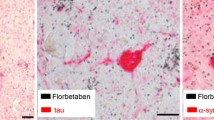
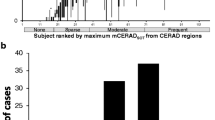
Abstract
Intravenous 18F-labelled florbetaben ([18F]florbetaben) [Neuraceq™] is a polyethylene glycol stilbene derivative that is approved in the USA, EU and South Korea for positron emission tomography (PET) imaging of the brain. It is used to estimate β-amyloid neuritic plaque density in adult patients with cognitive impairment who are being evaluated for Alzheimer’s disease and other causes of cognitive impairment. In vitro, [18F]florbetaben has high affinity and selectivity for β-amyloid. It has a short PET scan time (15–20 min). Visual assessment of regional and whole brain [18F]florbetaben PET images detected brain β-amyloid with high sensitivity and specificity, with good inter-reader agreement, in a phase III study in patients with various levels of cognitive function when compared with postmortem histopathological assessment. The whole brain visual assessment displayed high positive and negative predictive values, enabling amyloid pathology to be reliably detected or excluded. Quantitative PET analyses were generally consistent with the visual assessments. [18F]florbetaben was generally well tolerated in clinical trials. All adverse reactions in [18F]florbetaben recipients were mild to moderate in severity and the most common were injection-site-related (erythema, irritation and pain). There were no serious adverse reactions related to [18F]florbetaben. In summary, [18F]florbetaben is a highly accurate β-amyloid PET tracer that has the potential to support the clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease and other causes of cognitive decline.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hardy J, Selkoe DJ. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science. 2002;297(5580):353–6.
Dubois B, Feldman HH, Jacova C, et al. Advancing research diagnostic criteria for Alzheimer’s disease: the IWG-2 criteria. Lancet Neurol. 2014;13(6):614–29.
Jack CR Jr, Albert MS, Knopman DS, et al. Introduction to the recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011;7(3):257–62.
Rabinovici GD, Jagust WJ. Amyloid imaging in aging and dementia: testing the amyloid hypothesis in vivo. Behav Neurol. 2009;21(1):117–28.
Rowe CC, Villemagne VL. Brain amyloid imaging. J Nucl Med. 2011;52(11):1733–40.
Klunk WE, Engler H, Nordberg A, et al. Imaging brain amyloid in Alzheimer’s disease with Pittsburgh Compound-B. Ann Neurol. 2004;55(3):306–19.
Mathis CA, Mason NS, Lopresti BJ, et al. Development of positron emission tomography beta-amyloid plaque imaging agents. Semin Nucl Med. 2012;42(6):423–32.
Rowe CC, Ackerman U, Browne W, et al. Imaging of amyloid beta in Alzheimer’s disease with 18F-BAY94-9172, a novel PET tracer: proof of mechanism. Lancet Neurol. 2008;7(2):129–35.
Zhang W, Oya S, Kung MP, et al. F-18 polyethyleneglycol stilbenes as PET imaging agents targeting Aβ aggregates in the brain. Nucl Med Biol. 2005;32(8):799–809.
European Medicines Agency. Neuraceq 300 MBq/mL solution for injection: summary of product characteristics. 2014. http://www.ema.europa.eu. Accessed 13 Mar 2015.
Sabri O, Seibyl J, Rowe C, et al. Beta-amyloid imaging with florbetaben. Clin Transl Imaging. 2015;3(1):13–26.
Ni R, Gillberg PG, Bergfors A, et al. Amyloid tracers detect multiple binding sites in Alzheimer’s disease brain tissue. Brain. 2013;136(7):2217–27.
Fodero-Tavoletti MT, Brockschnieder D, Villemagne VL, et al. In vitro characterization of [18F]-florbetaben, an Aβ imaging radiotracer. Nucl Med Biol. 2012;39(7):1042–8.
Piramal Imaging. Neuraceq (florbetaben F 18 injection): US prescribing information. 2014. http://www.neuraceq.com. Accessed 13 Mar 2015.
Rominger A, Brendel M, Burgold S, et al. Longitudinal assessment of cerebral β-amyloid deposition in mice overexpressing Swedish mutant β-amyloid precursor protein using 18F-florbetaben PET. J Nucl Med. 2013;54(7):1127–34.
Brendel M, Jaworska A, Herms J, et al. Amyloid-PET predicts inhibition of de novo plaque formation upon chronic gamma-secretase modulator treatment. Mol Psychiatry. 2015;. doi:10.1038/mp.2015.74.
European Medicines Agency. Neuraceq [florbetaben (18F)]: assessment report for an initial marketing authorisation application. 2013. http://www.ema.europa.eu. Accessed 13 Mar 2015.
Senda M, Sasaki M, Yamane T, et al. Ethnic comparison of pharmacokinetics of 18F-florbetaben, a PET tracer for beta-amyloid imaging, in healthy Caucasian and Japanese subjects. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2015;42(1):89–96.
Patt M, Schildan A, Barthel H, et al. Metabolite analysis of [18F]florbetaben (BAY 94-9172) in human subjects: a substudy within a proof of mechanism clinical trial. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. 2010;284(3):557–62.
