Abstract
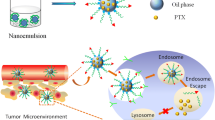
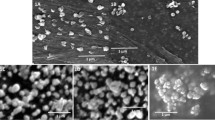
Aim of the investigation was to develop folate-functionalized lipid nanoemulsion (LNE) comprising chemo-radiotherapeutics for targeted delivery to nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). Soy lecithin nanoemulsion of doxorubicin (Dox) and yittrium-90 (90Y) was prepared by nanoprecipitation using ultrasonic homogenization technique followed by folic acid conjugation. Nanoemulsion (Dox-LNE) was characterized as positively charged (zeta potential), spherical shape (transmission electron microscopy) nano-droplets of uniform size distribution (polydispersity index). No significant variation in parameters such as particle size, zeta potential, and polydispersity index was observed when the stability of Dox-LNE was assessed during long-term storage at room temperature and at 8000 rpm, 121°C temperature, and 5000 time dilution in water. In vitro release of Dox from Dox-LNE was observed to be controlled for at least 48 h. Folate decoration over Dox-LNE surface (FD-Dox-LNE) and incorporation of 90Y in FD-Dox-LNE (FD-Dox + 90Y-LNE) changed droplet size up to 50 nm; however, surface charge of Dox-LNE did not change significantly. FD-Dox + 90Y-LNE inhibited growth of cancerous cell line like CNE1 (folate receptor rich) in vitro and alleviated tumor volume in NPC-induced nude mice significantly as compared to Dox + 90Y-LNE. Massive necrosis and hemorrhage of CNE1 cells were observed by FD-Dox + 90Y-LNE (89.9%); however, inhibition of growth of nasal epithelial cells (RPMI 2650; folate deficient) by FD-Dox + 90Y-LNE and Dox + 90Y-LNE was observed to be 21.5 and 43.65%, respectively. The investigation highlights the vast utility of folate-decorated lipid emulsion in delivering chemo-radiotherapeutics to the specific NPC site. FD-Dox + 90Y-LNE might offer a cost-effective, safe, efficacious, and clinically pertinent option to the available therapeutics.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pan Y, Zhang Q, Atsaves V, Yang H, Claret FX. Suppression of Jab1/CSN5 induces radio- and chemo-sensitivity in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through changes to the DNA damage and repair pathways. Oncogene. 2013;32(22):2756–66.
Peng X, Cao P, He D, Han S, Zhou J, Tan G, et al. MiR-634 sensitizes nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells to paclitaxel and inhibits cell growth both in vitro and in vivo. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7(10):6784–91.
Yang R, An Y, Miao F, Li M, Liu P, Tang Q. Preparation of folic acid-conjugated, doxorubicin-loaded, magnetic bovine serum albumin nanospheres and their antitumor effects in vitro and in vivo. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014;9:4231–43.
Werner ME, Karve S, Sukumar R, Cummings ND, Copp JA, Chen RC, et al. Folate-targeted nanoparticle delivery of chemo- and radiotherapeutics for the treatment of ovarian cancer peritoneal metastasis. Biomaterials. 2011;32(33):8548–54.
Kandadi P, Syed MA, Goparaboina S, Veerabrahma K. Albumin coupled lipid nanoemulsions of diclofenac for targeted delivery to inflammation. Nanomed Nanotech Biol Med. 2012;8(7):1162–71.
Kandadi P, Syed MA, Goparaboina S, Veerabrahma K. Brain specific delivery of pegylated indinavir submicron lipid emulsions. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2011;42(4):423–32.
Mishra N, Rai VK, Yadav KS, Sinha P, Kanaujia A, Chanda D, et al. Encapsulation of Mentha Oil in Chitosan Polymer Matrix Alleviates Skin Irritation. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2016;17(2):482–92.
Shah PP, Desai PR, Patel AR, Singh MS. Skin permeating nanogel for the cutaneous co-delivery of two anti-inflammatory drugs. Biomaterials. 2012;33(5):1607–17.
Marin MT, Margarit MV, Salcedo GE. Characterization and solubility study of solid dispersions of flunarizine and polyvinylpyrrolidone. Farmaco. 2002;57(9):723–7.
Rai VK, Yadav NP, Sinha P, Mishra N, Luqman S, Dwivedi H, et al. Development of cellulosic polymer based gel of novel ternary mixture of miconazole nitrate for buccal delivery. Carbohydr polym. 2014;103:126–33.
Dubey A, Prabhu P, Kabrawala H, Ghate V. Niosomal gel of Adapalene: Its formulation, physicochemical properties and evaluation for mild-acne. Adv biomed pharmacy. 2014;2(1).
Bae PK, Jung J, Lim SJ, Kim D, Kim SK, Chung BH. Bimodal perfluorocarbon nanoemulsions for nasopharyngeal carcinoma targeting. Mol Imaging Biol. 2013;15(4):401–10.
Nazir S, Qureshi MA, Chat OA. Anti-tumor, Anti-oxidant and Anti-microbial potential of Nymphaea alba and Nymphaea mexicana flowers a comparative study. Adv biomed pharmacy. 2015;2(4).
Deng X, Cao M, Zhang J, Hu K, Yin Z, Zhou Z, et al. Hyaluronic acid-chitosan nanoparticles for co-delivery of MiR-34a and doxorubicin in therapy against triple negative breast cancer. Biomaterials. 2014;35(14):4333–44.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (No. ZR2013HM107).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Yu, XM., Sun, RJ. et al. Folate-Functionalized Lipid Nanoemulsion to Deliver Chemo-Radiotherapeutics Together for the Effective Treatment of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. AAPS PharmSciTech 18, 1374–1381 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-016-0595-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-016-0595-y