Abstract
Purpose. To investigate whether the widely accepted advantages associated with the use of chitosan as a nasal drug delivery system, might be further improved by application of chitosan formulated as nanoparticles.
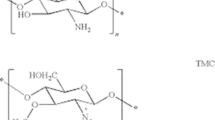
Methods. Insulin-chitosan nanoparticles were prepared by the ionotropic gelation of chitosan glutamate and tripolyphosphate pentasodium and by simple complexation of insulin and chitosan. The nasal absorption of insulin after administration in chitosan nanoparticle formulations and in chitosan solution and powder formulations was evaluated in anaesthetised rats and/or in conscious sheep.
Results. Insulin-chitosan nanoparticle formulations produced a pharmacological response in the two animal models, although in both cases the response in terms of lowering the blood glucose levels was less (to 52.9 or 59.7% of basal level in the rat, 72.6% in the sheep) than that of the nasal insulin chitosan solution formulation (40.1% in the rat, 53.0% in the sheep). The insulin-chitosan solution formulation was found to be significantly more effective than the complex and nanoparticle formulations. The hypoglycaemic response of the rat to the administration of post-loaded insulin-chitosan nanoparticles and insulin-loaded chitosan nanoparticles was comparable. As shown in the sheep model, the most effective chitosan formulation for nasal insulin absorption was a chitosan powder delivery system with a bioavailability of 17.0% as compared to 1.3% and 3.6% for the chitosan nanoparticles and chitosan solution formulations, respectively.
Conclusion. It was shown conclusively that chitosan nanoparticles did not improve the absorption enhancing effect of chitosan in solution or powder form and that chitosan powder was the most effective formulation for nasal delivery of insulin in the sheep model.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
L. Illum. Chitosan and Its Use as a Pharmaceutical Excipient. Pharm. Res. 15:1326–1331 (1998).
Y. Sawayanagi, N. Nambu, and T. Nagai. Directly compressed tablets containing chitin or chitosan in addition to lactose or potato starch. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 30:2935–2940 (1982).
T. Imai, S. Shiraishi, S. Saito, and M. Otagiri. Interaction of indomethacin with low molecular weight chitosan and improvements of some pharmaceutical properties of indomethacin by low molecular weight chitosan. Int. J. Pharm. 67:11–20 (1991).
K. Takayama, M. Hirata, Y. Machida, T. Sannan, and T. Nagai. Effect of interpolymer complex formations on the bioadhesive property and drug release phenomenon of compressed tablet consisting of chitosan and sodium hyaluronate. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 38:1993–1997 (1990).
L. Illum. N. F. Farraj, and S. S. Davis. Chitosan as a novel nasal delivery system for peptide drugs. Pharm. Res. 11:1186–1189 (1994).
P. Artursson. T Lindmark, S. S. Davis, and L Illum. Effect of chitosan on the permeability of monolayers of intestinal epithelial cells (Caco-2). Pharm. Res. 11:1358–1361 (1994).
L. Illum. Bioadhesive formulations for nasal peptide delivery. In E. Mathowitz, C. M. Lehr, and D. Chickering (eds). Bioadhesion in Drug Delivery-Issues in Fundamentals, novel approaches and development, Marcel Dekker, 1998 pp 507-539.
L. Illum. Intranasal morphine for pain management. Chinese J. Neuroanatomy 17Suppl.:93–95 (2001).
L. Illum. P. Watts, A. N. Fisher, M Hinchcliffe, H Norbury, I Jabbal-Gill, R Nankervis, and S S Davis. Intranasal delivery of morphine J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 301:391–400 (2002).
L. Illum, P. Watts, A. N. Fisher, I. Jabbal-Gill, and S. S. Davis. Novel chitosan-based delivery systems for the nasal administration of a LHRH-analogue. S. T. P. Pharma Sci. 10:89–94 (2000).
T. J. Aspden, L. Illum, and O. Skaugrud. Chitosan as a nasal delivery system: evaluation of insulin absorption enhancement and effect on nasal membrane integrity using rat models. Eur. J. Pharm Sci. 4:23–31 (1996).
V. Dodane, M. A. Khan, and J. R. Merwin. Effect of chitosan on epithelial permeability and structure. Int. J. Pharm. 182:21–32 (1999).
