Abstract
Background
Differential responses to donepezil treatment in patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) have been observed in clinical practice. It remains controversial whether, and to what extent, individual variation in the genes responsible for drug metabolism (CYP2D6) or those associated with AD pathogenesis (APOE) modulate the response to donepezil treatment.
Objective
The aim of this study was to better understand the potential link between donepezil treatment response and CYP2D6 or APOE polymorphisms.
Methods
We performed a meta-analysis based on data collected from 1266 donepezil-treated AD patients, and evaluated the association of CYP2D6 or APOE polymorphisms with treatment effectiveness.
Results
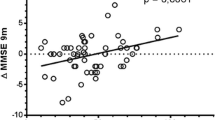
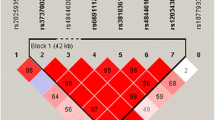
No significant difference was observed in the responder rate of donepezil treatment between the normal function CYP2D6 alleles group and the decreased/non-functional group [odds ratio (OR) 1.34, 95 % confidence interval (CI) 0.5–3.58; p = 0.56]. However, compared with the increased function CYP2D6 alleles group, the normal function group had a better response to donepezil treatment (OR 1.52, 95 % CI 1.14–2.03; p = 0.005). For the specific CYP2D6 single nucleotide polymorphism rs1080985, patients who carried the G allele had a significantly higher risk of poor response to donepezil treatment. After adjusting the data based on APOE genotype, it was observed that only individuals bearing both the APOE-ε4 allele and the rs1080985-G allele showed a significant increase in the frequency of treatment non-response (OR 1.73, 95 % CI 1.07–2.09; p = 0.03). No independent effect of APOE polymorphism on donepezil clinical responses was found (OR 1.08, 95 % CI 0.85–1.38; p = 0.53). Lastly, in a subgroup analysis based on ethnicity, all results remained consistent.
Conclusion
The CYP2D6 genotype may be potentially effective for predicting the response to donepezil treatment in AD patients.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reitz C, Brayne C, Mayeux R. Epidemiology of Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 2011;7(3):137–52.
Segal-Gidan F, Cherry D, Jones R, Williams B, Hewett L, Chodosh J, et al. Alzheimer’s disease management guideline: update 2008. Alzheimer Dement. 2011;7(3):e51–9.
Hort J, O’Brien JT, Gainotti G, Pirttila T, Popescu BO, Rektorova I, et al. EFNS guidelines for the diagnosis and management of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Neurol. 2010;17(10):1236–48.
Winblad B, Kilander L, Eriksson S, Minthon L, Batsman S, Wetterholm AL, et al. Donepezil in patients with severe Alzheimer’s disease: double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled study. Lancet. 2006;367(9516):1057–65.
Lopez-Pousa S, Bermejo-Pareja F, Frank A, Hernandez F, Leon T, Rejas-Gutierrez J, et al. The effect of donepezil in comparison with conventional treatment on cognitive functioning and the performance of the patient in a prospective cohort of patients with Alzheimer’s disease treated in routine clinical practice in Spain [in Spanish]. Rev Neurola. 2010;51(10):577–88.
Cacabelos R. Donepezil in Alzheimer’s disease: from conventional trials to pharmacogenetics. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2007;3(3):303–33.
Cacabelos R. Pharmacogenomics and therapeutic prospects in dementia. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2008;258(Suppl 1):28–47.
Noetzli M, Eap CB. Pharmacodynamic, pharmacokinetic and pharmacogenetic aspects of drugs used in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2013;52(4):225–41.
Ingelman-Sundberg M. Genetic polymorphisms of cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6): clinical consequences, evolutionary aspects and functional diversity. Pharmacogenomics J. 2005;5(1):6–13.
Lu Y, Qin X, Li S, Zhang X, He Y, Peng Q, et al. Quantitative assessment of CYP2D6 polymorphisms and risk of Alzheimer’s disease: a meta-analysis. J Neurol Sci. 2014;343(1–2):15–22.
Sachse C, Brockmoller J, Bauer S, Roots I. Cytochrome P450 2D6 variants in a Caucasian population: allele frequencies and phenotypic consequences. Am J Hum Genet. 1997;60(2):284–95.
Premkumar DR, Cohen DL, Hedera P, Friedland RP, Kalaria RN. Apolipoprotein E-epsilon4 alleles in cerebral amyloid angiopathy and cerebrovascular pathology associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Pathol. 1996;148(6):2083–95.
Coon KD, Myers AJ, Craig DW, Webster JA, Pearson JV, Lince DH, et al. A high-density whole-genome association study reveals that APOE is the major susceptibility gene for sporadic late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. J Clin Psychiatry. 2007;68(4):613–8.
Li G, Silverman JM, Altstiel LD, Haroutunian V, Perl DP, Purohit D, et al. Apolipoprotein E-epsilon 4 allele and familial risk in Alzheimer’s disease. Genet Epidemiol. 1996;13(3):285–98.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Int J Surg. 2010;8(5):336–41.
Yuhara H, Steinmaus C, Cohen SE, Corley DA, Tei Y, Buffler PA. Is diabetes mellitus an independent risk factor for colon cancer and rectal cancer? Am J Gastroenterol. 2011;106(11):1911–21 (quiz 22).
Albani D, Martinelli Boneschi F, Biella G, Giacalone G, Lupoli S, Clerici F, et al. Replication study to confirm the role of CYP2D6 polymorphism rs1080985 on donepezil efficacy in Alzheimer’s disease patients. J Alzheimers Dis. 2012;30(4):745–9.
