Abstract
Background and Objectives
OTX015 (MK-8628) is a novel inhibitor of the bromodomain and extraterminal (BET)-bromodomain (BRD) protein family, binding specifically to bromodomains BRD2/3/4 and impacting the epigenetic regulation of several oncogenes. We characterized the pharmacokinetics of this first-in-class BET-BRD inhibitor administered as a single agent, including population pharmacokinetic modelling.
Methods
A dose-escalation, phase Ib study was performed with oral OTX015 in patients with haematologic malignancies, at doses starting from 10 mg once daily (QD) with continuous or discontinuous schedules. Five or eight blood samples were collected per patient for pharmacokinetic analysis. OTX015 plasma concentrations were determined using validated ultra-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC–MS/MS) and analysed using a nonlinear mixed-effects modelling software program. A population pharmacokinetic model was fitted to the data, and patient demographics and clinical chemistry parameters were tested as predictive covariates on the model parameters.
Results
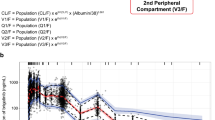
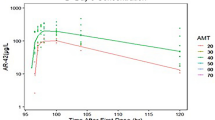
Blood samples were analysed from 81 patients treated with OTX015 at doses ranging from 10 to 160 mg QD or 40 mg twice daily (BID), and 633 time–plasma concentrations were available for analysis. A one-compartment open model with linear elimination adequately described OTX015 pharmacokinetics. The most significant covariate was lean body mass (LBM), which decreased the between-subject variability in apparent total body clearance (CL) and the volume of distribution (V). The estimated pharmacokinetic parameters were the absorption rate constant (k a) = 0.731 h−1, V = 71.4 L and CL = 8.47 L·h−1.
Conclusion
The pharmacokinetics of oral OTX015 in patients with haematologic malignancies can be described with a one-compartment model. Population pharmacokinetic modelling of OTX015 plasma concentrations showed that LBM influences V and CL. These findings do not suggest the need for dose adjustment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ott CJ, Kopp N, Bird L, Paranal RM, Qi J, Bowman T, et al. BET bromodomain inhibition targets both c-Myc and IL7R in high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2012;120:2843–52.
Zhang G, Liu R, Zhong Y, Plotnikov AN, Zhang W, Zeng L, et al. Down-regulation of NF-κB transcriptional activity in HIV-associated kidney disease by BRD4 inhibition. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:28840–51.
Herrmann H, Blatt K, Shi J, Gleixner KV, Cerny-Reiterer S, Müllauer L, et al. Small-molecule inhibition of BRD4 as a new potent approach to eliminate leukemic stem- and progenitor cells in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Oncotarget. 2012;1588–99.
Cheng Z, Gong Y, Ma Y, Lu K, Lu X, Pierce LA, et al. Inhibition of BET bromodomain targets genetically diverse glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19:1748–59.
Shimamura T, Chen Z, Soucheray M, Carretero J, Kikuchi E, Tchaicha JH, et al. Efficacy of BET bromodomain inhibition in KRAS-mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19:6183–92.
Noel JK, Iwata K, Ooike S, Sugahara K, Nakamura H, Daibata M. Development of the BET bromodomain inhibitor OTX015 (abstract no. C244). Mol Cancer Ther. 2013;12:C244.
Filippakopoulos P, Qi J, Picaud S, Shen Y, Smith WB, Fedorov O, et al. Selective inhibition of BET bromodomains. Nature. 2010;468:1067–73.
Mertz JA, Conery AR, Bryant BM, Sandy P, Balasubramanian S, Mele DA, et al. Targeting MYC dependence in cancer by inhibiting BET bromodomains. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2011;108:16669–74.
Todaro M, Boi M, Vurchio V, Ercole E, Machiorlatti R, Messana K, et al. OTX015, a novel BET inhibitor, is a promising anticancer agent for multiple myeloma (abstract no. 5531). Cancer Res. 2014;74:5531.
Boi M, Gaudio E, Bonetti P, Kwee I, Bernasconi E, Tarantelli C, et al. The BET bromodomain inhibitor OTX015 affects pathogenetic pathways in preclinical B-cell tumor models and synergizes with targeted drugs. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21:1628–38.
Wagner JG. History of pharmacokinetics. Pharmacol Ther. 1981;12:537–62.
Vozeh S, Steimer J-L, Rowland M, Morselli P, Mentré F, Balant L, et al. The use of population pharmacokinetics in drug development. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1996;30:81–93.
Althoff K, Beckers A, Bell E, Nortmeyer M, Thor T, Sprussel A, et al. A Cre-conditional MYCN-driven neuroblastoma mouse model as an improved tool for preclinical studies. Oncogene. 2015;34:3357–68.
Odore E, Lokiec F, Weill S, Noel JK, Herait P, Bekradda M, et al. Development and validation of an UPLC–MS/MS method for quantitative analysis of OTX015 in human plasma samples. Anal Methods. 2014;6:9108–15.
Kuhn E, Lavielle M. Maximum likelihood estimation in nonlinear mixed effects models. Comput Stat Data Anal. 2005;49:1020–38.
Friberg LE, Henningsson A, Maas H, Nguyen L, Karlsson MO. Model of chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression with parameter consistency across drugs. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:4713–21.
De Baerdemaeker LE, Mortier EP, Struys MM. Pharmacokinetics in obese patients. Contin Educ Anaesth Crit Care Pain. 2004;4:152–5.
Odore E, Rezai K, Riveiro E, Bourdel F, Herait P, Cvitkovic E, et al. A phase I pharmacokinetic study of OTX015 for the treatment of patients with hematologic malignancies (abstract no. LB-231). Cancer Res. 2014;74:LB-231.
Stathis A, Quesnel B, Amorim S, Thieblemont C, Zucca E, Raffoux E, et al. Results of a first-in-man phase I trial assessing OTX015, an orally available BET-bromodomain (BRD) inhibitor, in advanced hematologic malignancies (abstract no. 5LBA). Eur J Cancer. 2014;50:196.
Chalret du Rieu Q, Fouliard S, White-Koning M, Kloos I, Chatelut E, Chenel M. Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic modeling of abexinostat-induced thrombocytopenia across different patient populations: application for the determination of the maximum tolerated doses in both lymphoma and solid tumour patients. Invest New Drugs. 2014;32:985–94.
Financial Support
This study was funded by Oncoethix SA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
EC and PH are founders of Oncoethix. EO, MB, FB, CK and MER are employees of Oncology Therapeutic Development. FL, ER, AS, CT, BQ, DC and KR have no conflicts of interest that are directly relevant to the content of this manuscript.
Additional information
Oncoethix GmbH is a wholly owned subsidiary of Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. (formerly Oncoethix SA)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Odore, E., Lokiec, F., Cvitkovic, E. et al. Phase I Population Pharmacokinetic Assessment of the Oral Bromodomain Inhibitor OTX015 in Patients with Haematologic Malignancies. Clin Pharmacokinet 55, 397–405 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40262-015-0327-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40262-015-0327-6