N. G. M. Schipper, S. Olsson, J. A. Hoogstraate, A. G. de Boer, K. M. Varum, and P. Artursson. Chitosans as absorption enhancers for poorly absorbable drugs. 2. Mechanism of absorption enhancement. Pharm. Res. 14:923–929 (1997).
R. J. Soane, M. Frier, A. C. Perkins, N. S. Jones, S. S. Davis, and L. Illum. Evaluation of the clearance characteristics of bioadhesive systems in human. Int. J. Pharm. 178:55–65 (1999).
K A Janes. M. P. Fresneau, A Marazuela, A. Fabra, and M. J. Alonso. Chitosan nanoparticles as delivery systems for doxorubicin. J. Control. Release 73:255–267 (2001).
S. Dumitriu and E. Chornet. Inclusion and release of proteins from polysaccharide-based polyion complexes. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 31:223–246 (1998).
Y. Ohya, M. Shiratani, H. Kobayashi, and T. Ouchi. Release behavior of 5-fluorouracil from chitosan-gel nanospheres immobilizing 5-fluorouracil coated with polysaccharides and their cell specific cytotoxicity. Pure Appl. Chem. A31:629–642 (1994).
P. Calvo, C. Remunan-Lopez, J. L. Vila-Jato, and M. J. Alonso. Novel hydrophilic chitosan-polyethylene oxide nanoparticles as protein carriers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 63:125–132 (1997).
R. Fernandez-Urrusuna, D. Romani, P. Calvo, J. L. Vila-Jato, and M. J. Alonso. Development of a freeze dried formulation of insulin-loaded chitosan nanoparticles intended for nasal administration. S. T. P. Pharma. Sci. 5:429–436 (1999).
R. Fernandez-Urrusuna, P. Calvo, C. Remunan-Lopez, J. L. Vila-Jato, and M. J. Alonso. Enhancement of nasal absorption of insulin using chitosan nanoparticles. Pharm. Res. 16:1576–1581 (1999).
F. C. MacLaughlin, R. J. Mumper, J. Wang, J. M. Tagliaferri, I. Gill, M. Hinchcliffe, and A. P. Rolland. Chitosan and depolymerized chitosan oligomers as condensing carriers for in vivo plasmid delivery. J. Control. Release 56:259–272 (1998).
K. A. Janes. P. Calvo, and M. J. Alonso. Polysaccharide colloidal particles as delivery systems for macromolecules. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 47:83–97 (2001).
S. H. Major and L. Illum. Investigation of the effect of anaesthesia on nasal absorption of insulin in rats. Int. J. Pharm. 149:123–129 (1997).
F. W. H. M. Merkus. J. C. Verhoef, S. G. Romeijn, and N. G. M. Schipper. Interspecies differences in the nasal absorption of insulin. Pharm. Res. 8:1343 (1991).
R. J. Soane, M. Hinchcliffe, S. S. Davis, and L. Illum. Clearance characteristics of chitosan based formulations in the sheep nasal cavity. Int. J. Pharm. 217:183–191 (2001).
J. Brooking, S. S. Davis, and L. Illum. Transport of nanoparticles across the nasal mucosa. J. Drug Target. 9:267–279 (2001).
N. G. M. Schipper and K. M. Varum. and P Artursson. Chitosans as absorption enhancers for poorly soluble drugs. 1: Influence of molecular weight and degree of acetylation on drug transport across human intestinal epithelial (Caco-2) cells. Pharm. Res. 13:1686–1692 (1996).
T. J. Aspden. An evaluation of the potential use of chitosans in nasal peptide absorption systems. Ph. D. Thesis, Nottingham University, 1996.
R. J. Soane. Bioadhesive polymers as intranasal drug delivery systems for peptide and protein drugs. Ph. D. Thesis, Nottingham University, 1999.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dyer, A.M., Hinchcliffe, M., Watts, P. et al. Nasal Delivery of Insulin Using Novel Chitosan Based Formulations: A Comparative Study in Two Animal Models Between Simple Chitosan Formulations and Chitosan Nanoparticles. Pharm Res 19, 998–1008 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016418523014
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016418523014