Chianella C, Gragnaniello D, Maisano Delser P, Visentini MF, Sette E, Tola MR, et al. BCHE and CYP2D6 genetic variation in Alzheimer’s disease patients treated with cholinesterase inhibitors. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2011;67(11):1147–57.
Klimkowicz-Mrowiec A, Marona M, Spisak K, Jagiella J, Wolkow P, Szczudlik A, et al. Paraoxonase 1 gene polymorphisms do not influence the response to treatment in Alzheimer’s disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2011;32(1):26–31.
Klimkowicz-Mrowiec A, Wolkow P, Sado M, Dziubek A, Pera J, Dziedzic T, et al. Influence of rs1080985 single nucleotide polymorphism of the CYP2D6 gene on response to treatment with donepezil in patients with alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2013;9:1029–33.
Liu M, Zhang Y, Huo YR, Liu S, Liu S, Wang J, et al. Influence of the rs1080985 single nucleotide polymorphism of the CYP2D6 gene and APOE polymorphism on the response to donepezil treatment in patients with Alzheimer’s disease in China. Dement Geriatr Cogn Dis Extra. 2014;4(3):450–6.
Miranda LF, Gomes KB, Silveira JN, Pianetti GA, Byrro RM, Peles PR, et al. Predictive factors of clinical response to cholinesterase inhibitors in mild and moderate Alzheimer’s disease and mixed dementia: a one-year naturalistic study. J Alzheimers Dis. 2015;45(2):609–20.
Pilotto A, Franceschi M, D’Onofrio G, Bizzarro A, Mangialasche F, Cascavilla L, et al. Effect of a CYP2D6 polymorphism on the efficacy of donepezil in patients with Alzheimer disease. Neurology. 2009;73(10):761–7.
Seripa D, Bizzarro A, Pilotto A, D’Onofrio G, Vecchione G, Gallo AP, et al. Role of cytochrome P4502D6 functional polymorphisms in the efficacy of donepezil in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2011;21(4):225–30.
Zhong Y, Zheng X, Miao Y, Wan L, Yan H, Wang B. Effect of CYP2D6*10 and APOE polymorphisms on the efficacy of donepezil in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Med Sci. 2013;345(3):222–6.
Lu J, Fu J, Zhong Y, Chen P, Yang Q, Zhao Y, et al. The roles of apolipoprotein E3 and CYP2D6 (rs1065852) gene polymorphisms in the predictability of responses to individualized therapy with donepezil in Han Chinese patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett. 2016;614:43–8.
Tiseo PJ, Perdomo CA, Friedhoff LT. Metabolism and elimination of 14C-donepezil in healthy volunteers: a single-dose study. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1998;46(Suppl 1):19–24.
Noetzli M, Guidi M, Ebbing K, Eyer S, Wilhelm L, Michon A, et al. Population pharmacokinetic approach to evaluate the effect of CYP2D6, CYP3A, ABCB1, POR and NR1I2 genotypes on donepezil clearance. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2014;78(1):135–44.
Borroni B, Colciaghi F, Pastorino L, Archetti S, Corsini P, Cattabeni F, et al. ApoE genotype influences the biological effect of donepezil on APP metabolism in Alzheimer disease: evidence from a peripheral model. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2002;12(3):195–200.
Poirier J, Delisle MC, Quirion R, Aubert I, Farlow M, Lahiri D, et al. Apolipoprotein E4 allele as a predictor of cholinergic deficits and treatment outcome in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 1995;92(26):12260–4.
Wattmo C, Wallin AK, Londos E, Minthon L. Predictors of long-term cognitive outcome in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2011;3(4):23.
Bizzarro A, Marra C, Acciarri A, Valenza A, Tiziano FD, Brahe C, et al. Apolipoprotein E epsilon4 allele differentiates the clinical response to donepezil in Alzheimer’s disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2005;20(4):254–61.
Gauthier S. Pharmacotherapy of mild cognitive impairment. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2004;6(4):391–5.
Choi SH, Kim SY, Na HR, Kim BK, Yang DW, Kwon JC, et al. Effect of ApoE genotype on response to donepezil in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2008;25(5):445–50.
Nozawa M, Ichimiya Y, Nozawa E, Utumi Y, Sugiyama H, Murayama N, et al. Clinical effects of high oral dose of donepezil for patients with Alzheimer’s disease in Japan. Psychogeriatrics. 2009;9(2):50–5.
Santoro A, Siviero P, Minicuci N, Bellavista E, Mishto M, Olivieri F, et al. Effects of donepezil, galantamine and rivastigmine in 938 Italian patients with Alzheimer’s disease: a prospective, observational study. CNS Drugs. 2010;24(2):163–76.
Waring JF, Tang Q, Robieson WZ, King DP, Das U, Dubow J, et al. APOE-varepsilon4 carrier status and donepezil response in patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2015;47(1):137–48.
Rigaud AS, Traykov L, Latour F, Couderc R, Moulin F, Forette F. Presence or absence of at least one epsilon 4 allele and gender are not predictive for the response to donepezil treatment in Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmacogenetics. 2002;12(5):415–20.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No funding was provided for this analysis.
Conflict of interest
Tingting Xiao, Bin Jiao, Weiwei Zhang, Beisha Tang and Lu Shen declare no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, T., Jiao, B., Zhang, W. et al. Effect of the CYP2D6 and APOE Polymorphisms on the Efficacy of Donepezil in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. CNS Drugs 30, 899–907 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40263-016-0356-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40263-016-0356-1