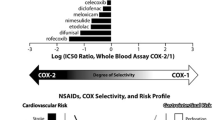
Abstract
In recent years, new direct-acting oral anticoagulants (DOACs) have been introduced into clinical practice that specifically inhibit either factor Ia or Xa. These drugs have, to a large extent, replaced warfarin for the treatment of venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, and non-valvular atrial fibrillation. They have potential advantages over warfarin in providing more stable anticoagulation and the lack of a need for regular venesection to monitor activity. They also have the promise of less drug and food interactions. All of these drugs are substrates for the permeability glycoprotein (P-gp) excretion system, and several are metabolised, in part, by cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A4. This current article assesses the interactions that do or may occur with the DOACs, particularly with respect to the P-gp and CYP3A4 systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ganetsky M, Babu KM, Salhanick SD, Brown RS, Boyer EW. Dabigatran: review of pharmacology and management of bleeding complications of this novel oral anticoagulant. J Med Toxicol. 2011;7(4):281–7.
Perzborn E, Roehrig S, Straub A, Kubitza D, Misselwitz F. The discovery and development of rivaroxaban, an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011;10(1):61–75.
Keating GM. Apixaban: a review of its use for reducing the risk of stroke and systemic embolism in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Drugs. 2013;73(8):825–43.
Anon. Edoxaban tosylate. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2011;11(2):129–35.
Finch A, Pillans P. P-glycoprotein and its role in drug-drug interactions. Aust Prescr. 2014;37:137–9.
Nutescu E, Chuatrisorn I, Hellenbart E. Drug and dietary interactions of warfarin and novel oral anticoagulants: an update. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2011;31(3):326–43.
Nielsen D, Skovsgaard T. P-glycoprotein as multidrug transporter: a critical review of current multidrug resistant cell lines. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992;1139(3):169–83.
Ambudkar SV, Kimchi-Sarfaty C, Sauna ZE, Gottesman MM. P-glycoprotein: from genomics to mechanism. Oncogene. 2003;22(47):7468–85.
Lippi G, Favaloro EJ, Mattiuzzi C. Combined administration of antibiotics and direct oral anticoagulants: a renewed indication for laboratory monitoring? Semin Thromb Hemost. 2014;40(7):756–65.
Straight Healthcare. P-glycoprotein. 2015. Available at: http://www.straighthealthcare.com/p-glycoprotein.html. Accessed 10 Nov 2015.
Mueck W, Kubitza D, Becka M. Co-administration of rivaroxaban with drugs that share its elimination pathways: pharmacokinetic effects in healthy subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2013;76(3):455–66.
Zhang D, He K, Herbst JJ, Kolb J, Shou W, Wang L, et al. Characterization of efflux transporters involved in distribution and disposition of apixaban. Drug Metab Dispos. 2013;41(4):827–35.
Product information: Pradaxa. 2015. Available at: https://www.ebs.tga.gov.au/ebs/picmi/picmirepository.nsf/pdf?OpenAgent&id=CP-2009-PI-01177-3. Accessed 10 Nov 2015.
Spinler S. The pharmacology and therapeutic use of dabigatran etexilate. J Clin Pharmacol. 2013;53(1):1–13.
Connolly SJ, Ezekowitz MD, Yusuf S, Eikelboom J, Oldgren J, Parekh A, et al. Dabigatran versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(12):1139–51.
Hennessy M, Kelleher D, Spiers JP, Barry M, Kavanagh P, Back D, et al. St Johns wort increases expression of P-glycoprotein: implications for drug interactions. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2002;53(1):75–82.
Rahimi R, Abdollahi M. An update on the ability of St. John’s wort to affect the metabolism of other drugs. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2012;8(6):691–708.
Stangier J, Stahle H, Rathgen K, Roth W, Reseski K, Kornicke T. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of dabigatran etexilate, an oral direct thrombin inhibitor, with coadministration of digoxin. J Clin Pharmacol. 2012;52(2):243–50.
Product information: Xarelto. 2015. Available at: https://www.ebs.tga.gov.au/ebs/picmi/picmirepository.nsf/PICMI?OpenForm&t=PI&q=xarelto&r=/. Accessed 10 Nov 2015.
Product information: Eliquis. 2015. Available at: https://www.ebs.tga.gov.au/ebs/picmi/picmirepository.nsf/PICMI?OpenForm&t=PI&q=dabigatran&r. Accessed 10 Nov 2015.
Bounameaux H, Camm AJ. Edoxaban: an update on the new oral direct factor Xa inhibitor. Drugs. 2014;74(11):1209–31.
Davidson BL, Verheijen S, Lensing AW, Gebel M, Brighton TA, Lyons RM, et al. Bleeding risk of patients with acute venous thromboembolism taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or aspirin. JAMA Intern Med. 2014;174(6):947–53.
Caldeira D, Barra M, Ferreira A, Rocha A, Augusto A, Pinto FJ, et al. Systematic review with meta-analysis: the risk of major gastrointestinal bleeding with non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015;42(11–12):1239–49.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No sources of funding were used to assist in the preparation of this article.
Conflict of interest
Laurie Howes has participated as an investigator in trials of rivaroxaban. John Leonard Fitzgerald has no conflicts of interest that are directly relevant to the content of this review.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fitzgerald, J.L., Howes, L.G. Drug Interactions of Direct-Acting Oral Anticoagulants. Drug Saf 39, 841–845 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40264-016-0443-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40264-016-0443-8