Abstract
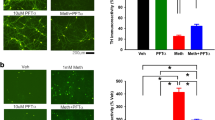
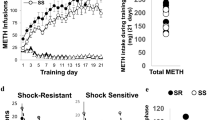
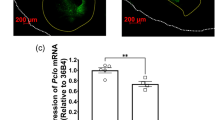
p53 plays an essential role in the regulation of cell death in dopaminergic (DA) neurons and its activation has been implicated in the neurotoxic effects of methamphetamine (MA). However, how p53 mediates MA neurotoxicity remains largely unknown. In this study, we examined the effect of DA-specific p53 gene deletion in DAT-p53KO mice. Whereas in vivo MA binge exposure reduced locomotor activity in wild-type (WT) mice, this was significantly attenuated in DAT-p53KO mice and associated with significant differences in the levels of the p53 target genes BAX and p21 between WT and DAT-p53KO. Notably, DA-specific deletion of p53 provided protection of substantia nigra pars reticulata (SNpr) tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) positive fibers following binge MA, with DAT-p53KO mice having less decline of TH protein levels in striatum versus WT mice. Whereas DAT-p53KO mice demonstrated a consistently higher density of TH fibers in striatum compared to WT mice at 10 days after MA exposure, DA neuron counts within the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) were similar. Finally, supportive of these results, administration of a p53-specific inhibitor (PFT-α) provided a similarly protective effect on MA binge-induced behavioral deficits. Neither DA specific p53 deletion nor p53 pharmacological inhibition affected hyperthermia induced by MA binge. These findings demonstrate a specific contribution of p53 activation in behavioral deficits and DA neuronal terminal loss by MA binge exposure.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aloyz RS, Bamji SX, Pozniak CD, Toma JG, Atwal J, Kaplan DR, Miller FD (1998) p53 is essential for developmental neuron death as regulated by the TrkA and p75 neurotrophin receptors. J Cell Biol 143:1691–1703
Amson R, Lassalle JM, Halley H, Prieur S, Lethrosne F, Roperch JP, Israeli D, Gendron MC, Duyckaerts C, Checler F, Dausset J, Cohen D, Oren M, Telerman A (2000) Behavioral alterations associated with apoptosis and down-regulation of presenilin 1 in the brains of p53-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:5346–5350
Armstrong JF, Kaufman MH, Harrison DJ, Clarke AR (1995) High-frequency developmental abnormalities in p 53-deficient mice. Curr Biol 5:931–936
Asanuma M, Miyazaki I, Higashi Y, Cadet JL, Ogawa N (2002) Methamphetamine-induced increase in striatal p53 DNA-binding activity is attenuated in Cu, Zn-superoxide dismutase transgenic mice. Neurosci Lett 325:191–194
Astarita G, Avanesian A, Grimaldi B, Realini N, Justinova Z, Panlilio LV, Basit A, Goldberg SR, Piomelli D (2015) Methamphetamine accelerates cellular senescence through stimulation of de novo ceramide biosynthesis. PLoS One 10:e0116961
Backman CM, Malik N, Zhang Y, Shan L, Grinberg A, Hoffer BJ, Westphal H, Tomac AC (2006) Characterization of a mouse strain expressing Cre recombinase from the 3′ untranslated region of the dopamine transporter locus. Genesis 44:383–390
Boger HA, Middaugh LD, Patrick KS, Ramamoorthy S, Denehy ED, Zhu H, Pacchioni AM, Granholm AC, McGinty JF (2007) Long-term consequences of methamphetamine exposure in young adults are exacerbated in glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor heterozygous mice. J Neurosci 27:8816–8825
Checler F, Alves da Costa C (2014) p53 in neurodegenerative diseases and brain cancers. Pharmacol Ther 142:99–113
Chen C, Qincao L, Xu J, Du S, Huang E, Liu C, Lin Z, Xie WB, Wang H (2016) Role of PUMA in methamphetamine-induced neuronal apoptosis. Toxicol Lett 240:149–160
Culmsee C, Zhu X, Yu QS, Chan SL, Camandola S, Guo Z, Greig NH, Mattson MP (2001) A synthetic inhibitor of p53 protects neurons against death induced by ischemic and excitotoxic insults, and amyloid beta-peptide. J Neurochem 77:220–228
Cusack CL, Swahari V, Hampton Henley W, Michael Ramsey J, Deshmukh M (2013) Distinct pathways mediate axon degeneration during apoptosis and axon-specific pruning. Nat Commun 4:1876
Dorszewska J (2013) Cell biology of normal brain aging: synaptic plasticity-cell death. Aging Clin Exp Res 25:25–34
