Abstract
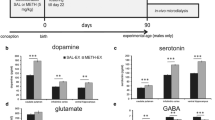
Neonatal exposure to methamphetamine (MA) and developmental chronic stress significantly alter neurodevelopmental profiles that show a variety of long-term physiological and behavioral effects. In the current experiment, Sprague-Dawley rats were exposed to one of two housing conditions along with MA. Rats were given 0 (saline), 5, or 7.5 mg/kg MA, four times per day from postnatal day (P)11 to 15 or P11 to 20. Half of the litters were reared in cages with standard bedding and half with no bedding. Separate litters were assessed at P15 or P20 for organ weights (adrenals, spleen, thymus); corticosterone; and monoamine assessments (dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine) and their metabolites within the neostriatum, hippocampus, and prefrontal cortex. Findings show neonatal MA altered monoamines, corticosterone, and organ characteristics alone, and as a function of developmental age and stress compared with controls. These alterations may in part be responsible for MA and early life stress-induced long-term learning and memory deficits.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Attar BK, Guerra NC, Tolan P (1994) Neighborhood disadvantage, stressful life events, and adjustment in urban elementary-school children. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology 23:391–400
Avishai-Eliner S, Gilles EE, Eghbal-Ahmadi M, Bar-El Y, Baram TZ (2001) Altered regulation of gene and protein expression of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis components in an immature rat model of chronic stress. J Neuroendocrinol 13:799–807
Baram TZ, Solodkin A, Davis EP, Stern H, Obenaus A, Sandman CA, Small SL (2012) Fragmentation and unpredictability of early-life experience in mental disorders. Am J Psychiatry 169:907–915
Barbosa Neto JB, Tiba PA, Faturi CB, de Castro-Neto EF, da Graca N-MM, de Jesus MJ, de Mello MF, Suchecki D (2012) Stress during development alters anxiety-like behavior and hippocampal neurotransmission in male and female rats. Neuropharmacology 62:518–526
Broom SL, Yamamoto BK (2005) Effects of subchronic methamphetamine exposure on basal dopamine and stress-induced dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens shell of rats. Psychopharmacology 181:467–476
Brunson KL, Kramar E, Lin B, Chen Y, Colgin LL, Yanagihara TK, Lynch G, Baram TZ (2005) Mechanisms of late-onset cognitive decline after early-life stress. The Journal of neuroscience: the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 25:9328–9338
Campbell LF, Bedi KS (1989) The effects of undernutrition during early life on spatial learning. Physiol Behav 45:883–890
Cappon GD, Morford LL, Vorhees CV (1997) Ontogeny of methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity and associated hyperthermic response. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 103:155–162
Champagne FA, Chretien P, Stevenson CW, Zhang TY, Gratton A, Meaney MJ (2004) Variations in nucleus accumbens dopamine associated with individual differences in maternal behavior in the rat. The Journal of neuroscience: the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 24:4113–4123
Chang L, Smith LM, LoPresti C, Yonekura ML, Kuo J, Walot I, Ernst T (2004) Smaller subcortical volumes and cognitive deficits in children with prenatal methamphetamine exposure. Psychiatry Res 132:95–106
Chang L, Cloak C, Jiang CS, Farnham S, Tokeshi B, Buchthal S, Hedemark B, Smith LM, Ernst T (2009) Altered neurometabolites and motor integration in children exposed to methamphetamine in utero. NeuroImage 48:391–397
Clancy B, Darlington RB, Finlay BL (2001) Translating developmental time across mammalian species. Neuroscience 105:7–17
Clancy B, Kersh B, Hyde J, Darlington RB, Anand KJ, Finlay BL (2007) Web-based method for translating neurodevelopment from laboratory species to humans. Neuroinformatics 5:79–94
Clearfield MW, Carter-Rodriguez A, Merali AR, Shober R (2014) The effects of SES on infant and maternal diurnal salivary cortisol output. Infant behavior & development 37:298–304
Crawford CA, Williams MT, Newman ER, McDougall SA, Vorhees CV (2003) Methamphetamine exposure during the preweanling period causes prolonged changes in dorsal striatal protein kinase A activity, dopamine D2-like binding sites, and dopamine content. Synapse 48:131–137
