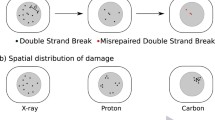
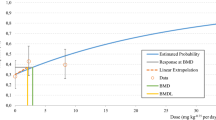
Abstract
The outline of a quantitative model is presented which can be used to derive the pathway from radiation-induced molecular damage, the DNA double strand break, to cellular effects such as cell killing, chromosomal aberrations and mutations and on to radiation-induced cancer. Evidence is provided to support the links in the chain which relate the different cellular end-points to each other and to cancer. The influence of differing dose rates and types of radiation on dose effect relationships are discussed. The extension to radiation induced cancer is made using a two mutation multi-step model for carcinogenesis and evidence is provided to support the assumption that radiation induced cancer arises from a somatic mutation. The dose response for radiation induced cancer is presented and various implications for radiation risks are outlined. The model is also extended to a consideration of deterministic effects by assuming that these effects arise as a result of multi-cell killing at high acute doses. The implications of the model for medical diagnostic radiology are discussed.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Académie des Sciences (1997) Problems associated with the effects of low doses of ionising radiations. Académie des Sciences, Rapport N° 38 (Technique and Documentation, Paris)
Albertini RJ, Clark LS, Nicklas JA et al (1997) Radiation quality affects the efficiency of induction and the molecular spectrum of HPRT mutations in human T cells. Radiat Res 148(Suppl):S76–S86
Barendsen GW (1964) Impairment of the proliferative capacity of human cells in culture by α-particles with different linear energy transfer. Int J Radiat Biol 8:453–466
Beachy PA, Karhadkar SS, Berman DM (2004) Tissue repair and stem cell renewal in carcinogenesis. Nature 432:324–331
Becker K (1997) Threshold or no threshold, that is the question. Radiat Prot Dosim 71:3–5
Benbow RM, Gaudette MF, Hines PJ et al (1985) Initiation of DNA replication in eukaryotes. In: Boynton AL, Leffert HL (eds) Control of Animal Cell Proliferation Vol 1. Academic Press, New York, pp 449–483
Bhambhani R, Kuspira J, Giblak RE (1973) A comparison of cell survival and chromosomal damage using CHO cells synchronised with and without colcemid. Can J Genet Cytol 15:605–618
Bithell JF, Stiller CA (1988) A new calculation of the carcinogenic risk of obstetric X-raying. Stat Med 7:857–864
Bond VP, Wielopolski L, Shani G (1996) Current misinterpretations of the linear no-threshold hypothesis. Health Phys 70:877–882
Brenner DJ, Ward JF (1992) Constraints on energy deposition and target size of multiply damaged sites associated with DNA double-strand breaks. Int J Radiat Biol 61:737–748
Brenner DJ, Doll R, Goodhead DT et al (2003) Cancer risks attributable to low doses of ionizing radiation: Assessing what we really know. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100:13761–13766
Buls N, de Mey J (2007) Dose reduction in CT fluotoscopy. In: Tack D, Genevois PA (eds) Radiation Dose from Adult and Pediatric Multidetector Computed Tomography. Diagnostic Imaging. Medical Radiology. Springer, Berlin, pp 195–222
Calabrese EJ (2002) Hormesis: changing view of the dose-response, a personal account of the history and current status. Mutat Res 511:181–189
Cardis E, Vrijheid M, Blettner M et al (2005) Risk of cancer after low doses of ionising radiation: retrospective cohort study in 15 countries. Br Med J 331:77–83
Chadwick KH, Leenhouts HP (1973) A molecular theory of cell survival. Phys Med Biol 18:78–87
Chadwick KH, Leenhouts HP (1975) The effect of an asynchronous population of cells on the initial slope of dose–effect curves. In: Alper T (ed) Cell survival after low doses of radiation: Theoretical and clinical implications. The Institute of Physics and John Wiley and Sons, London, pp 57–63
Chadwick KH, Leenhouts HP (1978) The rejoining of DNA double-strand breaks and a model for the formation of chromosomal rearrangements. Int J Radiat Biol 33:517–529
