Abstract
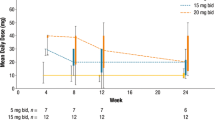
Ruxolitinib, a potent JAK1/JAK2 inhibitor, improved splenomegaly and myelofibrosis-associated symptoms and prolonged survival compared with placebo and best available therapy in the phase 3 COMFORT studies. Although cytopenias were the most common adverse events associated with ruxolitinib treatment, a COMFORT-I analysis showed that they were managed effectively with dose modifications, without a negative impact on the efficacy of ruxolitinib. Subsequently, studies A2202 and AJP01 showed that ruxolitinib is an effective treatment for Japanese patients with myelofibrosis. We conducted a pooled analysis of these two studies (N = 81) to evaluate the association between ruxolitinib dose and changes in spleen volume or symptoms in Japanese patients. Most patients began treatment at 15 or 20 mg twice daily (BID); 70% received a final titrated dose ≥ 10 mg BID. Overall, 91% of patients exhibited spleen volume reductions; patients with final titrated doses ≥ 10 mg BID had larger spleen volume reductions. Similarly, 83% of patients showed improvements in symptom scores; those with a final titrated dose of 20 or 25 mg BID had the greatest reductions. Consistent with COMFORT-I, this pooled analysis indicates that, despite dose adjustments, ruxolitinib provides spleen and symptom control in Japanese patients, with higher doses associated with better responses.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tefferi A. Primary myelofibrosis: 2014 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification, and management. Am J Hematol. 2014;89(9):915–25.
Abdel-Wahab OI, Levine RL. Primary myelofibrosis: update on definition, pathogenesis, and treatment. Annu Rev Med. 2009;60:233–45.
Cervantes F, Dupriez B, Pereira A, Passamonti F, Reilly JT, Morra E, et al. New prognostic scoring system for primary myelofibrosis based on a study of the International Working Group for Myelofibrosis Research and Treatment. Blood. 2009;113(13):2895–901.
James C, Ugo V, Le Couédic JP, Staerk J, Delhommeau F, Lacout C, et al. A unique clonal JAK2 mutation leading to constitutive signalling causes polycythaemia vera. Nature. 2005;434(7037):1144–8.
Kralovics R, Passamonti F, Buser AS, Teo SS, Tiedt R, Passweg JR, et al. A gain-of-function mutation of JAK2 in myeloproliferative disorders. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(17):1779–90.
Baxter EJ, Scott LM, Campbell PJ, East C, Fourouclas N, Swanton S, et al. Acquired mutation of the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in human myeloproliferative disorders. Lancet. 2005;365(9464):1054–61.
Levine RL, Wadleigh M, Cools J, Ebert BL, Wernig G, Huntly BJ, et al. Activating mutation in the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia, and myeloid metaplasia with myelofibrosis. Cancer Cell. 2005;7(4):387–97.
Tefferi A. Mutations galore in myeloproliferative neoplasms: would the real Spartacus please stand up? Leukemia. 2011;25(7):1059–63.
Pikman Y, Lee BH, Mercher T, McDowell E, Ebert BL, Gozo M, et al. MPLW515L is a novel somatic activating mutation in myelofibrosis with myeloid metaplasia. PLoS Med. 2006;3(7):e270.
Rumi E, Pietra D, Guglielmelli P, Bordoni R, Casetti I, Milanesi C, et al. Acquired copy-neutral loss of heterozygosity of chromosome 1p as a molecular event associated with marrow fibrosis in MPL-mutated myeloproliferative neoplasms. Blood. 2013;121(21):4388–95.
Klampfl T, Gisslinger H, Harutyunyan AS, Nivarthi H, Rumi E, Milosevic JD, et al. Somatic mutations of calreticulin in myeloproliferative neoplasms. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(25):2379–90.
Nangalia J, Massie CE, Baxter EJ, Nice FL, Gundem G, Wedge DC, et al. Somatic CALR mutations in myeloproliferative neoplasms with nonmutated JAK2. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(25):2391–405.
