Burk DH, Smith SR (2009) Reduced adipose tissue oxygenation in human obesity: evidence for rarefaction, macrophage chemotaxis, and inflammation without an angiogenic response. Diabetes 58(3):718–725. doi:10.2337/db08-1098
Krishnan J, Danzer C, Simka T, Ukropec J, Walter KM, Kumpf S, Mirtschink P, Ukropcova B, Gasperikova D, Pedrazzini T, Krek W (2012) Dietary obesity-associated Hif1alpha activation in adipocytes restricts fatty acid oxidation and energy expenditure via suppression of the Sirt2-NAD+ system. Genes Dev 26(3):259–270. doi:10.1101/gad.180406.111
Goldfine AB, Fonseca V, Jablonski KA, Pyle L, Staten MA, Shoelson SE (2010) The effects of salsalate on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med 152(6):346–357. doi:10.1059/0003-4819-152-6-201003160-00004
Rumore MM, Kim KS (2010) Potential role of salicylates in type 2 diabetes. Ann Pharmacother 44(7–8):1207–1221. doi:10.1345/aph.1M483
Uysal KT, Wiesbrock SM, Marino MW, Hotamisligil GS (1997) Protection from obesity-induced insulin resistance in mice lacking TNF-alpha function. Nature 389(6651):610–614. doi:10.1038/39335
Grunfeld C, Feingold KR (1991) The metabolic effects of tumor necrosis factor and other cytokines. Biotherapy 3(2):143–158
Hotamisligil GS, Murray DL, Choy LN, Spiegelman BM (1994) Tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibits signaling from the insulin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91(11):4854–4858
Rosenvinge A, Krogh-Madsen R, Baslund B, Pedersen BK (2007) Insulin resistance in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: effect of anti-TNFalpha therapy. Scand J Rheumatol 36(2):91–96. doi:10.1080/03009740601179605
Stanley TL, Zanni MV, Johnsen S, Rasheed S, Makimura H, Lee H, Khor VK, Ahima RS, Grinspoon SK (2011) TNF-alpha antagonism with etanercept decreases glucose and increases the proportion of high molecular weight adiponectin in obese subjects with features of the metabolic syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96(1):E146–E150. doi:10.1210/jc.2010-1170
Gonzalez-Gay MA, Gonzalez-Juanatey C, Vazquez-Rodriguez TR, Miranda-Filloy JA, Llorca J (2010) Insulin resistance in rheumatoid arthritis: the impact of the anti-TNF-alpha therapy. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1193:153–159. doi:NYAS5287[pii].10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.05287.x
Kiortsis DN, Mavridis AK, Vasakos S, Nikas SN, Drosos AA (2005) Effects of infliximab treatment on insulin resistance in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 64(5):765–766. doi:10.1136/ard.2004.026534.ard.2004.026534[pii]
Yazdani-Biuki B, Stelzl H, Brezinschek HP, Hermann J, Mueller T, Krippl P, Graninger W, Wascher TC (2004) Improvement of insulin sensitivity in insulin resistant subjects during prolonged treatment with the anti-TNF-alpha antibody infliximab. Eur J Clin Invest 34(9):641–642. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2362.2004.01390.x
Solomon DH, Massarotti E, Garg R, Liu J, Canning C, Schneeweiss S (2011) Association between disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and diabetes risk in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis. JAMA 305(24):2525–2531. doi:10.1001/jama.2011.878
Osborn O, Brownell SE, Sanchez-Alavez M, Salomon D, Gram H, Bartfai T (2008) Treatment with an interleukin 1 beta antibody improves glycemic control in diet-induced obesity. Cytokine 44(1):141–148. doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2008.07.004
Larsen CM, Faulenbach M, Vaag A, Volund A, Ehses JA, Seifert B, Mandrup-Poulsen T, Donath MY (2007) Interleukin-1-receptor antagonist in type 2 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 356(15):1517–1526. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa065213
Donath MY, Shoelson SE (2011) Type 2 diabetes as an inflammatory disease. Nat Rev Immunol 11(2):98–107. doi:10.1038/nri2925
Lehmann JM, Moore LB, Smith-Oliver TA, Wilkison WO, Willson TM, Kliewer SA (1995) An antidiabetic thiazolidinedione is a high affinity ligand for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR gamma). J Biol Chem 270(22):12953–12956
Sugii S, Olson P, Sears DD, Saberi M, Atkins AR, Barish GD, Hong SH, Castro GL, Yin YQ, Nelson MC, Hsiao G, Greaves DR, Downes M, Yu RT, Olefsky JM, Evans RM (2009) PPARgamma activation in adipocytes is sufficient for systemic insulin sensitization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(52):22504–22509. doi:0912487106[pii].10.1073/pnas.0912487106
Hevener AL, Olefsky JM, Reichart D, Nguyen MT, Bandyopadyhay G, Leung HY, Watt MJ, Benner C, Febbraio MA, Nguyen AK, Folian B, Subramaniam S, Gonzalez FJ, Glass CK, Ricote M (2007) Macrophage PPAR gamma is required for normal skeletal muscle and hepatic insulin sensitivity and full antidiabetic effects of thiazolidinediones. J Clin Invest 117(6):1658–1669. doi:10.1172/JCI31561
Hevener AL, He W, Barak Y, Le J, Bandyopadhyay G, Olson P, Wilkes J, Evans RM, Olefsky J (2003) Muscle-specific Pparg deletion causes insulin resistance. Nat Med 9(12):1491–1497. doi:10.1038/nm956.nm956[pii]