Chadwick KH, Leenhouts HP (1981) The molecular theory of radiation biology. Springer, Berlin
Chadwick KH, Leenhouts HP (1983) A quantitative analysis of UV-induced cell killing. Phys Med Biol 28:1369–1383
Chadwick KH, Leenhouts HP (1994) DNA double strand breaks from two single strand breaks and cell cycle radiation sensitivity. Radiat Prot Dosim 52:363–366
Chadwick KH, Leenhouts HP (2011) Radiation induced cancer arises from a somatic mutation. J Radiol Prot 31:41–48
Chadwick KH, Leenhouts HP, Brugmans MJP (2003) A contribution to the linear no-threshold discussion. J Radiol Prot 23:53–78
Chapman JD, Gillespie CJ, Reuvers AP et al (1975) The inactivation of Chinese hamster cells by X-rays: the effects of chemical modifiers on single- and double-events. Radiat Res 64:365–375
Clarke R (1998) Conflicting scientific views on the health risks of low-level ionising radiation. J Radiol Prot 18:159–160
Clarke R (1999) Control of low-level radiation exposure: time for a change? J Radiol Prot 19:107–115
Cornforth MN (1990) Testing the notion of the one-hit exchange. Radiat Res 121:21–27
Darroudi F, Natarajan AT, Savage JRK et al (2001) Induction of chromosomal aberrations by low and high LET radiations: mechanisms and spectra. In: Proceedings European Radiation Research, Dresden 2001 (ISBN 3-00-007790-1)
Dewey WC, Furman SC, Miller HH (1970) Comparison of lethality and chromosomal damage induced by X-rays in synchronised Chinese hamster cell in vitro. Radiat Res 43:561–581
Dewey WC, Stone LE, Miller HH et al (1971a) Radiosensitization with 5-bromodeoxyuridine of Chinese hamster cells irradiated during different phases of the cell cycle. Radiat Res 47:672–688
Dewey WC, Miller HH, Leeper DB (1971b) Chromosomal aberrations and mortality of X-irradiated mammalian cells: emphasis on repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 68:667–671
Dewey WC, Saparetto SA, Betten DA (1978) Hyperthermic radiosensitization of synchronised Chinese hamster cells: relationship between lethality and chromosomal aberrations. Radiat Res 76:48–59
Doll R, Darby S (1991) Leukaemia: some unsolved problems. Brit Inst Radiol Rep 22:1–6
Edwards R (1997) Radiation roulette. New Sci. (11 October), pp 36–40
Essers J, Hendriks RW, Swagemakers SMA et al (1997) Disruption of mouse RAD54 reduces ionizing radiation resistance and homologous recombination. Cell 89:195–204
Franken NA P, Ruurs P, Ludwikow G et al (1999) Correlation between cell reproductive death and chromosome aberrations assessed by FISH for low and high doses of radiation and sensitization by iodo-deoxyuridine in human SW-1573 cells. Int J Radiat Biol 75:293–299
Frankenberg D, Kelnhofer K, Bar K et al (2002) Enhanced neoplastic transformation by mammography X-rays relative to 200 kVp X-rays: indication for a strong dependence on photon energy of the RBEM for various end points. Radiat Res 157:99–105
Friedland W, Jacob P, Paretzke HG et al (1998) Monte Carlo simulation of the production of short DNA fragments by low-linear energy transfer radiation using high-order DNA models. Radiat Res 150:170–182
Friedland W, Jacob P, Paretzke HG et al (1999) Simulation of DNA-fragment distribution after irradiation with photons. Radiat Environ Biophys 38:39–47
Gaudette MF, Benbow RM (1986) Replication forks are under-represented in chromosomal DNA of Xenopus laevis embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:5953–5957
Gillespie CJ, Chapman JD, Reuvers AP et al (1975a) The inactivation of Chinese hamster cells by X-rays: synchronized and exponential cell populations. Radiat Res 64:353–364
Gillespie CJ, Chapman JD, Reuvers AP et al (1975b) Survival of X-irradiated hamster cells: analysis in terms of the Chadwick–Leenhouts model. In: Alper T (ed) Cell survival after low doses of radiation: Theoretical and clinical implications. The Institute of Physics and John Wiley and Sons, London, pp 25–31
Gofman JW, Tamplin AR (1971) The question of safe radiation thresholds for alpha-emitting bone seekers in man. Health Phys 21:47–51
