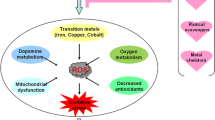
Abstract
This study examined the role of alpha-synuclein in regulating cadmium (Cd)-induced neurotoxicity using the N27 dopaminergic neuronal model of Parkinson’s disease (PD) that stably expresses wild-type human α-synuclein (α-Syn) or empty vector (Vec) control. We report that α-Syn significantly increased Cd-induced cytotoxicity as compared to Vec control cells upon 24 h exposure. To explore the cellular mechanisms, we examined oxidative stress, caspase activation, and Cd uptake and intracellular accumulation. Expression of α-Syn coupled with Cd-induced cytotoxicity increased oxidative stress. Inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) revealed an increase in Cd uptake and intracellular accumulation in α-Syn-expressing cells upon Cd exposure. Analysis of the mitochondrial mediated apoptotic pathway showed greater activation of caspase-9 and caspase-3 in α-Syn cells. To functionally evaluate the role of metal transporters in the altered Cd phenotype, we examined Cd toxicity in the presence of nontoxic levels of divalent manganese Mn(II) and iron Fe(II). Co-treatment with Fe(II) or Mn(II) did not significantly attenuate Cd-induced cytotoxicity. We report that Cd exposure decreased the divalent metal transporter 1 and Akt protein levels in the α-Syn-expressing cells without altering native PKCδ protein levels in both Vec control and α-Syn lines. In addition, we show decreased basal metallothionein-3 protein expression in α-Syn-expressing cells. Co-treatment with N-acetyl-l-cysteine was sufficient to attenuate and abolish the α-Syn × Cd-induced cytotoxicity. Collectively, these results demonstrate that α-Syn exhibits neurotoxic properties upon acute Cd exposure to cause cell death by causing oxidative stress, increasing Cd uptake, altering caspase-9 and caspase-3 activation, and diminishing the neuroprotective effect of Akt in a dopaminergic neuronal model of PD.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afeseh Ngwa H, Kanthasamy A, Anantharam V, Song C, Witte T, Houk R, Kanthasamy AG (2009) Vanadium induces dopaminergic neurotoxicity via protein kinase Cdelta dependent oxidative signaling mechanisms: relevance to etiopathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 240:273–285. doi:10.1016/j.taap. 2009.07.025
Anantharam V, Kitazawa M, Wagner J, Kaul S, Kanthasamy AG (2002) Caspase-3-dependent proteolytic cleavage of protein kinase Cdelta is essential for oxidative stress-mediated dopaminergic cell death after exposure to methylcyclopentadienyl manganese tricarbonyl. J Neurosci 22:1738–1751
Bisaglia M, Tessari I, Mammi S, Bubacco L (2009) Interaction between alpha-synuclein and metal ions, still looking for a role in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. NeuroMolecular Med 11:239–251
Bornhorst J, Chakraborty S, Meyer S, Lohren H, Brinkhaus SG, Knight AL, Caldwell KA, Caldwell GA, Karst U, Schwerdtle T, Bowman A, Aschner M (2014) The effects of pdr1, djr1.1 and pink1 loss in manganese-induced toxicity and the role of α-synuclein in C. elegans. Metallomics 6:476–490. doi:10.1039/c3mt00325f
Brunet A, Datta SR, Greenberg ME (2001) Transcription-dependent and -independent control of neuronal survival by the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Curr Opin Neurobiol 11:297–305
Calo L, Wegrzynowicz M, Santivañez-Perez J, Grazia Spillantini M (2016) Synaptic failure and α-synuclein. Mov Disord 31:169–177. doi:10.1002/mds.26479
Chen L, Liu L, Huang S (2008) Cadmium activates the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway via induction of reactive oxygen species and inhibition of protein phosphatases 2A and 5. Free Radic Biol Med 45:1035–1044. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.07.011
Chen S, Ren Q, Zhang J, Ye Y, Zhang Z, Xu Y, Guo M, Ji H, Xu C, Gu C, Gao W, Huang S, Chen L (2014) N-acetyl-L-cysteine protects against cadmium-induced neuronal apoptosis by inhibiting ROS-dependent activation of Akt/mTOR pathway in mouse brain. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 40:759–777. doi:10.1111/nan.12103
Cox AD, Noble AE, Saito MA (2014) Cadmium enriched stable isotope uptake and addition experiments with natural phytoplankton assemblages in the Costa Rica Upwelling Dome. Mar Chem 166:70–81. doi:10.1016/j.marchem.2014.09.009
Dexter DT, Carayon A, Javoy-Agid F, Agid Y, Wells FR, Daniel SE, Lees AJ, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1991) Alterations in the levels of iron, ferritin and other trace metals in Parkinson’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases affecting the basal ganglia. Brain 114(Pt 4):1953–1975
