Abstract
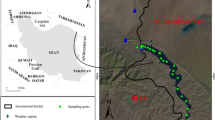
This paper investigates evaporation at Algardabiya Reservoir, Sirte, Libya. Evaporation from Algardabiya Reservoir is the main problem faced which contributes in water loss. Libya is considered as arid region with limited water resources. Modeling of evaporation from the reservoir is crucial for water management at the area. Three evaporation models, Linacre, DeBruin and Harbeck, were selected to predict reservoir evaporation, and meteorological data were input to the models from a weather station at the reservoir site. Daily evaporation also was measured, and statistical tests were conducted to check model accuracy. These tests showed that the models produced reasonable accuracy, with biases in model prediction of 6.5, 8.5 and 9.4 for the DeBruin, Linacre and Harbeck models, respectively. Based on the model testing, the Linacre model can be used to predict evaporation from the Reservoir when available meteorological data are limited to air temperature only. However, we recommend application of the DeBruin and Harbeck models when more meteorological data are available.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singh V.P., Xu C.Y.: Evaluation and generalization of 13 mass-transfer equations for determining free water evaporation. J. Hydrol. Process. 11, 311–323 (1997)
McCuen R.H.: Hydrologic analysis and design. Prentice-Hall, NJ (2005)
Linsley R.K., Kohler M.A., Paulhus J.L.H.: Evaporation and transpiration. In: Applied Hydrology, pp. 154–181. McGraw-Hill Inc, New York (1949)
Chow V.T.: Evapotranspiration. In: Handbook of Applied Hydrology, pp. 11–38. McGraw-Hill Inc, New York (1964)
Webb E.K.: A pan-lake evaporation relationship. J. Hydrol. 4(1), 1–11 (1966)
Hounam, C.E.: Comparison between pan and lake evaporation. World Meteorological organization, Geneva (1973)
Goodridge, J.R.: Evaporation from water surfaces in California. In: California Department of Water Resources, Bulletin, pp. 73–79 (1979)
Abtew W.: Evaporation estimation for Lake Okeechobee in south Florida. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. ASCE. 127(3), 140–147 (2001)
Molina Martínez J.M. et al.: A simulation model for predicting hourly pan evaporation from meteorological data. J. Hydrol. 318, 250–261 (2006)
Waranka K., Pochop L.: Analayses of equation for free water evaporation estimates. Water Resour. Res. 24(7), 979–984 (1988)
Linacre, E.T.: Climate data and resources. Routledge (1992)
Allen, R.G.; et al.: Crop evapotranspiration: guidelines for computing crop water requirements. Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56, FAO, Rome (1998)
Xu C.-Y., Singh V.P.: Dependence of evaporation on meteorological variables at different time scales and intercomparison of estimation methods. Hydrol. Process 12, 429–442 (1998)
Finch J.W., Gash J.H.C.: Application of a simple finite difference model for estimating evaporation from open water. J. Hydrology 255, 253–259 (2002)
Coulomb C.V. et al.: Lake evaporation estimates in tropical Africa (Lake Ziway, Ethiopia). J. Hydrol. 245, 1–18 (2001)
Rosenberry D.O. et al.: Comparison of 15 evaporation methods applied to a small mountain lake in the northeastern USA. J. Hydrol. 340, 149–166 (2007)
Kohler, M.A.; Nordenson, T.J.; Fox W.E.: Evaporation from Pans and Lakes. US Deptartment of Commerce, Weather Bureau Research Paper 38 (1955)
Shuttleworth W.J.: Macrohydrology—the new challenge for process hydrology. J. Hydrol. 100, 31–56 (1988)
Anderson, R.E.: Energy-budget studies. In: Water-loss Investigations—Lake Hefiier studies. Technical Report: US Geological Survey Professional Paper 269, pp. 71–119 (1954)
Harbeck G.E.J.: A practical field technique for measuring reservoir evaporation utilizing mass-transfer theory. US Geological Survey 272(E), 101–105 (1962)
Penman H.L.: Natural evaporation from open water, bare soil and grass. Proc. Roy. Soc. Lond A193, 120–146 (1948)
Linacre E.T.: A simple formula for estimating evaporation rates in various climates, using temperature data alone. Agric. Meteorol. 18, 409–424 (1977)
Moghaddamnia, A.; et al.: Evaporation estimation using support vector machines technique. World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology, pp. 14–22 (2008)
de Bruin H.A.R.: A simple model for shallow lake evaporation. J. Appl. Meteorol. 17, 1132–1134 (1978)
Singh V.P., Xu C.-Y.: Sensitivity of mass transfer-based evaporation equations to errors in daily and monthly input data. Hydrol. Process 11, 1465–1473 (1997)
Xu C.-Y., Singh V.P.: Evaluation and generalization of temperature-based methods for calculating evaporation. Hydrol. Process 15, 305–319 (2001)
Mosner, M.S.; Aulenbach, B.T.: Comparison of methods used to estimate lake evaporation for a water budget of Lake Seminole, south western Georgia and north western Florida. In: Proceedings of the Georgia Water Resources Conference (2003)