Goodhead DT, Thacker J, Cox R (1979) Effectiveness of 0.3 keV carbon ultrasoft X-rays for the inactivation and mutation of cultured mammalian cells. Int J Radiat Biol 36:101–114
Goodhead DT, Virsik RP, Harder D et al (1980) Ultrasoft X-rays as a tool to investigate radiation-induced dicentric chromosome aberrations. In: Booz J, Ebert HG, Hartfield HD (eds) Proceedings of the seventh symposium on microdosimetry EUR 7147. Harewood Academic Press, London, pp 1275–1285
Griffin CS, Stevens DL, Savage JRK (1996) Ultrasoft 1.5 keV aluminium X-rays are efficient producers of complex chromosome exchange aberrations revealed by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Radiat Res 146:144–150
Griffin CS, Hill MA, Papworth DG et al (1998) Effectiveness of 0.28 keV carbon K ultrasoft X-rays at producing simple and complex chromosome exchanges in human fibroblasts in vitro detected using FISH. Int J Radiat Biol 73:591–598
Hammond EC (1966) Smoking in relation to the death rates of one million men and women. In: Epidemiological study of cancer and other chronic diseases. National Cancer Institute Monograph 19, pp 127—204
Heidenreich WF, Paretzke HG, Jacob P (1997a) No evidence for increased tumor rates below 200 mSv in the atomic bomb survivors data. Radiat Environ Biophys 36:205–207
Heidenreich WF, Paretzke HG, Jacob P (1997b) Reply to the ‘Commentary’ by D. A. Pierce and D. L. Preston. Radiat Environ Biophys 36:211–212
Heyes GJ, Mill AJ (2004) The neoplastic transformation potential of mammography X-rays and atomic bomb radiation. Radiat Res 162:120–127
Heyes GJ, Mill AJ, Charles MW (2006) Enhanced biological effectiveness of low energy X-rays and implications for the UK breast screening programme. Brit J Radiol 79:195–200
Heyes GJ, Mill AJ, Charles MW (2009) Mammography—oncogenicity at low doses. J Radiol Prot 29:A123–A132
ICRP 1991 (1990) Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection. ICRP Publication 60. Annals of the ICRP 21:1–3
ICRP (2003) The evolution of the current system of radiological protection: the justification for new ICRP recommendations (a memorandum from the International Commission on Radiological Protection). J Radiol Prot 23:129–142
Iliakis G (1984) The influence of conditions affecting repair and fixation of potentially lethal damage on the induction of 6-thioguanine resistance after exposure of mammalian cells to X-rays. Mutat Res 126:215–225
Kellerer AM (2000) Risk estimates for radiation-induced cancer—the epidemiological evidence. Radiat Environ Biophys 39:17–24
Kellerer AM, Nekolla EA (2000) The LNT-controversy and the concept of “Controllable Dose”. Health Phys 74:412–418
Kesavan PC, Sugahara T (1992) Perspectives in mechanistic considerations of biological effects of low dose radiations. In: Sugahara T, Sagan L, Aoyama T (eds) Low dose irradiation and biological defence mechanisms. Excerpta Medica International Congress Series 1013. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 439–443
Knudson AG (1971) Mutation and cancer: statistical study of retinoblastoma gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 68:620–623
Knudson AG (1985) Hereditary cancer, oncogenes and antioncogenes. Cancer Res 45:1437–1443
Knudson AG (1991) Overview: genes that predispose to cancer. Mutat Res 247:185–190
Lea DE (1946) Actions of radiations on living cells. University Press, Cambridge
Lea DE, Catcheside DG (1942) The mechanism of induction by radiation of chromosome aberrations in Tradescantia. J Genet 44:216–245
Leenhouts HP (1999) Radon-induced lung cancer in smokers and non-smokers: risk implications using a two mutation carcinogenesis model. Radiat Environ Biophys 38:57–71
Leenhouts HP, Brugmans MJP (2000) An analysis of bone and head sinus cancers in radium dial painters using a two-mutation carcinogenesis model. J Radiol Prot 20:169–188
Leenhouts HP, Brugmans MJP (2001) Calculation of the 1995 lung cancer incidence in the Netherlands and Sweden caused by smoking and radon: risk implications for radon. Radiat Environ Biophys 40:11–21