Dickson DW (2012) Parkinson’s disease and parkinsonism: neuropathology. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a009258
Dorian C, Gattone VH, Klaassen CD (1992) Accumulation and degradation of the protein moiety of cadmium-metallothionein (CdMT) in the mouse kidney. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 117:242–248
Endo T, Kimura O, Sakata M (2002) Effects of P-glycoprotein inhibitors on cadmium accumulation in cultured renal epithelial cells, LLC-PK1, and OK. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 185:166–171
Erfurt C, Roussa E, Thévenod F (2003) Apoptosis by Cd2+ or CdMT in proximal tubule cells: different uptake routes and permissive role of endo/lysosomal CdMT uptake. Am J Physiol, Cell Physiol 285:C1367–C1376. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00217.2003
Faroon O, Ashizawa A, Wright S, Tucker P, Jenkins K, Ingerman L, Rudisill C (2012) Toxicological Profile for Cadmium. Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry Toxicological Profile, Atlanta, Georgia
Flanagan PR, McLellan JS, Haist J, Cherian G, Chamberlain MJ, Valberg LS (1978) Increased dietary cadmium absorption in mice and human subjects with iron deficiency. Gastroenterology 74:841–846
Flora SJS, Mittal M, Mehta A (2008) Heavy metal induced oxidative stress & its possible reversal by chelation therapy. Indian J Med Res 128:501–523
Fuhr BJ, Rabenstein DL (1973) Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the solution chemistry of metal complexes. IX. The binding of cadmium, zinc, lead, and mercury by glutathione. J Am Chem Soc 95:6944–6950
Geret F, Serafim A, Barreira L, Bebianno MJ (2002) Effect of cadmium on antioxidant enzyme activities and lipid peroxidation in the gills of the clam Ruditapes decussatus. Biomarkers 7:242–256. doi:10.1080/13547500210125040
Goering PL, Waalkes MP, Klaassen CD (1995) Toxicology of cadmium. In: Goyer RA, Cherian MG (eds) Toxicology of metals, handbook of experimental pharmacology. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 189–214. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-79162-8_9
Gonçalves JF, Fiorenza AM, Spanevello RM, Mazzanti CM, Bochi GV, Antes FG, Stefanello N, Rubin MA, Dressler VL, Morsch VM, Schetinger MRC (2010) N-Acetylcysteine prevents memory deficits, the decrease in acetylcholinesterase activity and oxidative stress in rats exposed to cadmium. Chem Biol Interact 186:53–60. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2010.04.011
Gonzalez-Horta A (2015) The interaction of alpha-synuclein with membranes and its implication in Parkinson’s disease: a literature review. Nat Prod Commun 10:1775–1778
Gorell JM, Johnson CC, Rybicki BA, Peterson EL, Kortsha GX, Brown GG, Richardson RJ (1999) Occupational exposure to manganese, copper, lead, iron, mercury and zinc and the risk of Parkinson’s disease. Neurotoxicology 20:239–247
Guo JT, Chen AQ, Kong Q, Zhu H, Ma CM, Qin C (2008) Inhibition of vesicular monoamine transporter-2 activity in alpha-synuclein stably transfected SH-SY5Y cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol 28:35–47. doi:10.1007/s10571-007-9227-0
Harischandra DS, Jin H, Anantharam V, Kanthasamy A, Kanthasamy AG (2015) α-Synuclein protects against manganese neurotoxic insult during the early stages of exposure in a dopaminergic cell model of Parkinson’s disease. Toxicol Sci 143:454–468. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfu247
Himeno S, Yanagiya T, Enomoto S, Kondo Y, Imura N (2002) Cellular cadmium uptake mediated by the transport system for manganese. Tohoku J Exp Med 196:43–50
Hirsch EC, Brandel JP, Galle P, Javoy-Agid F, Agid Y (1991) Iron and aluminum increase in the substantia nigra of patients with Parkinson’s disease: an X-ray microanalysis. J Neurochem 56:446–451
Hussain T, Shukla GS, Chandra SV (1987) Effects of cadmium on superoxide dismutase and lipid peroxidation in liver and kidney of growing rats: in vivo and in vitro studies. Pharmacol Toxicol 60:355–358
Jenner P (2003) Oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 53(Suppl 3):S26–S36; discussion S36. doi:10.1002/ana.10483
Jin T, Lu J, Nordberg M (1998) Toxicokinetics and biochemistry of cadmium with special emphasis on the role of metallothionein. Neurotoxicology 19:529–535
Jin H, Kanthasamy A, Ghosh A, Yang Y, Anantharam V, Kanthasamy AG (2011a) alpha-Synuclein negatively regulates protein kinase Cdelta expression to suppress apoptosis in dopaminergic neurons by reducing p300 histone acetyltransferase activity. J Neurosci 31:2035–2051
