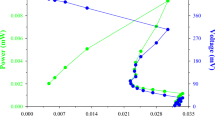
Lipase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa LP602, a bacterial strain isolated from a domestic wastewater sample, was preliminarily characterized. The enzyme exhibited maximum lipolytic activity at pH 8.0 where it was also stably maintained. At 55°C, the lipase had the highest activity but not stability. The enzyme was insensitive to EDTA and to many ions tested except Zn2+. It was sensitive to SDS but not to Tween-20, Tween-80 or Triton X-100. The enzyme was active towards a number of commercial food grade fats and oils. A suitable medium formula for lipase production was MMP containing 6.25% whey as a carbon source, 1% soybean oil as inducer and 0.5% yeast extract supplement. The culture was fed with glucose to a final concentration of 0.1% at the 15th hour of incubation. Lipase production under this condition was 3.5 U ml−1. Both P. aeruginosa LP602 cells and the lipase were shown to be usable for lipid-rich wastewater treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 21 April 1998/ Accepted in revised form 6 August 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dharmsthiti, S., Kuhasuntisuk, B. Lipase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa LP602: biochemical properties and application for wastewater treatment. J Ind Microbiol Biotech 21, 75–80 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jim.2900563
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jim.2900563