Abstract
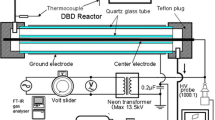
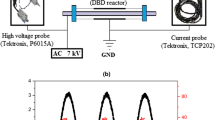
The main target of this work is to realize the function of pre-oxidizing NO from diesel engine’s exhaust by using self-designed double-dielectric Non-thermal Plasma (NTP) reactor. The majorized discharge frequency and discharge peak to peak voltage (Vp-p) range for NTP reactor were obtained through air discharge test. The diesel engine test bench was established to observe the effect of NTP on the volume fraction of NO. The results showed that there were more active substances and fewer by-products in NTP reactor when discharge frequency was 9 kHz and Vp-p was between 9 kV and 23 kV; Exhaust flows had insignificant effect on the performance of NTP pre-oxidizing NO; The ability of NTP to pre-oxidize NO gradually weakened with the increase of engine load, and when the engine load were 0 % and 25 %, the ratio of NO/NO2 could reach 1. In such working conditions, SCR system could improve the conversion rate of the NOx at low-temperature zone through quick reaction combined with NTP.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Vp-p :
-
voltage peak-peak value, kV
References
Cho, B. K., Lee, J. H., Crellin, C. C., Olson, K. L., Hilden, D. L., Kim, M. K., Kim, P. S., Heo, I. J., Oh, S. H. and Nam, I. S. (2012). Selective catalytic reduction of NOx by diesel fuel: Plasma-assisted HC/SCR system. Catalysis Today 191, 1, 20–24.
Chen, Q., Guan, B., Lin, H. and Huang, Z. (2010). Removing NOx emission from diesel engine with plasmaassisted NH3-SCR. Vehicle Engine, 186, 33–36.
Chen, Z. B., Wang, X. C., Pei, Y. Q., Zhang, C. L., Xiao, M. W. and He, J. G. (2015). Experimental investigation of the performance and emissions of diesel engines by a novel emulsified diesel fuel. Energy Conversion and Management, 95, 334–341.
Ciardelli, C., Nova, I., Tronconi, E., Chatterjee, D., Bandl-Konrad, B., Weibel, M. and Krutzsch, B. (2007). Reactivity of NO/NO2-NH3 SCR system for diesel exhaust aftertreatment: Identification of the reaction network as a function of temperature and NO2 feed content. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental 70, 1–4, 80–90.
Jolibois, J., Takashima, K. and Mizuno, A. (2012). Application of a non-thermal surface plasma discharge in wet condition for gas exhaust treatment: NOx removal. J. Electrostatics 70, 3, 300–308.
Liu, L. D., Shi, W. Y., Gao, J. H. and Zhang, Z. R. (2013). A research of the effects of non-thermal plasma on the emission control of diesel engine. Automobile Engineering 8, 6, 116–120.
Mohamed, F., Dawody, A. and Bhatti, S. K. (2013). Optimization strategies to reduce the biodiesel NOx effect in diesel engine with experimental verification. Energy Conversion and Management, 68, 96–104.
Tan, F. and Lin, L. (2015). The characteristics of ammonia storage and the development of model-based control for diesel engine Urea-SCR system. J. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry, 28, 97–109.
Tran, Q. V., Shuya, W., Tomohiko, F. and Masataka, A. (2012). Fundamental study of NOx removal from diesel exhaust gas by dielectric barrier discharge reactor. J. Mechanical Science and Technology 26, 6, 1921–1928.
Wang, J., Cai, Y. X., Wang, P., Zhuang, F. Z. and Ran, D. L. (2009). Conversion of NO in NO/O2/N2 system by dielectric barrier discharge plasmas. Acta Chimica Sinica 67, 20, 2315–2318.
Wang, W. T., Herreros, J. M., Tsolakis, A. and York, A. P. E. (2015a). Increased NO2 concentration in the diesel engine exhaust for improved Ag/Al2O3 catalyst NH3-SCR activity. Chemical Engineering J., 270, 582–589.
Wang, Q., Zhang, D., He, Z. X., Wang, J. and Li, S. (2015b). Numerical simulation of diesel engine Urea-SCR system and its mixer structure optimization. Chinese Internal Combustion Engine Engineering 36, 3, 51–57.
Xin, Z., Zhang, Y., Wang, S. X., Zhang, Y. L. and Liu, J. X. (2011). Influence factors of deNOx behavior in Urea-SCR catalytic converter of diesel. Trans. Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery 42, 9, 30–34.
Yoshida, K., Kuwahara, T., Kuroki, T. and Okubo, M. (2012). Diesel NOx aftertreatment by combined process using temperature swing adsorption, NOx reduction by nonthermal plasma, and NOx recirculation: Improvement of the recirculation process. J. Hazardous Materials, 231-232, 18–25.
Zheng, Q. P., Shen, Y. S., Zhang, J. Z., Li, S. and Zhong, M. (2013). Effect of structure parameters of diesel engine Urea-SCR system on NOx conversion rate. Chinese Internal Combustion Engine Engineering 34, 6, 31–35.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., He, T. & Li, C. Majorization of working parameters for non-thermal plasma reactor and impact on no oxidation of diesel engine. Int.J Automot. Technol. 18, 229–233 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12239-017-0022-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12239-017-0022-8