Villemagne VL, Ong K, Mulligan RS, et al. Amyloid imaging with 18F-florbetaben in Alzheimer disease and other dementias. J Nucl Med. 2011;52(8):1210–7.
Barthel H, Luthardt J, Becker G, et al. Individualized quantification of brain β-amyloid burden: results of a proof of mechanism phase 0 florbetaben PET trial in patients with Alzheimer’s disease and healthy controls. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2011;38(9):1702–14.
Barthel H, Gertz HJ, Dresel S, et al. Cerebral amyloid-β PET with florbetaben (18F) in patients with Alzheimer’s disease and healthy controls: a multicentre phase 2 diagnostic study. Lancet Neurol. 2011;10(5):424–35.
Sabri O, Seibyl J, Ishihara K, et al. Close to clinical routine phase 2 trial on florbetaben PET imaging of β-amyloid (Aβ) in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) [abstract no. 299]. J Nucl Med. 2013;54(Suppl 2).
Villemagne VL, Mulligan RS, Pejoska S, et al. Comparison of 11C-PiB and 18F-florbetaben for Aβ imaging in ageing and Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2012;39(6):983–9.
US National Institutes of Health. ClinicalTrials.gov. 2014. http://www.clinicaltrials.gov/. Accessed 13 Mar 2015.
Jennings D, Seibyl J, Sabbagh M, et al. Age dependence of brain β-amyloid deposition in Down syndrome: an [18F]florbetaben PET study. Neurology. 2015;84(5):500–7.
Ong KT, Villemagne VL, Bahar-Fuchs A, et al. Aβ imaging with 18F-florbetaben in prodromal Alzheimer’s disease: a prospective outcome study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2015;86(4):431–6.
US Food and Drug Administration. Neuraceq (florbetaben F 18 injection): clinical pharmacology and biopharmaceutics review(s). 2014. http://www.fda.gov/. Accessed 13 Mar 2015.
Sattler B, Barthel H, Patt M, et al. Radiation exposure by [F18]florbetaben, a new PET tracer for detection of cerebral β-amyloid in Caucasian and Asian healthy volunteers [abstract no. OP432]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2010;37(Suppl 2):S274.
O’Keefe GJ, Saunder TH, Ng S, et al. Radiation dosimetry of β-amyloid tracers 11C-PiB and 18F-BAY94-9172. J Nucl Med. 2009;50(2):309–15.
Sabri O, Sabbagh MN, Seibyl J, et al. Florbetaben PET imaging to detect amyloid plaques in Alzheimer’s disease: phase 3 study. Alzheimers Dement. 2015. doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2015.02.004.
Seibyl J, Barthel H, Stephens A, et al. Reliability, reproducibility and efficacy of the 18F florbetaben β-amyloid PET scan visual assessment method as trained via a computer-based instructional tool [abstract no. 300]. J Nucl Med. 2013;54(Suppl 2).
Piramal Imaging SA. Piramal Imaging SA and Ci-Co Healthcare announce commercial approval of Neuraceq™ in Korea [media release]. 2 Jun 2015. http://www.piramal.com.
Sperling RA, Aisen PS, Beckett LA, et al. Toward defining the preclinical stages of Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011;7(3):280–92.
Albert MS, DeKosky ST, Dickson D, et al. The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011;7(3):270–9.
McKhann GM, Knopman DS, Chertkow H, et al. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011;7(3):263–9.
American Psychiatric Association. Neurocognitive disorders. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 5th ed. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
Johnson KA, Minoshima S, Bohnen NI, et al. Appropriate use criteria for amyloid PET: a report of the Amyloid Imaging Task Force, the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, and the Alzheimer’s Association. Alzheimers Dement. 2013;9(1):e-1–16.
Schipke CG, Peters O, Heuser I, et al. Impact of beta-amyloid-specific florbetaben PET imaging on confidence in early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2012;33(6):416–22.
Saidlitz P, Voisin T, Vellas B, et al. Amyloid imaging in Alzheimer’s disease: a literature review. J Nutr Health Aging. 2014;18(7):723–40.
Klunk WE, Koeppe RA, Price JC, et al. The Centiloid project: standardizing quantitative amyloid plaque estimation by PET. Alzheimers Dement. 2015;11(1):1–15 e1–4.
Data on file, Piramal Imaging. 2015.
Disclosure
The preparation of this review was not supported by any external funding. Yahiya Y. Syed and Emma Deeks are salaried employees of Adis/Springer. During the peer review process, the manufacturer of the agent under review was offered an opportunity to comment on this article. Changes resulting from comments received were made by the author(s) on the basis of scientific and editorial merit.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The manuscript was reviewed by: H. Barthel, Department of Nuclear Medicine, Leipzig University Hospital, Leipzig, Germany; K. Ong, Department of Nuclear Medicine, Austin Hospital, Melbourne, Australia; R. Vandenberghe, Laboratory for Cognitive Neurology, Catholic University Leuven, Leuven, Belgium.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Syed, Y.Y., Deeks, E. [18F]Florbetaben: A Review in β-Amyloid PET Imaging in Cognitive Impairment. CNS Drugs 29, 605–613 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40263-015-0258-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40263-015-0258-7