Verstovsek S, Mesa RA, Gotlib J, Levy RS, Gupta V, DiPersio JF, et al. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of ruxolitinib for myelofibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(9):799–807.
Harrison C, Kiladjian JJ, Al-Ali HK, Gisslinger H, Waltzman R, Stalbovskaya V, et al. JAK inhibition with ruxolitinib versus best available therapy for myelofibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(9):787–98.
Verstovsek S, Mesa RA, Gotlib J, Levy RS, Gupta V, DiPersio JF, et al. Efficacy, safety, and survival with ruxolitinib in patients with myelofibrosis: results of a median 3-year follow-up of COMFORT-I. Haematologica. 2015;100(4):479–88.
Cervantes F, Vannucchi AM, Kiladjian JJ, Al-Ali HK, Sirulnik A, Stalbovskaya V, et al. Three-year efficacy, safety, and survival findings from COMFORT-II, a phase 3 study comparing ruxolitinib with best available therapy for myelofibrosis. Blood. 2013;122(25):4047–53.
Harrison CN, Vannucchi AM, Kiladjian JJ, Al-Ali HK, Gisslinger H, Knoops L, et al. Long-term findings from COMFORT-II, a phase 3 study of ruxolitinib vs best available therapy for myelofibrosis. Leukemia. 2016;30(8):1701–7.
Verstovsek S, Gotlib J, Gupta V, Atallah E, Mascarenhas J, Quintas-Cardama A, et al. Management of cytopenias in patients with myelofibrosis treated with ruxolitinib and effect of dose modifications on efficacy outcomes. Onco Targets Ther. 2013;7:13–21.
Jung CW, Shih LY, Xiao Z, Jie J, Hou HA, Du X, et al. Efficacy and safety of ruxolitinib in Asian patients with myelofibrosis. Leuk Lymphoma. 2015;56(7):2067–74.
Oritani K, Okamoto S, Tauchi T, Saito S, Ohishi K, Handa H, et al. A multinational, open-label, phase 2 study of ruxolitinib in Asian patients with myelofibrosis: Japanese subset analysis. Int J Hematol. 2015;101(3):295–304.
Komatsu N, Kirito K, Shimoda K, Ishikawa T, Ohishi K, Ohyashiki K, et al. Assessing the safety and efficacy of ruxolitinib in a multicenter, open-label, study in Japanese patients with myelofibrosis. Int J Hematol. 2017;105:309–17.
Mesa RA, Gotlib J, Gupta V, Catalano JV, Deininger MW, Shields AL, et al. Effect of ruxolitinib therapy on myelofibrosis-related symptoms and other patient-reported outcomes in COMFORT-I: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(10):1285–92.
Aaronson NK, Ahmedzai S, Bergman B, Bullinger M, Cull A, Duez NJ, et al. The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer QLQ-C30: a quality-of-life instrument for use in international clinical trials in oncology. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1993;85(5):365–76.
Vannucchi AM, Kantarjian HM, Kiladjian JJ, Gotlib J, Cervantes F, Mesa RA, et al. A pooled analysis of overall survival in COMFORT-I and COMFORT-II, 2 randomized phase 3 trials of ruxolitinib for the treatment of myelofibrosis. Haematologica. 2015;100(9):1139–45.
Acknowledgements
Editorial assistance was provided by Karen Chinchilla, PhD, of ArticulateScience LLC and was funded by Novartis Pharma KK.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
KK reports personal fees from Novartis Pharma KK, during conduct of the study. K. Shimoda reports grants and personal fees from Novartis Pharma KK, outside the submitted work. K. Oritani reports personal fees for lectures and scholarship contributions from Novartis Pharma KK, outside the submitted work. HO, TA, K Suzuki, and TY are employees of Novartis Pharma KK. SO, K. Ohishi, TT, HH, SS, KT, KA, and NK have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
About this article
Cite this article
Kirito, K., Okamoto, S., Ohishi, K. et al. Evaluation of the dose and efficacy of ruxolitinib in Japanese patients with myelofibrosis. Int J Hematol 107, 92–97 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-017-2332-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-017-2332-z