Della Grotta S, LaGasse LL, Arria AM, Derauf C, Grant P, Smith LM, Shah R, Huestis M, Liu J, Lester BM (2010) Patterns of methamphetamine use during pregnancy: results from the infant development, environment, and lifestyle (IDEAL) study. Matern Child Health J 14:519–527
Derauf C, Kekatpure M, Neyzi N, Lester B, Kosofsky B (2009) Neuroimaging of children following prenatal drug exposure. Semin Cell Dev Biol 20:441–454
Diaz SD, Smith LM, LaGasse LL, Derauf C, Newman E, Shah R, Arria A, Huestis MA, Della Grotta S, Dansereau LM, Neal C, Lester BM (2014) Effects of prenatal methamphetamine exposure on behavioral and cognitive findings at 7.5 years of age. J Pediatr 164:1333–1338
Evans GW, Kantrowitz E (2002) Socioeconomic status and health: the potential role of environmental risk exposure. Annu Rev Public Health 23:303–331
Evans GW, Kim P (2010) Multiple risk exposure as a potential explanatory mechanism for the socioeconomic status-health gradient. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1186:174–189
Gilles EE, Schultz L, Baram TZ (1996) Abnormal corticosterone regulation in an immature rat model of continuous chronic stress. Pediatr Neurol 15:114–119
Goodlett CR, Valentino ML, Morgane PJ, Resnick O (1986) Spatial cue utilization in chronically malnourished rats: task-specific learning deficits. Dev Psychobiol 19:1–15
Grace CE, Schaefer TL, Herring NR, Skelton MR, McCrea AE, Vorhees CV, Williams MT (2008) (+)-Methamphetamine increases corticosterone in plasma and BDNF in brain more than forced swim or isolation in neonatal rats. Synapse 62:110–121
Grace CE, Schaefer TL, Graham DL, Skelton MR, Williams MT, Vorhees CV (2010a) Effects of inhibiting neonatal methamphetamine-induced corticosterone release in rats by adrenal autotransplantation on later learning, memory, and plasma corticosterone levels. International journal of developmental neuroscience: the official journal of the International Society for Developmental Neuroscience 28:331–342
Grace CE, Schaefer TL, Gudelsky GA, Williams MT, Vorhees CV (2010b) Neonatal methamphetamine-induced corticosterone release in rats is inhibited by adrenal autotransplantation without altering the effect of the drug on hippocampal serotonin. Neurotoxicol Teratol 32:356–361
Graham DL, Grace CE, Braun AA, Schaefer TL, Skelton MR, Tang PH, Vorhees CV, Williams MT (2011) Effects of developmental stress and lead (Pb) on corticosterone after chronic and acute stress, brain monoamines, and blood Pb levels in rats. International journal of developmental neuroscience: the official journal of the International Society for Developmental Neuroscience 29:45–55
Graham DL, Amos-Kroohs RM, Braun AA, Grace CE, Schaefer TL, Skelton MR, Williams MT, Vorhees CV (2013) Neonatal + − methamphetamine exposure in rats alters adult locomotor responses to dopamine D1 and D2 agonists and to a glutamate NMDA receptor antagonist, but not to serotonin agonists. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 16:377–391
Ivy AS, Brunson KL, Sandman C, Baram TZ (2008) Dysfunctional nurturing behavior in rat dams with limited access to nesting material: a clinically relevant model for early-life stress. Neuroscience 154:1132–1142
Jablonski SA, Williams MT, Vorhees CV (2016a) Mechanisms involved in the neurotoxic and cognitive effects of developmental methamphetamine exposure. Birth defects research Part C, Embryo today: reviews 108:131–141
Jablonski SA, Williams MT, Vorhees CV (2016b) Neurobehavioral effects from developmental methamphetamine exposure. Curr Top Behav Neurosci 29:183–230
Johnson EA, O'Callaghan JP, Miller DB (2002) Chronic treatment with supraphysiological levels of corticosterone enhances D-MDMA-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity in the C57BL/6J female mouse. Brain Res 933:130–138
Kioukia-Fougia N, Antoniou K, Bekris S, Liapi C, Christofidis I, Papadopoulou-Daifoti Z (2002) The effects of stress exposure on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, thymus, thyroid hormones and glucose levels. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 26:823–830