Leenhouts HP, Chadwick KH (1976) Stopping power and the radiobiological effects of electrons, gamma rays and ions. In: Booz J, Ebert HG, Smith BGR (eds) Fifth Symposium on Microdosimetry. Commission of the European Communities EUR 5452, Luxembourg, pp 289–308
Leenhouts HP, Chadwick KH (1978) An analysis of synergistic sensitization. Br J Cancer 37:198–201
Leenhouts HP, Chadwick KH (1984) A quantitative analysis of the cytotoxic action of chemical mutagens. Mutat Res 129:345–357
Leenhouts HP, Chadwick KH (1989) The molecular basis of stochastic and nonstochastic effects. Health Phys 57(Suppl. 1):343–348
Leenhouts HP, Chadwick KH (1990) The influence of dose rate on the dose–effect relationship. J Radiat Prot 10:95–102
Leenhouts HP, Chadwick KH (1994a) A two-mutation model of radiation carcinogenesis: applications to lung tumours in rodents and implications for risk evaluations. J Radiol Prot 14:115–130
Leenhouts HP, Chadwick KH (1994b) Analysis of radiation induced carcinogenesis using a two stage carcinogenesis model: Implications for dose-effect relationships. Radiat Protect Dosim 52:465–469
Leenhouts HP, Chadwick KH (2011) Dose-effect relationships, epidemiological analysis and the derivation of low dose risk. J Radiol Prot 31:95–105
Leenhouts HP, Brugmans MJP, Chadwick KH (2000) Analysis of thyroid cancer data from the Ukraine after ‘Chernobyl’ using a two-mutation carcinogenesis model. Radiat Environ Biophys 39:89–98
Ljungman M (1991) The influence of chromatin structure on the frequency of radiation-induced DNA breaks: a study using nuclear and nucleoid monolayers. Radiat Res 126:58–64
Ljungman M, Nyberg S, Nygren J et al (1991) DNA-bound proteins contribute much more than soluble intracellular compounds to the intrinsic protection against radiation-induced DNA strand breaks in human cells. Radiat Res 127:171–176
Lloyd DC, Purrott RJ, Dolphin GW et al (1976) Chromosome aberrations induced in human lymphocytes by neutron irradiation. Int J Radiat Biol 29:169–182
Lloyd DC, Edwards AA, Prosser JS et al (1984) The dose response relationship obtained at constant irradiation times for the induction of chromosome aberrations in human lymphocytes by cobalt-60 gamma rays. Radiat Environ Biophys 23:179–189
Lloyd DC, Edwards AA, Leonard A et al (1988) Frequencies of chromosomal aberrations induced in human blood lymphocytes by low doses of X-rays. Int J Radiat Biol 53:49–55
Lloyd DC, Edwards AA, Leonard A et al (1992) Chromosomal aberrations in human lymphocytes induced in vitro by very low doses of X-rays. Int J Radiat Biol 61:335–343
Luckey TD (1997) Low-dose irradiation reduces cancer deaths. Radiat Prot Manag 14 (6): pp 58–64
Ludwików G, Xiao Y, Hoebe RA et al (2002) Induction of chromosome aberrations in unirradiated chromatin after partial irradiation of a cell nucleus. Int J Radiat Biol 78:239–247
Metting NF, Braby LA, Roesch WC et al (1985) Dose-rate evidence for two kinds of radiation damage in stationary-phase mammalian cells. Radiat Res 103:204–212
Mill AJ, Frankenberg D, Bettega D et al (1998) Transformation of C3H 10T1/2 cells by low doses of ionising radiation: a collaborative study by six European laboratories strongly supporting a linear dose -response relationship. J Radiol Prot 18:79–100
Milligan JR, Ng JY-Y, Wu CCL et al (1995) DNA repair by thiols in air shows two radicals make a double-strand break. Radiat Res 143:273–280
Milligan JR, Aguilera JA, Nguyen T-TD et al (2000) DNA strand-break yields after post-irradiation incubation with base excision repair endonucleases implicate hydroxyl radical pairs in double-strand break formation. Int J Radiat Biol 76:1475–1483
Moolgavkar SH, Knudson AG (1981) Mutation and cancer: a model for human carcinogenesis. J Natl Cancer Inst 68:1037–1052
Moolgavkar SH, Venzon D (1979) Two-event models for carcinogenesis. Incidence curves for childhood and adult tumors. Math Biosci 47:55–77
Muirhead CR, Goodill AA, Haylock RGE et al (1999) Occupational radiation exposure and mortality: second analysis of the National Registry for Radiation Workers. J Radiol Prot 19:3–26
