Abstract
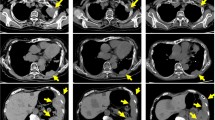
We present the case of a 63-year-old male with pure white cell aplasia (PWCA), a rare complication of thymoma, who was successfully treated with cyclosporine A (CyA) and thymectomy. The patient presented with high fever and agranulocytosis. Complete blood count revealed a white blood cell count of 0.9 × 109/L (3% neutrophils), a hemoglobin level of 15.8 g/dL, and a platelet count of 308 × 109/L. Bone marrow (BM) aspiration revealed a hypocellular marrow lacking granulocytes. Computed tomography showed a large anterior mediastinal mass, and the patient was diagnosed with PWCA associated with thymoma. Thirteen days after the initiation of CyA treatment, myeloid cells appeared in the BM, and the neutrophil count in peripheral blood started to increase on day 18. Thymectomy was performed 3 months later. Although CyA treatment was discontinued after thymectomy, complete remission has been maintained for over 4 years. In vitro colony-forming unit granulocyte–macrophage (CFU-GM) assay using the patient’s serum showed severe suppression of CFU-GM colonies in the presence of the patient’s serum, suggesting the presence of CFU-GM inhibitor in the patient’s serum. The efficacy of the immunosuppressive therapy and the CFU-GM assay suggests the potential involvement of an immunological mechanism in patients with thymoma-associated PWCA.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Levitt LJ. Chlorpropamide-induced pure white cell aplasia. Blood. 1987;69:394–400.
Tamura H, Okamoto M, Yamashita T, Sato C, Watanabe A, Kondo A, et al. Pure white cell aplasia: report of the first case associated with primary biliary cirrhosis. Int J Hematol. 2007;85:97–100.
Levitt LJ, Ries CA, Greenberg PL. Pure white-cell aplasia. Antibody-mediated autoimmune inhibition of granulopoiesis. N Engl J Med. 1983;308:1141–6.
Iida S, Noda T, Banno S, Nitta M, Takada K, Yamamoto M. Pure white cell aplasia (PWCA) with an inhibitor against colony-forming unit of granulocyte-macrophage (CFU-GM). Rinsho Ketsueki. 1990;31:1726–30.
Ackland SP, Bur ME, Adler SS, Robertson M, Baron JM. White blood cell aplasia associated with thymoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 1988;89:260–3.
Mamus SW, Burton JD, Groat JD, Schulte DA, Lobell M, Zanjani ED. Ibuprofen-associated pure white-cell aplasia. N Engl J Med. 1986;314:624–5.
Herzog-Tzarfati K, Shiloah E, Koren-Michowitz M, Minha S, Rapoport MJ. Successful treatment of prolonged agranulocytosis caused by acute parvovirus B19 infection with intravenous immunoglobulins. Eur J Intern Med. 2006;17:439–40.
Yip D, Rasko JE, Lee C, Kronenberg H, O’Neill B. Thymoma and agranulocytosis: two case reports and literature review. Br J Haematol. 1996;95:52–6.
Risitano AM, Selleri C, Serio B, Torelli GF, Kulagin A, Maury S, et al. Alemtuzumab is safe and effective as immunosuppressive treatment for aplastic anaemia and single-lineage marrow failure: a pilot study and a survey from the EBMT WPSAA. Br J Haematol. 2010;148:791–6.
Alvares CL, Svasti-Salee D, Rowley M, Gordon-Smith EC, Marsh JCW. Remission induced by Campath-1H for thymoma-associated agranulocytosis. Ann Hematol. 2004;83:398–400.
Postiglione K, Ferris R, Jaffe JP, Stroncek D. Immune mediated agranulocytosis and anemia associated with thymoma. Am J Hematol. 1995;49:336–40.
Degos L, Faille A, Housset M, Boumsell L, Rabian C, Parames T. Syndrome of neutrophil agranulocytosis, hypogammaglobulinemia, and thymoma. Blood. 1982;60:968–72.
Kobayashi M, Hasegawa T, Iwabuchi S, Fukushima M, Koie H, Kannari K. The effect of thymectomy on myasthenia gravis, thrombocytopenia, and granulocytopenia associated with thymoma: report of a case. Surg Today. 1995;25:1061–5.
Baldwin TA, Hogquist KA, Jameson SC. The fourth way? Harnessing aggressive tendencies in the thymus. J Immunol. 2004;173:6515–20.
Fumeaux Z, Beris P, Borisch B, Sarasin FP, Roosnek E, Dayer J-M, et al. Complete remission of pure white cell aplasia associated with thymoma, autoimmune thyroiditis and type 1 diabetes. Eur J Haematol. 2003;70:186–9.
Wu X, Wang S, Lu X, Shen W, Qiao C, Wu Y, et al. Response to cyclosporine A and corticosteroids in adult patients with acquired pure red cell aplasia: serial experience at a single center. Int J Hematol. 2018;108:123–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Kobayashi, Y., Ando, K., Hata, T. et al. Complete remission of pure white cell aplasia associated with thymoma after thymectomy and cyclosporine administration. Int J Hematol 109, 346–350 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-018-02573-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-018-02573-y