Jin H, Kanthasamy A, Ghosh A, Yang Y, Anantharam V, Kanthasamy AG (2011b) α-Synuclein negatively regulates protein kinase Cδ expression to suppress apoptosis in dopaminergic neurons by reducing p300 histone acetyltransferase activity. J Neurosci 31:2035–2051. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5634-10.2011
Jing Y, Liu L-Z, Jiang Y, Zhu Y, Guo NL, Barnett J, Rojanasakul Y, Agani F, Jiang B-H (2012) Cadmium increases HIF-1 and VEGF expression through ROS, ERK, and AKT signaling pathways and induces malignant transformation of human bronchial epithelial cells. Toxicol Sci 125:10–19. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfr256
Jung K-T, Kim H-R, Lee B-H, Kim S-H, So K-Y, An T-H, Lee H-Y, Oh S-H (2015) Differential effects of p38 and JNK activation by GSK3 on cadmium-induced autophagy and apoptosis. Toxicol Res 4:976–985. doi:10.1039/C5TX00007F
Kägi JH, Schäffer A (1988) Biochemistry of metallothionein. Biochemistry 27:8509–8515
Kamiyama T, Miyakawa H, Li JP, Akiba T, Liu JH, Liu J, Marumo F, Sato C (1995) Effects of one-year cadmium exposure on livers and kidneys and their relation to glutathione levels. Res Commun Mol Pathol Pharmacol 88:177–186
Kaul S, Kanthasamy A, Kitazawa M, Anantharam V, Kanthasamy AG (2003) Caspase-3 dependent proteolytic activation of protein kinase C delta mediates and regulates 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+)-induced apoptotic cell death in dopaminergic cells: relevance to oxidative stress in dopaminergic degeneration. Eur J Neurosci 18:1387–1401
Kaul S, Anantharam V, Kanthasamy A, Kanthasamy AG (2005) Wild-type alpha-synuclein interacts with pro-apoptotic proteins PKCdelta and BAD to protect dopaminergic neuronal cells against MPP+−induced apoptotic cell death. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 139:137–152. doi:10.1016/j.molbrainres.2005.05.022
Klaassen CD, Liu J, Choudhuri S (1999) Metallothionein: an intracellular protein to protect against cadmium toxicity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 39:267–294. doi:10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.39.1.267
Kogan I, Ramjeesingh M, Li C, Kidd JF, Wang Y, Leslie EM, Cole SPC, Bear CE (2003) CFTR directly mediates nucleotide-regulated glutathione flux. EMBO J 22:1981–1989. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdg194
Kwakye GF, Paoliello MMB, Mukhopadhyay S, Bowman AB, Aschner M (2015) Manganese-induced parkinsonism and Parkinson’s disease: shared and distinguishable features. Int J Environ Res Public Health 12:7519–7540. doi:10.3390/ijerph120707519
de Lau LML, Breteler MMB (2006) Epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol 5:525–535. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(06)70471-9
Liu J, Cheng M-L, Yang Q, Shan K-R, Shen J, Zhou Y, Zhang X, Dill AL, Waalkes MP (2007) Blood metallothionein transcript as a biomarker for metal sensitivity: low blood metallothionein transcripts in arsenicosis patients from Guizhou, China. Environ Health Perspect 115:1101–1106. doi:10.1289/ehp.10035
Maret W (2000) The function of zinc metallothionein: a link between cellular zinc and redox state. J Nutr 130:1455S–1458S
McDonnell MA, Wang D, Khan SM, Vander Heiden MG, Kelekar A (2003) Caspase-9 is activated in a cytochrome c-independent manner early during TNFalpha-induced apoptosis in murine cells. Cell Death Differ 10:1005–1015. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4401271
Middleton FA, Strick PL (2000) Basal ganglia and cerebellar loops: motor and cognitive circuits. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 31:236–250
Milnerowicz H, Jabłonowska M, Bizoń A (2009) Change of zinc, copper, and metallothionein concentrations and the copper-zinc superoxide dismutase activity in patients with pancreatitis. Pancreas 38:681–688. doi:10.1097/MPA.0b013e3181a53d1
Okuda B, Iwamoto Y, Tachibana H, Sugita M (1997) Parkinsonism after acute cadmium poisoning. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 99:263–265
Palmiter RD, Findley SD, Whitmore TE, Durnam DM (1992) MT-III, a brain-specific member of the metallothionein gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89:6333–6337
Prozialeck WC, Edwards JR (2012) Mechanisms of cadmium-induced proximal tubule injury: new insights with implications for biomonitoring and therapeutic interventions. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 343:2–12. doi:10.1124/jpet.110.166769