Kirlic N, Newman E, Lagasse LL, Derauf C, Shah R, Smith LM, Arria AM, Huestis MA, Haning W, Strauss A, Dellagrotta S, Dansereau LM, Abar B, Neal CR, Lester BM (2013) Cortisol reactivity in two-year-old children prenatally exposed to methamphetamine. Journal of studies on alcohol and drugs 74:447–451
Kokoshka JM, Fleckenstein AE, Wilkins DG, Hanson GR (2000) Age-dependent differential responses of monoaminergic systems to high doses of methamphetamine. J Neurochem 75:2095–2102
LaGasse LL, Wouldes T, Newman E, Smith LM, Shah RZ, Derauf C, Huestis MA, Arria AM, Della Grotta S, Wilcox T, Lester BM (2011) Prenatal methamphetamine exposure and neonatal neurobehavioral outcome in the USA and New Zealand. Neurotoxicol Teratol 33:166–175
Loria AS, Brands MW, Pollock DM, Pollock JS (2013) Early life stress sensitizes the renal and systemic sympathetic system in rats. American journal of physiology Renal physiology 305:F390–F395
Makisumi T, Yoshida K, Watanabe T, Tan N, Murakami N, Morimoto A (1998) Sympatho-adrenal involvement in methamphetamine-induced hyperthermia through skeletal muscle hypermetabolism. Eur J Pharmacol 363:107–112
Masis-Calvo M, Sequeira-Cordero A, Mora-Gallegos A, Fornaguera-Trias J (2013) Behavioral and neurochemical characterization of maternal care effects on juvenile Sprague-Dawley rats. Physiol Behav 118:212–217
Matuszewich L, Yamamoto BK (2004) Chronic stress augments the long-term and acute effects of methamphetamine. Neuroscience 124:637–646
Mazer C, Muneyyirci J, Taheny K, Raio N, Borella A, Whitaker-Azmitia P (1997) Serotonin depletion during synaptogenesis leads to decreased synaptic density and learning deficits in the adult rat: a possible model of neurodevelopmental disorders with cognitive deficits. Brain Res 760:68–73
McDonnell-Dowling K, Kelly JP (2015) Sources of variation in the design of preclinical studies assessing the effects of amphetamine-type stimulants in pregnancy and lactation. Behav Brain Res 279:87–99
Moriceau S, Raineki C, Holman JD, Holman JG, Sullivan RM (2009a) Enduring neurobehavioral effects of early life trauma mediated through learning and corticosterone suppression. Front Behav Neurosci 3:22
Moriceau S, Shionoya K, Jakubs K, Sullivan RM (2009b) Early-life stress disrupts attachment learning: the role of amygdala corticosterone, locus ceruleus corticotropin releasing hormone, and olfactory bulb norepinephrine. The Journal of neuroscience: the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 29:15745–15755
Ohta K, Miki T, Warita K, Suzuki S, Kusaka T, Yakura T, Liu JQ, Tamai M, Takeuchi Y (2014) Prolonged maternal separation disturbs the serotonergic system during early brain development. International journal of developmental neuroscience: the official journal of the International Society for Developmental Neuroscience 33:15–21
Oro AS, Dixon SD (1987) Perinatal cocaine and methamphetamine exposure: maternal and neonatal correlates. J Pediatr 111:571–578
Pruett S, Hebert P, Lapointe JM, Reagan W, Lawton M, Kawabata TT (2007) Characterization of the action of drug-induced stress responses on the immune system: evaluation of biomarkers for drug-induced stress in rats. J Immunotoxicol 4:25–38
Ramkissoon A, Wells PG (2015) Methamphetamine oxidative stress, neurotoxicity, and functional deficits are modulated by nuclear factor-E2-related factor 2. Free Radic Biol Med 89:358–368
Reho JJ, Fisher SA (2015) The stress of maternal separation causes misprogramming in the postnatal maturation of rat resistance arteries. Am J Phys Heart Circ Phys 309:H1468–H1478
Rice D, Barone S Jr (2000) Critical periods of vulnerability for the developing nervous system: evidence from humans and animal models. Environ Health Perspect 108(Suppl 3):511–533
Schaefer TL, Ehrman LA, Gudelsky GA, Vorhees CV, Williams MT (2006) Comparison of monoamine and corticosterone levels 24 h following (+)methamphetamine, (+/−)3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine, cocaine, (+)fenfluramine or (+/−)methylphenidate administration in the neonatal rat. J Neurochem 98:1369–1378
Schaefer TL, Skelton MR, Herring NR, Gudelsky GA, Vorhees CV, Williams MT (2008) Short- and long-term effects of (+)-methamphetamine and (+/−)-3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine on monoamine and corticosterone levels in the neonatal rat following multiple days of treatment. J Neurochem 104:1674–1685