Finch J.W.: A comparison between measured and modeled open water evaporation from a reservoir in South-East England. Hydrol. Process 15, 2771–2778 (2001)
IMB: Grain production project of Wadi Barjuj. Final Report, Secretariat of Agrarian Reform and Land Reclamation, Socialist People’s Libyan Arab Jamahiriya, Libya (1980)
McKenzie H.S., Elsaleh B.O.: The Libyan Great Man Made River Project, project overview. Proc. Instn Civ Engr. Wat. Marit. and Energy. Proc. ICE Water Marit. Energy 106(2), 103–122 (1994)
GMRA system implementation and management city of Sirte, Evaporation from Algardibyia Reservoir, Report, 11, pp 12, Report to Great Manmade River Authority, Tripoli (2000)
Dingman, S.L.: Physical Hydrology, vol. xiv, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, p. 575 (1994)
Brutsaert, W.H.: Evaporation into the atmosphere: theory, history and applications, Reidel, Dordrecht, p. 299. ISBN: 9027712476.299p.1982
Meyer S.J., Hubard K.G., Wilhite D.A.: Estimating potential evapotranspiration: the effect of random and systematic errors. Agric. For. Meteorol 46, 285–296 (1989)
Linacre E.T.: Data-sparse estimation of Lake Evaporation, using a simplified Penman equation. Agric. Forest Meteorol. 64, 237–256 (1993)
Doorenbos, J.; Pruitt, N.O.: Guidelines for prediction of crop water requirements, 2nd edn. Italy FAQ Irrig. And Drain. Paper, 24, FAO, Rome, p. 156 (1977)
Winter T.C.: Uncertainties in estimating the water balances of lakes. Water Resour. Bull. 17(1), 82–115 (1981)
Farnsworth, R.K.; Thomson, E.S.; Peck, E.L.: Evaporation atlas for contiguous 48 United States. NOAA Technical Report NWS 33 (1982)
Linsley R.K., Kohler M.A., Paulhus J.L.H.: Hydrology for Engineers. McGraw-Hill, New York (1982)
Anyadike R.N.C.: The Linacre evaporation formula tested and compared to others in various climates over West Africa. Agric. Forest Meteorol. 39, 111–119 (1987)
Linacre E.T.: Empirical relationships involving global-radiation intensity and ambient temperature at various latitudes and altitudes. Archiv. Meteorol. Geophys. Bioklimatol 17, 1–20 (1969)
Jensen M.E.: Consumptive use of water and irrigation requirements. ASAE, New York (1973)
Sutton O.G.: Wind structure and evaporation in a turbulent atmosphere. Proc. Rov. Soc. Lond A146, 701–722 (1934)
Sutton O.G.: The application to micrometeorology of the theory of turbulent flow over rough surfaces. Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 75, 236 (1949)
Sverdrup H.U.: The humidity gradient over the sea surface. J. Meteorol. 3, 1–8 (1946)
Meyer, A.F.: Evaporation from lakes and reservoirs. Minnesota Resources Commission, St. Paul (1944)
Thornthwaite C.W., Holzman B.: The determination of land and water surfaces. Month. Weather Rev. 67, 4–11 (1939)
Dalton J.: Meteorological observations. Mem. Manch. Lit. Phil. Soc. 5, 346–372 (1802)
Yamamuto G.: Investigations of evaporation from pans. Am. Geophys. Union Trans. 31, 349–366 (1950)
Marciano J.J., Harbeck G.E.J: Mass-transfer studies In: Water-loss Investigations-Lake Hefiier studies, Technical Report. US Geol. Surv. 269, 46–70 (1954)
Survey, U.S.G.: Water-loss investigations: Lake Hefner studies. Technical Report, U. S. G. S. Professional papers, 269 (1954)
Priestly C.H.B., Taylor R.J.: On the assessment of the surface heat flux and evaporation using large-scale parameters. Mon. Water Rev. 100, 81–92 (1972)
Sweers H.E.: A nomogram to estimate the heat exchange coefficient at the air-water interface as a function of wind speed and temperature; a critical survey of some literature. J. Hydrol. 30, 375–401 (1976)
Knapp H.V., Yu V.S., Poggel E.C.: Monthly evaporation for Milford lake in Kansas. J. Irrig. Drain. Div. ASCE. 110(2), 138–148 (1984)
Fox D.G.: Judging air quality model performance. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 62, 599–609 (1981)
Willmott C.J.: Some comments on the evaluation of model performance. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 63, 1309–1313 (1982)
Willmott C.J. et al.: Statistics for the evaluation and comparison of models. Geophys. Res. 90, 8995–9005 (1985)
Kennedy J.B., Neville A.M.: Basic statistical methods for Engineers and Scientists, 3rd edn. Harper and Row, New York (1986)
Ma C.C.Y., Iqbal M.: Statistical comparison of solar radiation correlations-Monthly average global and diffuse radiation on horizontal surfaces. Sol. Energy. 33, 143–148 (1984)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benzaghta, M.A., Mohammed, T.A., Ghazali, A.H. et al. Validation of Selected Models for Evaporation Estimation from Reservoirs Located in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions. Arab J Sci Eng 37, 521–534 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-012-0194-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-012-0194-5