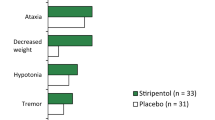
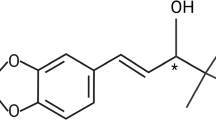
Abstract
Stiripentol is a structurally unique antiepileptic drug that has several possible mechanisms of action, including diverse effects on the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-A receptor and novel inhibition of lactate dehydrogenase. Because of its inhibition of several cytochrome P450 enzymes, it has extensive pharmacokinetic interactions, which often necessitates reduction in doses of certain co-therapies, particularly clobazam. Stiripentol also has a neuroprotective action, by reducing calcium-mediated neurotoxicity. Evidence of its efficacy is most robust for Dravet syndrome, where stiripentol added to clobazam and valproic acid reduces seizure frequency and severity in the majority of cases. Small case series have also suggested benefit for malignant migrating partial seizures in infancy, super-refractory status epilepticus, and intractable focal epilepsy, although larger prospective studies are needed in these disorders.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
May TW, Boor R, Mayer T, Jurgens U, Rambeck B, Holert N, et al. Concentrations of stiripentol in children and adults with epilepsy: the influence of dose, age, and comedication. Ther Drug Monit. 2012;34:390–7.
Farwell JR, Anderson GD, Kerr BM, Tor JA, Levy RH. Stiripentol in atypical absence seizures in children: an open trial. Epilepsia. 1993;34:305–11.
Jacob S, Nair AB. An updated overview on therapeutic drug monitoring of recent antiepileptic drugs. Drugs R D. 2016;16:303–16.
Darwish HW, Abdelhameed AS, Attia MI, Bakheit AH, Khalil NY, Al-Majed AA. A stability-indicating HPLC-DAD method for determination of stiripentol: development, validation, kinetics, structure elucidation and application to commercial dosage form. J Anal Methods Chem. 2014;2014:638951.
Chiron C. Stiripentol. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2005;14:905–11.
Moreland TA, Astoin J, Lepage F, Tombret F, Levy RH, Baillie TA. The metabolic fate of stiripentol in man. Drug Metab Dispos. 1986;14:654–62.
Levy RH, Lin HS, Blehaut HM, Tor JA. Pharmacokinetics of stiripentol in normal man: evidence of nonlinearity. J Clin Pharmacol. 1983;23:523–33.
Levy RH, Loiseau P, Guyot M, Blehaut HM, Tor J, Moreland TA. Stiripentol kinetics in epilepsy: nonlinearity and interactions. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1984;36:661–9.
Peigne S, Rey E, Le Guern ME, Dulac O, Chiron C, Pons G, et al. Reassessment of stiripentol pharmacokinetics in healthy adult volunteers. Epilepsy Res. 2014;108:909–16.
Quilichini PP, Chiron C, Ben-Ari Y, Gozlan H. Stiripentol, a putative antiepileptic drug, enhances the duration of opening of GABA-A receptor channels. Epilepsia. 2006;47:704–16.
Fisher JL. The anti-convulsant stiripentol acts directly on the GABA (A) receptor as a positive allosteric modulator. Neuropharmacology. 2009;56:190–7.
Laurie DJ, Wisden W, Seeburg PH. The distribution of thirteen GABAA receptor subunit mRNAs in the rat brain. III. Embryonic and postnatal development. J Neurosci. 1992;12:4151–72.
Fisher JL. The effects of stiripentol on GABA (A) receptors. Epilepsia. 2011;52(Suppl 2):76–8.
Grosenbaugh DK, Mott DD. Stiripentol in refractory status epilepticus. Epilepsia. 2013;54(Suppl 6):103–5.
Goodkin HP, Joshi S, Mtchedlishvili Z, Brar J, Kapur J. Subunit-specific trafficking of GABA(A) receptors during status epilepticus. J Neurosci. 2008;28:2527–38.
Rho JM. Inhibition of lactate dehydrogenase to treat epilepsy. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:187–9.
Sada N, Lee S, Katsu T, Otsuki T, Inoue T. Epilepsy treatment. Targeting LDH enzymes with a stiripentol analog to treat epilepsy. Science. 2015;347:1362–7.
Tran A, Vauzelle-Kervroedan F, Rey E, Pous G, d’Athis P, Chiron C, et al. Effect of stiripentol on carbamazepine plasma concentration and metabolism in epileptic children. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1996;50:497–500.