Schaefer TL, Grace CE, Gudelsky GA, Vorhees CV, Williams MT (2010) Effects on plasma corticosterone levels and brain serotonin from interference with methamphetamine-induced corticosterone release in neonatal rats. Stress 13:469–480
Schoenfeld NM, Leathem JH, Rabii J (1980) Maturation of adrenal stress responsiveness in the rat. Neuroendocrinology 31:101–105
Skelton MR, Williams MT, Schaefer TL, Vorhees CV (2007) Neonatal (+)-methamphetamine increases brain derived neurotrophic factor, but not nerve growth factor, during treatment and results in long-term spatial learning deficits. Psychoneuroendocrinology 32:734–745
Smith LM, Chang L, Yonekura ML, Gilbride K, Kuo J, Poland RE, Walot I, Ernst T (2001) Brain proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy and imaging in children exposed to cocaine in utero. Pediatrics 107:227–231
Smith L, Yonekura ML, Wallace T, Berman N, Kuo J, Berkowitz C (2003) Effects of prenatal methamphetamine exposure on fetal growth and drug withdrawal symptoms in infants born at term. Journal of developmental and behavioral pediatrics: JDBP 24:17–23
Smith LM, Lagasse LL, Derauf C, Grant P, Shah R, Arria A, Huestis M, Haning W, Strauss A, Della Grotta S, Fallone M, Liu J, Lester BM (2008) Prenatal methamphetamine use and neonatal neurobehavioral outcome. Neurotoxicol Teratol 30:20–28
Smith LM, Diaz S, LaGasse LL, Wouldes T, Derauf C, Newman E, Arria A, Huestis MA, Haning W, Strauss A, Della Grotta S, Dansereau LM, Neal C, Lester BM (2015) Developmental and behavioral consequences of prenatal methamphetamine exposure: a review of the infant development, environment, and lifestyle (IDEAL) study. Neurotoxicol Teratol 51:35–44
Spencer RL, Miller AH, Stein M, McEwen BS (1991) Corticosterone regulation of type I and type II adrenal steroid receptors in brain, pituitary, and immune tissue. Brain Res 549:236–246
Stappenbeck TS, Virgin HW (2016) Accounting for reciprocal host-microbiome interactions in experimental science. Nature 534:191–199
Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, Center for Behavioral Health Statistics and Quality. (April 3, 2014). The TEDS report: Gender differences in primary substance of abuse across age groups. Rockville, MD.
Sulzer D, Sonders MS, Poulsen NW, Galli A (2005) Mechanisms of neurotransmitter release by amphetamines: a review. Prog Neurobiol 75:406–433
Tata DA, Raudensky J, Yamamoto BK (2007) Augmentation of methamphetamine-induced toxicity in the rat striatum by unpredictable stress: contribution of enhanced hyperthermia. Eur J Neurosci 26:739–748
Terplan M, Smith EJ, Kozloski MJ, Pollack HA (2009) Methamphetamine use among pregnant women. Obstet Gynecol 113:1285–1291
Twomey J, LaGasse L, Derauf C, Newman E, Shah R, Smith L, Arria A, Huestis M, DellaGrotta S, Roberts M, Dansereau L, Neal C, Lester B (2013) Prenatal methamphetamine exposure, home environment, and primary caregiver risk factors predict child behavioral problems at 5 years. The American journal of orthopsychiatry 83:64–72
Vliegenthart J, Noppe G, van Rossum EF, Koper JW, Raat H, van den Akker EL (2016) Socioeconomic status in children is associated with hair cortisol levels as a biological measure of chronic stress. Psychoneuroendocrinology 65:9–14
Vorhees CV, Ahrens KG, Acuff-Smith KD, Schilling MA, Fisher JE (1994) Methamphetamine exposure during early postnatal development in rats: I. Acoustic startle augmentation and spatial learning deficits Psychopharmacology 114:392–401
Vorhees CV, Inman-Wood SL, Morford LL, Broening HW, Fukumura M, Moran MS (2000) Adult learning deficits after neonatal exposure to D-methamphetamine: selective effects on spatial navigation and memory. The Journal of neuroscience: the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 20:4732–4739
Vorhees CV, Reed TM, Morford LL, Fukumura M, Wood SL, Brown CA, Skelton MR, McCrea AE, Rock SL, Williams MT (2005) Periadolescent rats (P41-50) exhibit increased susceptibility to D-methamphetamine-induced long-term spatial and sequential learning deficits compared to juvenile (P21-30 or P31-40) or adult rats (P51-60). Neurotoxicol Teratol 27:117–134
Vorhees CV, Skelton MR, Williams MT (2007) Age-dependent effects of neonatal methamphetamine exposure on spatial learning. Behav Pharmacol 18:549–562