Murray D, Prager A, Milas L (1989) Radioprotection of cultured mammalian cells by amniothiols WR-1065 and WR-255591: correlation between protection against DNA double-strand breaks and cell killing after γ-radiation. Radiat Res 120:154–163
Murray D, Prager A, Vanankeren SC (1990) Comparative effect of the thiols dithiothreitol, cysteamine and WR-151326 on survival and on the induction of DNA damage in cultured Chinese hamster ovary cells exposed to γ-radiation. Int J Radiat Biol 58:71–91
NCRP (2001) Evaluation of the linear-nonthreshold dose-response model for ionizing radiation. NCRP Report No. 136. National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements, Washington
Nikjoo H, O’Neill P, Terrisol M et al (1994) Modelling of radiation-induced DNA damage: the early physical and chemical events. Int J Radiat Biol 66:453–457
Nikjoo H, O’Neill P, Terrissol M et al (1999) Quantitative modelling of DNA damage using Monte Carlo track structure method. Radiat Environ Biophys 37:1–8
Nygren J, Ljungman L, Ahnstrom G (1995) Chromatin structure and radiation-induced DNA strand breaks in human cells: soluble scavengers and DNA-bound proteins offer a better protection against single- than double-strand breaks. Int J Radiat Biol 68:11–18
Pierce DA, Preston DL (1997) On 'No evidence for increased tumor rates below 200 mSv in the atomic bomb survivors data'. Radiat Environ Biophys 36:209–210
Pierce DA, Shimuzu Y, Preston DL et al (1996) Studies of the mortality of atomic bomb survivors. Report 12, Part I. Cancer: 1950–1990. Radiat Res 146:1–27
Pohl-Ruhling J, Fischer P, Haas O et al (1983) Effects of low-dose acute X-irradiation on the frequencies of chromosomal aberrations in human peripheral lymphocytes in vitro. Mutat Res 110:71–82
Pohl-Ruling J, Fischer P, Lloyd DC et al (1986) Chromosomal damage induced in human lymphocytes by low doses of D-T neutrons. Mutat Res 173:267–272
Prise KM, Davies S, Michael BD (1987) The relationship between radiation-induced DNA double-strand breaks and cell kill in hamster V79 fibroblasts irradiated with 250-kVp X-rays, 2.3 MeV neutrons or 238Pu α-particles. Int J Radiat Biol 52:893–902
Prise KM, Davies S, Michael BD (1993) Evidence for induction of DNA double-strand breaks at paired radical sites. Radiat Res 134:102–106
Prise KM, Gillies NE, Michael BD (1999) Further evidence for double-strand breaks originating from a paired radical precursor from studies of oxygen fixation processes. Radiat Res 151:635–641
Radford IR (1985) The level of induced DNA double-strand breakage correlates with cell killing after X-irradiation. Int J Radiat Biol 48:45–54
Radford IR (1986) Evidence for a general relationship between the induced level of DNA double-strand breakage and cell killing after X-irradiation of mammalian cells. Int J Radiat Biol 49:611–620
Rao BS, Hopwood LE (1982) Modification of mutation frequency in plateau Chinese hamster ovary cells exposed to gamma radiation during recovery from potentially lethal damage. Int J Radiat Biol 42:501–508
Resnick MA (1976) The repair of double-strand breaks in DNA: a model involving recombination. J Theor Biol 59:97–106
Revell SH (1963) Chromatid aberrations—the general theory. In: Wolff S (ed) Radiation induced chromosome aberrations. Columbia University Press, New York, pp 41–72
Revell SH (1974) The breakage-and-reunion theory and the exchange theory for chromosomal aberrations induced by ionizing radiation: a short history. Adv Radiat Biol 4:367–416
Richold M, Holt PD (1974) The effect of differing neutron energies on mutagenesis in cultured Chinese hamster cells. In: Biological Effects of Neutron Irradiation (IAEA, Vienna) pp 237–244
Rowland RE (1994) Radium in humans: a review of US studies. US Department of Commerce. Technology Administration, National Technical Information Service, Springfield
Sagan L (1992) It’s time to re-think the radiation paradigm. In: Sugahara T, Sagan L, Aoyama T (eds) Low dose irradiation and biological defence mechanisms. Excerpta Medica International Congress Series 1013. Elsevier, Amsterdam pp 3–12