Cazali N, Tran A, Treluyer JM, Rey E, d’Athis P, Vincent J, et al. Inhibitory effect of stiripentol on carbamazepine and saquinavir metabolism in human. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2003;56:526–36.
Mudigoudar B, Weatherspoon S, Wheless JW. Emerging antiepileptic drugs for severe pediatric epilepsies. Semin Pediatr Neurol. 2016;23:167–79.
Ferguson RJ, De Morais SM, Benhamou S, Bouchardy C, Blaisdell J, Ibeanu G, et al. A new genetic defect in human CYP2C19: mutation of the initiation codon is responsible for poor metabolism of S-mephenytoin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1998;284:356–61.
Inoue Y, Ohtsuka Y, Oguni H, Tohyama J, Baba H, Fukushima K, et al. Stiripentol open study in Japanese patients with Dravet syndrome. Epilepsia. 2009;50:2362–8.
Kosaki K, Tamura K, Sato R, Samejima H, Tanigawara Y, Takahashi T. A major influence of CYP2C19 genotype on the steady-state concentration of N-desmethylclobazam. Brain Dev. 2004;26:530–4.
Kouga T, Shimbo H, Iai M, Yamashita S, Ishii A, Ihara Y, et al. Effect of CYP2C19 polymorphisms on stiripentol administration in Japanese cases of Dravet syndrome. Brain Dev. 2015;37:243–9.
Auvin S, Lecointe C, Dupuis N, Desnous B, Lebon S, Gressens P, et al. Stiripentol exhibits higher anticonvulsant properties in the immature than in the mature rat brain. Epilepsia. 2013;54:2082–90.
Verleye M, Buttigieg D, Steinschneider R. Neuroprotective activity of stiripentol with a possible involvement of voltage-dependent calcium and sodium channels. J Neurosci Res. 2016;94:179–89.
Perez J, Chiron C, Musial C, Rey E, Blehaut H, d’Athis P, et al. Stiripentol: efficacy and tolerability in children with epilepsy. Epilepsia. 1999;40:1618–26.
Chiron C, Tonnelier S, Rey E, Brunet ML, Tran A, d’Athis P, et al. Stiripentol in childhood partial epilepsy: randomized placebo-controlled trial with enrichment and withdrawal design. J Child Neurol. 2006;21:496–502.
Inoue Y, Ohtsuka Y, Group S-S. Long-term safety and efficacy of stiripentol for the treatment of Dravet syndrome: a multicenter, open-label study in Japan. Epilepsy Res. 2015;113:90–7.
Chiron C. Stiripentol. Neurotherapeutics. 2007;4:123–5.
Trojnar MK, Wojtal K, Trojnar MP, Czuczwar SJ. Stiripentol. A novel antiepileptic drug. Pharmacol Rep. 2005;57:154–60.
Rascol O, Squalli A, Montastruc JL, Garat A, Houin G, Lachau S, et al. A pilot study of stiripentol, a new anticonvulsant drug, in complex partial seizures uncontrolled by carbamazepine. Clin Neuropharmacol. 1989;12:119–23.
Chiron C, Marchand MC, Tran A, Rey E, d’Athis P, Vincent J, et al. Stiripentol in severe myoclonic epilepsy in infancy: a randomised placebo-controlled syndrome-dedicated trial. STICLO study group. Lancet. 2000;356:1638–42.
De Liso P, Chemaly N, Laschet J, Barnerias C, Hully M, Leunen D, et al. Patients with dravet syndrome in the era of stiripentol: a French cohort cross-sectional study. Epilepsy Res. 2016;125:42–6.
Aras LM, Isla J, Mingorance-Le Meur A. The European patient with Dravet syndrome: results from a parent-reported survey on antiepileptic drug use in the European population with Dravet syndrome. Epilepsy Behav. 2015;44:104–9.
Thanh TN, Chiron C, Dellatolas G, Rey E, Pons G, Vincent J. et al [Long-term efficacy and tolerance of stiripentaol in severe myoclonic epilepsy of infancy (Dravet’s syndrome)]. Arch Pediatr. 2002;9:1120–7.
Inoue Y, Ohtsuka Y. Effectiveness of add-on stiripentol to clobazam and valproate in Japanese patients with Dravet syndrome: additional supportive evidence. Epilepsy Res. 2014;108:725–31.