Vorhees CV, Herring NR, Schaefer TL, Grace CE, Skelton MR, Johnson HL, Williams MT (2008) Effects of neonatal (+)-methamphetamine on path integration and spatial learning in rats: effects of dose and rearing conditions. International journal of developmental neuroscience: the official journal of the International Society for Developmental Neuroscience 26:599–610
Vorhees CV, Skelton MR, Grace CE, Schaefer TL, Graham DL, Braun AA, Williams MT (2009) Effects of (+)-methamphetamine on path integration and spatial learning, but not locomotor activity or acoustic startle, align with the stress hyporesponsive period in rats. International journal of developmental neuroscience: the official journal of the International Society for Developmental Neuroscience 27:289–298
Vorhees CV, Graham DL, Amos-Kroohs RM, Braun AA, Grace CE, Schaefer TL, Skelton MR, Erikson KM, Aschner M, Williams MT (2014) Effects of developmental manganese, stress, and the combination of both on monoamines, growth, and corticosterone. Toxicology reports 1:1046–1061
Whitaker-Azmitia PM, Druse M, Walker P, Lauder JM (1996) Serotonin as a developmental signal. Behav Brain Res 73:19–29
Williams MT, Inman-Wood SL, Morford LL, McCrea AE, Ruttle AM, Moran MS, Rock SL, Vorhees CV (2000) Preweaning treatment with methamphetamine induces increases in both corticosterone and ACTH in rats. Neurotoxicol Teratol 22:751–759
Williams MT, Blankenmeyer TL, Schaefer TL, Brown CA, Gudelsky GA, Vorhees CV (2003) Long-term effects of neonatal methamphetamine exposure in rats on spatial learning in the Barnes maze and on cliff avoidance, corticosterone release, and neurotoxicity in adulthood. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 147:163–175
Williams MT, Moran MS, Vorhees CV (2004) Behavioral and growth effects induced by low dose methamphetamine administration during the neonatal period in rats. International journal of developmental neuroscience: the official journal of the International Society for Developmental Neuroscience 22:273–283
Williams MT, Schaefer TL, Furay AR, Ehrman LA, Vorhees CV (2006) Ontogeny of the adrenal response to (+)-methamphetamine in neonatal rats: the effect of prior drug exposure. Stress 9:153–163
Workman AD, Charvet CJ, Clancy B, Darlington RB, Finlay BL (2013) Modeling transformations of neurodevelopmental sequences across mammalian species. The Journal of neuroscience: the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 33:7368–7383
Wouldes TA, Lagasse LL, Huestis MA, Dellagrotta S, Dansereau LM, Lester BM (2014) Prenatal methamphetamine exposure and neurodevelopmental outcomes in children from 1 to 3 years. Neurotoxicol Teratol 42:77–84
Yodlowski ML, Fredieu JR, Landis SC (1984) Neonatal 6-hydroxydopamine treatment eliminates cholinergic sympathetic innervation and induces sensory sprouting in rat sweat glands. The Journal of neuroscience: the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 4:1535–1548
Zhang TY, Chretien P, Meaney MJ, Gratton A (2005) Influence of naturally occurring variations in maternal care on prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle and the medial prefrontal cortical dopamine response to stress in adult rats. The Journal of neuroscience: the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 25:1493–1502
Zuloaga DG, Siegel JA, Acevedo SF, Agam M, Raber J (2013) Developmental methamphetamine exposure results in short- and long-term alterations in hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal-axis-associated proteins. Dev Neurosci 35:338–346
Zuloaga DG, Jacobskind JS, Raber J (2015) Methamphetamine and the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. Front Neurosci 9:178
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by NIH training grant T32 ES007051 (SAJ and DLG).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict Statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jablonski, S.A., Graham, D.L., Vorhees, C.V. et al. Effects of Neonatal Methamphetamine and Stress on Brain Monoamines and Corticosterone in Preweanling Rats. Neurotox Res 31, 269–282 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-016-9680-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-016-9680-y