Sax K (1940) X-ray-induced chromosomal aberrations in Tradescantia. Genetics 25:41–68
Shrimpton PC, Hillier MC, Lewis MA et al (2003) Data from computed tomography (CT) examinations in the UK—2003 Review. NRPB—67, National Radiological Protection Board, Chilton
Simpson P, Savage JRK (1996) Dose-response curves for simple and complex chromosome aberrations induced by X-rays and detected using fluorescence in situ hybridization. Int J Radiat Biol 69:429–436
Sinclair WK (1966) The shape of radiation survival curves of mammalian cells cultured in vitro. In: Biophysical aspects of radiation quality, Techn Rep Ser 58. International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, pp 21–43
Skarsgard LD, Wilson DJ, Durrand RE (1993) Survival at low dose in asynchronous and partially synchronized Chinese hamster V79–171 cells. Radiat Res 133:102–107
Smith-Bindman R (2010) Is computed tomography safe? New eng. J Med 363:1–4
Stewart AM, Kneale GW (1990) A-bomb radiation and evidence of late effects other than cancer. Health Phys 58:729–735
Stewart AM, Webb J, Giles D et al (1956) Malignant disease in childhood and diagnostic radiation in utero. Lancet 2:p 447
Stewart AM, Webb J, Hewitt D (1958) A survey of childhood malignancies. Br Med J 1:1495–1508
Thacker J, Cox R (1975) Mutation induction and inactivation in mammalian cells exposed to ionizing radiation. Nature 258:429–431
Thacker J, Stretch A, Stephens MA (1977) The induction of thioguanine-resistant mutants of Chinese hamster cells by γ-rays. Mutat Res 42:313–326
Thacker J, Wilkinson RE, Goodhead DT (1986) The induction of chromosome exchange aberrations by carbon ultrasoft X-rays in V79 hamster cells. Int J Radiat Biol 49:645–656
Todd P (1967) Heavy-ion irradiation of cultured human cells. Radiat Res Suppl 7:196–207
Traynor JE, Still ET (1968) Dose rate effect on LD50/30 in mice exposed to cobalt-60 gamma irradiation. Brooks Air Force Base, TX:USAF School of Aerospace Medicine; Rep. SAM-TR-68-97
Tubiana M (1998) The report of the French Academy of Science: problems associated with the effects of low doses of ionising radiations. J Radiat Prot 18:243–248
Tubiana M (2000) Radiation risks in perspective: radiation-induced cancer among cancer risks. Radiat Environ Biophys 39:3–16
Underbrink AG, Sparrow AH, Sautkulis D, Mills RE (1975) Oxygen enhancement ratios (OERs) for somatic mutations in Tradescantia stamen hairs. Radiat Bot 15:161–168
UNSCEAR (2000) Sources and effects of ionizing radiation. United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation Report to the General Assembly, New York
Upton AC, Jenkins VK, Conklin JW (1964) Myeloid leukemia in the mouse. Ann N Y Acad Sci 114:189–202
Virsik RP, Schafer CH, Harder D et al (1980) Chromosome aberrations induced in human lymphocytes by ultrasoft Al-K and Cu X-rays. Int J Radiat Biol 38:545–557
Vivek Kumar PR, Mohankumar MN, Zareena Hamza V et al (2006) Dose-rate effect on the induction of HPRT mutants in Human G0 lymphocytes exposed in vitro to gamma radiation. Radiat Res 165:43–50
Wakeford R (2005) Cancer risk among nuclear workers. J Radiat Prot 25:225–228
Wakeford R, Doll R, Bithell JF (1997) Childhood cancer and intrauterine irradiation, In: Health effects of low dose radiation: challenges of the 21st century. British Nuclear Energy Society, London, pp 114–119
Wells RL, Bedford JS (1983) Dose-rate effects in mammalian cells IV: repairable and non-repairable damage in non-cycling C3H 10T1/2 cells. Radiat Res 94:105–134
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Chadwick, K.H., Leenhouts, H.P. (2012). Risks from Ionising Radiation. In: Tack, D., Kalra, M., Gevenois, P. (eds) Radiation Dose from Multidetector CT. Medical Radiology(). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/174_2011_400
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/174_2011_400
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-24534-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-24535-0
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)