Ryan KK, Li B, Grayson BE, Matter EK, Woods SC, Seeley RJ (2011) A role for central nervous system PPAR-gamma in the regulation of energy balance. Nat Med 17(5):623–626. doi:nm.2349[pii].10.1038/nm.2349
Lu M, Sarruf DA, Talukdar S, Sharma S, Li P, Bandyopadhyay G, Nalbandian S, Fan W, Gayen JR, Mahata SK, Webster NJ, Schwartz MW, Olefsky JM (2011) Brain PPAR-gamma promotes obesity and is required for the insulin-sensitizing effect of thiazolidinediones. Nat Med 17(5):618–622. doi:nm.2332[pii].10.1038/nm.2332
Straus DS, Glass CK (2007) Anti-inflammatory actions of PPAR ligands: new insights on cellular and molecular mechanisms. Trends Immunol 28(12):551–558. doi:10.1016/j.it.2007.09.003
Cariou B, Zair Y, Staels B, Bruckert E (2011) Effects of the new dual PPAR alpha/delta agonist GFT505 on lipid and glucose homeostasis in abdominally obese patients with combined dyslipidemia or impaired glucose metabolism. Diabetes Care 34(9):2008–2014. doi:10.2337/dc11-0093
Calder PC (2006) n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, inflammation, and inflammatory diseases. Am J Clin Nutr 83(6 suppl):1505S–1519S
Mozaffarian D, Wu JH (2012) (n-3) fatty acids and cardiovascular health: are effects of EPA and DHA shared or complementary? J Nutr 142(3):614S–625S. doi:10.3945/jn.111.149633
Renier G, Skamene E, DeSanctis J, Radzioch D (1993) Dietary n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids prevent the development of atherosclerotic lesions in mice. Modulation of macrophage secretory activities. Arterioscler Thromb 13(10):1515–1524
Meydani SN, Endres S, Woods MM, Goldin BR, Soo C, Morrill-Labrode A, Dinarello CA, Gorbach SL (1991) Oral (n-3) fatty acid supplementation suppresses cytokine production and lymphocyte proliferation: comparison between young and older women. J Nutr 121(4):547–555
Caughey GE, Mantzioris E, Gibson RA, Cleland LG, James MJ (1996) The effect on human tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1 beta production of diets enriched in n-3 fatty acids from vegetable oil or fish oil. Am J Clin Nutr 63(1):116–122
Ben-Neriah Y, Karin M (2011) Inflammation meets cancer, with NF-kappaB as the matchmaker. Nat Immunol 12(8):715–723. doi:10.1038/ni.2060.ni.2060[pii]
Seki E, Brenner DA, Karin M (2012) A liver full of JNK: signaling in regulation of cell function and disease pathogenesis, and clinical approaches. Gastroenterology 143(2):307–320. doi:S0016-5085(12)00820-7[pii].10.1053/j.gastro.2012.06.004
Coussens LM, Werb Z (2002) Inflammation and cancer. Nature 420(6917):860–867
Gallagher EJ, LeRoith D (2011) Minireview: IGF, insulin, and cancer. Endocrinology 152(7):2546–2551. doi:10.1210/en.2011-0231
Aaltonen KJ, Virkki LM, Malmivaara A, Konttinen YT, Nordstrom DC, Blom M (2012) Systematic review and meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of existing TNF blocking agents in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS One 7(1):e30275. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0030275
van Dartel SA, Fransen J, Kievit W, Flendrie M, den Broeder AA, Visser H, Hartkamp A, van de Laar MA, van Riel PL (2012) Difference in the risk of serious infections in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with adalimumab, infliximab and etanercept: results from the Dutch Rheumatoid Arthritis Monitoring (DREAM) registry. Ann Rheum Dis Published online first: 11 August 2012. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-201338
Dreyer L, Mellemkjaer L, Andersen AR, Bennett P, Poulsen UE, Juulsgaard Ellingsen T, Hansen TH, Jensen DV, Linde L, Lindegaard HM, Loft AG, Nordin H, Omerovic E, Rasmussen C, Schlemmer A, Tarp U, Hetland ML (2013) Incidences of overall and site specific cancers in TNFalpha inhibitor treated patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other arthritides—a follow-up study from the DANBIO Registry. Ann Rheum Dis 72(1):79–82. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-201969
Lee RK, Hittel DS, Nyamandi VZ, Kang L, Soh J, Sensen CW, Shearer J (2012) Unconventional microarray design reveals the response to obesity is largely tissue specific: analysis of common and divergent responses to diet-induced obesity in insulin-sensitive tissues. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 37(2):257–268. doi:10.1139/h11-159
Chen G, Bentley A, Adeyemo A, Shriner D, Zhou J, Doumatey A, Huang H, Ramos E, Erdos M, Gerry N, Herbert A, Christman M, Rotimi C (2012) Genome-wide association study identifies novel loci association with fasting insulin and insulin resistance in African Americans. Hum Mol Genet 21(20):4530–4536. doi:10.1093/hmg/dds282
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by NIH grant U54CA155435 and DOD grant BC102147.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Ellies, L.G., Johnson, A., Olefsky, J.M. (2013). Obesity, Inflammation, and Insulin Resistance. In: Dannenberg, A., Berger, N. (eds) Obesity, Inflammation and Cancer. Energy Balance and Cancer, vol 7. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-6819-6_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-6819-6_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4614-6818-9
Online ISBN: 978-1-4614-6819-6
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)