Abstract
Background and Objective
The anti-epileptic drug levetiracetam is excreted renally. The objective of this trial was to evaluate the pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam in Japanese patients with renal impairment including end-stage renal disease (ESRD) to confirm that existing dosing instructions—based on data from European patients—are appropriate in a Japanese population.
Methods
This was a nonrandomised, open-label trial. Six participants were allocated to each of five groups (normal renal function, mild, moderate and severe renal impairment and ESRD); 30 participants in total. Participants received a single dose of levetiracetam 500 mg (normal or mild), 250 mg (moderate or severe), or 500 mg followed by 250 mg post-haemodialysis (ESRD). Blood and urine samples were obtained serially for levetiracetam and metabolite determinations. Noncompartmental pharmacokinetic parameters were calculated and steady-state profiles were simulated using the superposition method.
Results
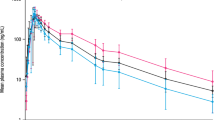
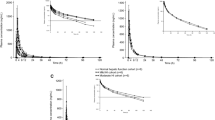
In this trial, levetiracetam total clearance decreased proportionally with creatinine clearance: 52, 31, 25, 20 and 11 mL/min/1.73 m2 in healthy controls and in patients with mild, moderate, severe renal impairment, and ESRD, respectively. Simulated levetiracetam plasma profiles using the recommended dose adjustments were within the range for normal renal function. Overall, results from this trial were consistent with historical European data.
Conclusion
These findings confirm that the dosing instructions are appropriate for Japanese patients with renal impairment including ESRD.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stockis A, Lu S, Tonner F, Otoul C. Clinical pharmacology of levetiracetam for the treatment of epilepsy. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2009;2(4):339–50.
Toublanc N, Lacroix BD, Yamamoto J. Development of an integrated population pharmacokinetic model for oral levetiracetam in populations of various ages and ethnicities. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2014;29(1):61–8.
Pigeolet E, Jacqmin P, Sargentini-Maier ML, Stockis A. Population pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam in Japanese and Western adults. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2007;46(6):503–12.
Patsalos PN. Pharmacokinetic profile of levetiracetam: toward ideal characteristics. Pharmacol Ther. 2000;85(2):77–85.
Perucca E, Gidal BE, Baltès E. Effects of antiepileptic comedication on levetiracetam pharmacokinetics: a pooled analysis of data from randomized adjunctive therapy trials. Epilepsy Res. 2003;53(1–2):47–56.
Gidal BE, Baltès E, Otoul C, Perucca E. Effect of levetiracetam on the pharmacokinetics of adjunctive antiepileptic drugs: a pooled analysis of data from randomized clinical trials. Epilepsy Res. 2005;64(1–2):1–11.
Ramael S, De Smedt F, Toublanc N, Otoul C, Boulanger P, Riethuisen JM, Stockis A. Single-dose bioavailability of levetiracetam intravenous infusion relative to oral tablets and multiple-dose pharmacokinetics and tolerability of levetiracetam intravenous infusion compared with placebo in healthy subjects. Clin Ther. 2006;28(5):734–44.
Toublanc N, Sargentini-Maier ML, Lacroix B, Jacqmin P, Stockis A. Retrospective population pharmacokinetic analysis of levetiracetam in children and adolescents with epilepsy: dosing recommendations. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2008;47(5):333–41.
Strolin-Benedetti M, Whomsley R, Nicolas JM, Young C, Baltès E. Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of 14C-levetiracetam, a new antiepileptic agent, in healthy volunteers. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2003;59(8–9):621–30.
Baltès E, Coupez R. Levetiracetam dose adjustment for patients on hemodialysis [abstract]. Epilepsia. 2000;41:254.
French J. Use of levetiracetam in special populations. Epilepsia. 2001;42(Suppl 4):40–3.
Patsalos PN. Clinical pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2004;43(11):707–24.
E-Keppra, Japanese package insert. Available at http://www.info.pmda.go.jp/downfiles/ph/PDF/820110_1139010F1024_1_10.pdf. Accessed 19 Sept 2014.
Rouits E, Burton I, Guénolé E, Troenaru MM, Stockis A, Sargentini-Maier ML. Pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam XR 500 mg tablets. Epilepsy Res. 2009;84(2–3):224–31.
Lee CS, Marbury TC. Drug therapy in patients undergoing haemodialysis, clinical pharmacokinetic considerations. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1984;9:42–66.
Massry SG, Glassock RJ. Dialysis therapy. In: Massry and Glassock’s Textbook of Nephrology. vol. 84, 4th edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2000, p. 1474–90.
Lalonde RL, Wagner JA. Drug development perspective on pharmacokinetic studies of new drugs in patients with renal impairment. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2009;86(5):557–61.
Olyaei AJ, Steffl JL. A quantitative approach to drug dosing in chronic kidney disease. Blood Purif. 2011;31(1–3):138–45.
Verbeeck RK, Musuamba FT. Pharmacokinetics and dosage adjustment in patients with renal dysfunction. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2009;65(8):757–73.
Brodie MJ, Elder AT, Kwan P. Epilepsy in later life. Lancet Neurol. 2009;8(11):1019–30.
Cockcroft DW, Gault MH. Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron. 1976;16(1):31–41.
DuBois D, DuBois EF. A formula to estimate the approximate surface area if height and weight be known. Arch Intern Med. 1916;17(6–2):863–71.
Acknowledgments
UCB Pharma sponsored this study and was involved in the design and conduct of the study, and collection, management, and analysis of the data. Nathalie Toublanc, Armel Stockis and Junichi Yamamoto are employees of UCB Pharma. Yuji Kumagai was the medical advisor and is a Professor of the Kitasato Clinical Research Center, Kitasato University, Japan. The authors thank Katsumi Yoshida, RPh for statistical assistance, Ludovicus Staelens (both UCB Pharma) who was responsible for the bioanalysis, and the principal investigators Teruo Fukumoto, MD, Tadayuki Hiroki, MD (both from Kurume Clinical Pharmacology Clinic), and Tokuro Kobayashi, MD (Moriya Keiyu Hospital). Fiona Swain of Mediwrite Ltd, United Kingdom provided medical writing support funded by UCB Pharma, and Azita Tofighy, UCB Pharma, provided editorial support and coordinated the manuscript development process.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamamoto, J., Toublanc, N., Kumagai, Y. et al. Levetiracetam Pharmacokinetics in Japanese Subjects with Renal Impairment. Clin Drug Investig 34, 819–828 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40261-014-0237-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40261-014-0237-7