Wirrell EC, Laux L, Franz DN, Sullivan J, Saneto RP, Morse RP, et al. Stiripentol in Dravet syndrome: results of a retrospective US study. Epilepsia. 2013;54:1595–604.
Balestrini S, Sisodiya SM. Audit of use of stiripentol in adults with Dravet syndrome. Acta Neurol Scand. 2017;135:73–9.
Coppola G. Malignant migrating partial seizures in infancy: an epilepsy syndrome of unknown etiology. Epilepsia. 2009;50(Suppl 5):49–51.
Ishii A, Shioda M, Okumura A, Kidokoro H, Sakauchi M, Shimada S, et al. A recurrent KCNT1 mutation in two sporadic cases with malignant migrating partial seizures in infancy. Gene. 2013;531:467–71.
Ohba C, Kato M, Takahashi S, Lerman-Sagie T, Lev D, Terashima H, et al. Early onset epileptic encephalopathy caused by de novo SCN8A mutations. Epilepsia. 2014;55:994–1000.
Poduri A, Chopra SS, Neilan EG, Elhosary PC, Kurian MA, Meyer E, et al. Homozygous PLCB1 deletion associated with malignant migrating partial seizures in infancy. Epilepsia. 2012;53:e146–50.
Carranza Rojo D, Hamiwka L, McMahon JM, Dibbens LM, Arsov T, Suls A, et al. De novo SCN1A mutations in migrating partial seizures of infancy. Neurology. 2011;77:380–3.
Dhamija R, Wirrell E, Falcao G, Kirmani S, Wong-Kisiel LC. Novel de novo SCN2A mutation in a child with migrating focal seizures of infancy. Pediatr Neurol. 2013;49:486–8.
Milh M, Falace A, Villeneuve N, Vanni N, Cacciagli P, Assereto S, et al. Novel compound heterozygous mutations in TBC1D24 cause familial malignant migrating partial seizures of infancy. Hum Mutat. 2013;34:869–72.
Djuric M, Kravljanac R, Kovacevic G, Martic J. The efficacy of bromides, stiripentol and levetiracetam in two patients with malignant migrating partial seizures in infancy. Epileptic Disord. 2011;13:22–6.
Merdariu D, Delanoe C, Mahfoufi N, Bellavoine V, Auvin S. Malignant migrating partial seizures of infancy controlled by stiripentol and clonazepam. Brain Dev. 2013;35:177–80.
Howell KB, McMahon JM, Carvill GL, Tambunan D, Mackay MT, Rodriguez-Casero V, et al. SCN2A encephalopathy: a major cause of epilepsy of infancy with migrating focal seizures. Neurology. 2015;85:958–66.
Boerma RS, Braun KP, van den Broek MP, van Berkestijn FM, Swinkels ME, Hagebeuk EO, et al. Remarkable phenytoin sensitivity in 4 children with SCN8A-related epilepsy: a molecular neuropharmacological approach. Neurotherapeutics. 2016;13:192–7.
Mikati MA, Jiang YH, Carboni M, Shashi V, Petrovski S, Spillmann R, et al. Quinidine in the treatment of KCNT1-positive epilepsies. Ann Neurol. 2015;78:995–9.
Bearden D, Strong A, Ehnot J, DiGiovine M, Dlugos D, Goldberg EM. Targeted treatment of migrating partial seizures of infancy with quinidine. Ann Neurol. 2014;76:457–61.
Shorvon S, Ferlisi M. The treatment of super-refractory status epilepticus: a critical review of available therapies and a clinical treatment protocol. Brain. 2011;134:2802–18.
Strzelczyk A, Kortland LM, Knake S, Rosenow F. Stiripentol for the treatment of super-refractory status epilepticus. Acta Neurol Scand. 2015;132:435–9.
Uchida Y, Kato D, Toyoda T, Oomura M, Ueki Y, Ohkita K, et al. Combination of ketogenic diet and stiripentol for super-refractory status epilepticus: a case report. J Neurol Sci. 2017;373:35–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No funding.
Conflicts of interest
Dr. Nickels and Dr. Wirrell have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nickels, K.C., Wirrell, E.C. Stiripentol in the Management of Epilepsy. CNS Drugs 31, 405–416 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40263-017-0432-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40263-017-0432-1