Singleton AB, Farrer M, Johnson J, Singleton A, Hague S, Kachergus J, Hulihan M, Peuralinna T, Dutra A, Nussbaum R, Lincoln S, Crawley A, Hanson M, Maraganore D, Adler C, Cookson MR, Muenter M, Baptista M, Miller D, Blancato J, Hardy J, Gwinn-Hardy K (2003) alpha-Synuclein locus triplication causes Parkinson’s disease. Science (New York, NY) 302:841
Spillantini MG, Crowther RA, Jakes R, Cairns NJ, Lantos PL, Goedert M (1998) Filamentous alpha-synuclein inclusions link multiple system atrophy with Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurosci Lett 251:205–208
Stefanis L (2012) α-Synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2:a009399. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a009399
Thévenod F (2009) Cadmium and cellular signaling cascades: to be or not to be? Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 238:221–239. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2009.01.013
Tommasini R, Evers R, Vogt E, Mornet C, Zaman GJ, Schinkel AH, Borst P, Martinoia E (1996) The human multidrug resistance-associated protein functionally complements the yeast cadmium resistance factor 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:6743–6748. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.13.6743
Uchida Y (1994) Growth-inhibitory factor, metallothionein-like protein, and neurodegenerative diseases. Biol Signals 3:211–215
Waldron KJ, Robinson NJ (2009) How do bacterial cells ensure that metalloproteins get the correct metal? Nat Rev Microbiol 7:25–35. doi:10.1038/nrmicro2057
Williams BB, Kwakye GF, Wegrzynowicz M, Li D, Aschner M, Erikson KM, Bowman AB (2010a) Altered manganese homeostasis and manganese toxicity in a Huntington’s disease striatal cell model are not explained by defects in the iron transport system. Toxicol Sci 117:169–179. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfq174
Williams BB, Li D, Wegrzynowicz M, Vadodaria BK, Anderson JG, Kwakye GF, Aschner M, Erikson KM, Bowman AB (2010b) Disease-toxicant screen reveals a neuroprotective interaction between Huntington’s disease and manganese exposure. J Neurochem 112:227–237. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06445.x
Wu J, Li Q, Wang X, Yu S, Li L, Wu X, Chen Y, Zhao J, Zhao Y (2013) Neuroprotection by curcumin in ischemic brain injury involves the Akt/Nrf2 pathway. PLoS One 8:e59843. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0059843
Xu Y, Feng L, Jeffrey PD, Shi Y, Morel FMM (2008) Structure and metal exchange in the cadmium carbonic anhydrase of marine diatoms. Nature 452:56–61. doi:10.1038/nature06636
Yang Z, Yang S, Qian SY, Hong J-S, Kadiiska MB, Tennant RW, Waalkes MP, Liu J (2007) Cadmium-induced toxicity in rat primary mid-brain neuroglia cultures: role of oxidative stress from microglia. Toxicol Sci 98:488–494. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfm106
Zhu M, Qin Z-J, Hu D, Munishkina LA, Fink AL (2006) Alpha-synuclein can function as an antioxidant preventing oxidation of unsaturated lipid in vesicles. Biochemistry 45:8135–8142. doi:10.1021/bi052584t
Zuo P, Qu W, Cooper RN, Goyer RA, Diwan BA, Waalkes MP (2009) Potential role of alpha-synuclein and metallothionein in lead-induced inclusion body formation. Toxicol Sci 111:100–108. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfp132
Acknowledgements
This research was supported in part by Oberlin College Office of Foundation, Government and Corporate Grants (GFK), Robert Rich Research Grant at Oberlin College and Nu Rho Psi (WC), and support from the National Science Foundation and Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation (MAS). We are grateful to Edmund Mawuli Korley (Oberlin College) for his technical support.
Author Contributions
GFK conceived the research idea, designed the experiments, coordinated the study, and wrote the paper. WC, JJ, MM, and MAS provided language help and proof read the article. GFK, WC, and JJ performed the experiments and analyzed the results shown in Figs. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9. MM and MAS performed the ICP-MS experiments shown in Fig. 5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chong, W., Jiménez, J., McIIvin, M. et al. α-Synuclein Enhances Cadmium Uptake and Neurotoxicity via Oxidative Stress and Caspase Activated Cell Death Mechanisms in a Dopaminergic Cell Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Neurotox Res 32, 231–246 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-017-9725-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-017-9725-x