Abstract
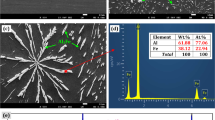
In this study, the Taguchi robust design method is used for optimizing ball milling parameters including milling time, rotation speed and ball to powder weight ratio in the planetary ball milling of nanostructured nickel ferrite powder. In fact, the current work deals with NiFe2O4 nanoparticles mechanochemically synthesized from NiO and Fe2O3 powders. The Taguchi robust design technique of system optimization with the L9 orthogonal array is performed to verify the best experimental levels and contribution percentages (% ρ) of each parameter. Particle size measurement using SEM gives the average particle size value in the range of 59–67 nm. X-ray diffraction using Cu Kα radiation is also carried out to identify the formation of NiFe2O4 single phase. The XRD results suggest that NiFe2O4 with a crystallite size of about 12 nm is present in 30 h activated specimens. Furthermore, based on the results of the Taguchi approach the greatest effect on particle size (42.10 %) is found to be due to rotation speed followed by milling time (37.08 %) while ball to powder weight ratio exhibits the least influence.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang J., Shi J., Gong M., J. Solid State Chem., 182(8) (2009), 2135.
Safarik I., Safarikova M., Nanostruct. Mater., Springer, Vienna, (2002), 1.
Pileni M.P., Nat. Mater., 2 (2003), 145.
Sun J., Zhou S., Hou P., Yang Y., Weng J., Li X., Li M., J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A, 80A (2007), 333.
Salavati-Niasari M., Davar F., Mahmoudi T., Polyhedron, 28 (2009), 1455.
Mathew D.S., Juang R.S., Chem. Eng. J., 129 (2007), 51.
Kodama R.H., Berkowitz A.E., Mcniff E., Foner J., Foner S., Phys. Rev. Lett., 77 (1996), 394.
Srivastava M., Ojha A.K., Chaubey S., Materny A., J. Alloy. Compd., 481 (2009), 515.
Maensiri S., Masingboon C., Boonchom B., Supapan S., Scripta Mater., 56 (2007), 797.
Xu Q., Wei Y., Liu Y., Ji X., Yang L., Gu M., Solid State Sci., 11 (2009) 472.
Arulmurugan R., Vaidyanathan G., Sendhilnathan S., Jeyadevan B., J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 298 (2006), 83.
Muthuselvam I.P., Bhowmik R.N., Solid State Sci., 11 (2009), 719.
Suryanarayana C., Prog. Mater. Sci.+, 46 (2001), 1.
Maurice D.R., Courtney T.H., Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 21 (1990), 289.
Maurice D.R., Courtney T.H., Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 26 (1995), 2431.
Cook T.M., Courtney T.H., Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 26 (1995), 2389.
Abdellaoui M., Gaffet E., J. Alloy. Compd., 209 (1994), 351.
Garcia-diaz A., Philips D.T., Principles of experimental design and analysis, Chapman and Hall, London, 1995.
Montgomery D.C., Design and analysis of experiments, 4th ed., John Wiley and Sons, New York, 1997.
Klug H.P., Alexander L.E., X-ray Diffraction Procedures for Polycrystalline and Amorphous Materials, 2nd ed., John Wiley and Sons, New York, 1974.
Monshi A., Foroughi M.R., Monshi M.R., World J. Nano Sci. Eng., 2 (2012), 154.
Gheisari Kh., Javadpour S., Oh J.T., Ghaffari M., J. Alloy. Compd., 472 (2009), 416.
Cullity B.D., Elements of X-ray Diffraction, Addison Wesley Pub. Co. Inc., 1956, 42.
Qi W.H., Wang M.P., Mater. Chem. Phys., 88 (2004), 280.
Roy R.K., A Primer on the Taguchi Method, 2nd ed., Society of Manufacturing Engineers, 2010.
Ross P.J., Taguchi G., Techniques for Quality Engineering, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1988.
Paiva-Santos C.O., Gouveia H., Las W.C., Varela J.A., Mater. Struct., 6 (1999), 111.
Ross P.J., Taguchi Techniques for Quality Engineering, 2nd ed., McGraw-Hill, Singapore, 1996.
Bendell A., Disney J., Pridmore W.A., Taguchi Methods: Applications in World Industry, IFS Publications, UK, 1989.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Hajalilou, A., Hashim, M., Ebrahimi-Kahrizsangi, R. et al. Parametric optimization of NiFe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized by mechanical alloying. Mater Sci-Pol 32, 281–291 (2014). https://doi.org/10.2478/s13536-013-0173-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s13536-013-0173-x