Ekthuwapranee K, Sotthibundhu A, Govitrapong P (2015) Melatonin attenuates methamphetamine-induced inhibition of proliferation of adult rat hippocampal progenitor cells in vitro. J Pineal Res 58:418–428
Endo H, Saito A, Chan PH (2006) Mitochondrial translocation of p53 underlies the selective death of hippocampal CA1 neurons after global cerebral ischaemia. Biochem Soc Trans 34:1283–1286
Filichia E, Hoffer B, Qi X, Luo Y (2016) Inhibition of Drp1 mitochondrial translocation provides neural protection in dopaminergic system in a Parkinson’s disease model induced by MPTP. Sci Rep 6:32656
Filichia E, Shen H, Zhou X, Qi X, Jin K, Greig N, Hoffer B, Luo Y (2015) Forebrain neuronal specific ablation of p53 gene provides protection in a cortical ischemic stroke model. Neuroscience 295:1–10
Gilman CP, Chan SL, Guo Z, Zhu X, Greig N, Mattson MP (2003) p53 is present in synapses where it mediates mitochondrial dysfunction and synaptic degeneration in response to DNA damage, and oxidative and excitotoxic insults. NeuroMolecular Med 3:159–172
Grace CE, Schaefer TL, Herring NR, Graham DL, Skelton MR, Gudelsky GA, Williams MT, Vorhees CV (2010) Effect of a neurotoxic dose regimen of (+)-methamphetamine on behavior, plasma corticosterone, and brain monoamines in adult C57BL/6 mice. Neurotoxicol Teratol 32:346–355
Greig NH, Mattson MP, Perry T, Chan SL, Giordano T, Sambamurti K, Rogers JT, Ovadia H, Lahiri DK (2004) New therapeutic strategies and drug candidates for neurodegenerative diseases: p 53 and TNF-alpha inhibitors, and GLP-1 receptor agonists. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1035:290–315
Gudkov AV, Komarova EA (2010) Pathologies associated with the p53 response. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2:a001180
Hirata H, Cadet JL (1997) p53-knockout mice are protected against the long-term effects of methamphetamine on dopaminergic terminals and cell bodies. J Neurochem 69:780–790
Jayanthi S, Deng X, Bordelon M, McCoy MT, Cadet JL (2001) Methamphetamine causes differential regulation of pro-death and anti-death Bcl-2 genes in the mouse neocortex. FASEB J: Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol 15:1745–1752
Jayanthi S, Deng X, Ladenheim B, McCoy MT, Cluster A, Cai NS, Cadet JL (2005) Calcineurin/NFAT-induced up-regulation of the Fas ligand/Fas death pathway is involved in methamphetamine-induced neuronal apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:868–873
Jayanthi S, McCoy MT, Beauvais G, Ladenheim B, Gilmore K, Wood W 3rd, Becker K, Cadet JL (2009) Methamphetamine induces dopamine D1 receptor-dependent endoplasmic reticulum stress-related molecular events in the rat striatum. PLoS One 4:e6092
Jebelli J, Hooper C, Pocock JM (2014) Microglial p 53 activation is detrimental to neuronal synapses during activation-induced inflammation: implications for neurodegeneration. Neurosci Lett 583:92–97
Jimenez A, Jorda EG, Verdaguer E, Pubill D, Sureda FX, Canudas AM, Escubedo E, Camarasa J, Camins A, Pallas M (2004) Neurotoxicity of amphetamine derivatives is mediated by caspase pathway activation in rat cerebellar granule cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 196:223–234
Jonkers J, Meuwissen R, van der Gulden H, Peterse H, van der Valk M, Berns A (2001) Synergistic tumor suppressor activity of BRCA2 and p 53 in a conditional mouse model for breast cancer. Nat Genet 29:418–425
Krasnova IN, Cadet JL (2009) Methamphetamine toxicity and messengers of death. Brain Res Rev 60:379–407
Larsen KE, Fon EA, Hastings TG, Edwards RH, Sulzer D (2002) Methamphetamine-induced degeneration of dopaminergic neurons involves autophagy and upregulation of dopamine synthesis. J Neurosci 22:8951–8960
Luo Y, Kuo CC, Shen H, Chou J, Greig NH, Hoffer BJ, Wang Y (2009) Delayed treatment with a p53 inhibitor enhances recovery in stroke brain. Ann Neurol 65:520–530
Luo Y, Wang Y, Kuang SY, Chiang YH, Hoffer B (2010) Decreased level of Nurr1 in heterozygous young adult mice leads to exacerbated acute and long-term toxicity after repeated methamphetamine exposure. PLoS One 5:e15193
Merlo P, Frost B, Peng S, Yang YJ, Park PJ, Feany M (2014) p53 prevents neurodegeneration by regulating synaptic genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:18055–18060
Miller DB, O'Callaghan JP (1994) Environment-, drug- and stress-induced alterations in body temperature affect the neurotoxicity of substituted amphetamines in the C57BL/6J mouse. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 270:752–760
Pereira FC, Lourenco ES, Borges F, Morgadinho T, Ribeiro CF, Macedo TR, Ali SF (2006) Single or multiple injections of methamphetamine increased dopamine turnover but did not decrease tyrosine hydroxylase levels or cleave caspase-3 in caudate-putamen. Synapse 60:185–193
Perier C, Bove J, Wu DC, Dehay B, Choi DK, Jackson-Lewis V, Rathke-Hartlieb S, Bouillet P, Strasser A, Schulz JB, Przedborski S, Vila M (2007) Two molecular pathways initiate mitochondria-dependent dopaminergic neurodegeneration in experimental Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:8161–8166
Porat S, Simantov R (1999) Bcl-2 and p53: role in dopamine-induced apoptosis and differentiation. Ann N Y Acad Sci 893:372–375
Qi X, Davis B, Chiang YH, Filichia E, Barnett A, Greig NH, Hoffer B, Luo Y (2016) Dopaminergic neuron-specific deletion of p53 gene is neuroprotective in an experimental Parkinson's disease model. J Neurochem 138:746–757
Raghupathi R (2004) Cell death mechanisms following traumatic brain injury. Brain Pathol 14:215–222
Raineri M, Gonzalez B, Goitia B, Garcia-Rill E, Krasnova IN, Cadet JL, Urbano FJ, Bisagno V (2012) Modafinil abrogates methamphetamine-induced neuroinflammation and apoptotic effects in the mouse striatum. PLoS One 7:e46599
Reiner DJ, Yu SJ, Shen H, He Y, Bae E, Wang Y (2014) 9-cis retinoic acid protects against methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity in nigrostriatal dopamine neurons. Neurotox Res 25:248–261
Ricaurte GA, Guillery RW, Seiden LS, Schuster CR, Moore RY (1982) Dopamine nerve terminal degeneration produced by high doses of methylamphetamine in the rat brain. Brain Res 235:93–103
Schoenmann Z, Assa-Kunik E, Tiomny S, Minis A, Haklai-Topper L, Arama E, Yaron A (2010) Axonal degeneration is regulated by the apoptotic machinery or a NAD+-sensitive pathway in insects and mammals. J Neurosci 30:6375–6386
Shen H, Luo Y, Yu SJ, Wang Y (2011) Enhanced neurodegeneration after a high dose of methamphetamine in adenosine A3 receptor null mutant mice. Neuroscience 194:170–180
Strom E, Sathe S, Komarov PG, Chernova OB, Pavlovska I, Shyshynova I, Bosykh DA, Burdelya LG, Macklis RM, Skaliter R, Komarova EA, Gudkov AV (2006) Small-molecule inhibitor of p 53 binding to mitochondria protects mice from gamma radiation. Nat Chem Biol 2:474–479
Tedeschi A, Di Giovanni S (2009) The non-apoptotic role of p 53 in neuronal biology: enlightening the dark side of the moon. EMBO Rep 10:576–583
Trimmer PA, Smith TS, Jung AB, Bennett JP Jr (1996) Dopamine neurons from transgenic mice with a knockout of the p53 gene resist MPTP neurotoxicity. Neurodegen: J Neurodegenerative Disorders, Neuroprotection, and Neuroregeneration 5:233–239
Wang DB, Kinoshita C, Kinoshita Y, Morrison RS (2014) p53 and mitochondrial function in neurons. Biochim Biophys Acta 1842:1186–1197
Zhou X, Pace J, Filichia E, Lv T, Davis B, Hoffer B, Selman W, Luo Y (2016) Effect of the sonic hedgehog receptor smoothened on the survival and function of dopaminergic neurons. Exp Neurol 283:235–245
Zhu X, Yu QS, Cutler RG, Culmsee CW, Holloway HW, Lahiri DK, Mattson MP, Greig NH (2002) Novel p53 inactivators with neuroprotective action: syntheses and pharmacological evaluation of 2-imino-2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7-hexahydrobenzothiazole and 2-imino-2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7-hexahydrobenzoxazole derivatives. J Med Chem 45:5090–5097
Acknowledgements
This research was supported in part by a grant from (i) The National Institutes of Health NINDS grant RO1NS094152 and (ii) the Intramural Research Program of the National Institute on Aging, NIH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, T., Kim, P.P., Greig, N.H. et al. Dopaminergic Neuron-Specific Deletion of p53 Gene Attenuates Methamphetamine Neurotoxicity. Neurotox Res 32, 218–230 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-017-9723-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-017-9723-z