Abstract
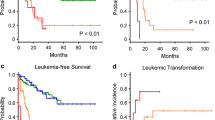
Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) is relatively common in the elderly, and aging of populations is progressing in developed nations, notably so in Japan. The major age group in Japan and Sado Island are distributed between 30 and 60 and between 50 and 80, respectively. The aim of this study was to analyze the features of MDS in the population of Sado Island to anticipate the characteristics of the disease in the near future. One-hundred and fifty-three patients (71 male, 82 female, 19–94 years old, median 73 years old) with de novo MDS between 1985 and 2005 were retrospectively evaluated. All patients were reclassified according to WHO-2001 criteria. The predictive power of the international prognostic scoring system and the WHO classification-based prognostic scoring system were evaluated. The major causes of death were leukemic transformation (38%) in refractory anemia with an excess of blasts and infection (48%) for total MDS. Age was another independent prognostic factor. Elderly patients exhibited a significantly poorer prognosis mainly due to infections such as pneumonia. Although novel remedies for MDS and hyperferremia have recently been developed, prevention of infection remains important in MDS, particularly for older patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT, Flandrin G, Galton DA, Gralnick HR, et al. Proposals for the classification of the myelodysplastic syndromes. Br J Haematol. 1982;51:189–99.
Jaffe WS, Harris NL, Stein H. World Health Organization Classification of Tumors. Pathology and genetics, tumor of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. IARC Press, Lyon, 2001.
Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL. WHO Classification of tumours of heamatopoietic and lymphoid tissues. Lyon: IARC Press; 2008.
Greenberg P, Cox C, LeBeau MM, Fenaux P, Morel P, Sanz G, et al. International scoring system for evaluating prognosis in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood. 1997;91:2079–88.
Malcovati L, Germing U, Kuendgen A, Della Porta MG, Pascutto C, Invernizzi R, et al. Time-dependent prognostic scoring system for predicting survival and leukemic evolution in myelodysplastic syndromes. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:3503–10.
Iwanaga M, Hsu WL, Soda M, Takasaki Y, Tawara M, Joh T, et al. Risk of myelodysplastic syndromes in people exposed to ionizing radiation: a retrospective cohort study of Nagasaki atomic bomb survivors. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:428–34.
Matsuda A, Germing U, Jinnai I, Misumi M, Kuendgen A, Knipp S, et al. Difference in clinical features between Japanese and German patients with refractory anemia in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood. 2005;106:2633–40.
Haase D, Germing U, Schanz J, Pfeilstöcker M, Nösslinger T, Hildebrandt B, et al. New insights into the prognostic impact of the karyotype in MDS and correlation with subtypes: evidence from a core dataset of 2124 patients. Blood. 2007;110:4385–95.
Tasaka T, Tohyama K, Kishimoto M, Ohyashiki K, Mitani K, Hotta T, et al. Myelodysplastic syndrome with chromosome 5 abnormalities: a nationwide survey in Japan. Leukemia. 2008;22:1874–81.
Li L, Liu XP, Nie L, Yu MH, Zhang Y, Qin TJ, et al. Unique cytogenetic features of primary myelodysplastic syndromes in Chinese patients. Leuk Res. 2009;33(9):1194–8.
Williamson PJ, Kruger AR, Reynolds PJ, Hamblin TJ, Oscier DG. Establishing the incidence of myelodysplastic syndrome. Br J Haematol. 1994;87:743–5.
Aul C, Gattermann N, Schneider W. Age-related incidence and other epidemiological aspects of myelodysplastic syndromes. Br J Haematol. 1992;82:358–67.
Rådlund A, Thiede T, Hansen S, Carlsson M, Engquist L. Incidence of myelodysplastic syndromes in a Swedish population. Eur J Haematol. 1995;54:153–6.
Maynadié M, Verret C, Moskovtchenko P, Mugneret F, Petrella T, Caillot D, et al. Epidemiological characteristics of myelodysplastic syndrome in a well-defined French population. Br J Cancer. 1996;74:288–90.
Oguma S, Yoshida Y, Uchino H, Maekawa T, Nomura T, Mizoguchi H. Clinical characteristics of Japanese patients with primary myelodysplastic syndromes: a co-operative study based on 838 cases. Anemia Study Group of the Ministry of Health and Welfare. Leuk Res. 1995;19:219–25.
Oguma S, Yoshida Y, Okuma M, Uchino H, Maekawa T, Nomura T, et al. Mode of disease progression in primary myelodysplastic syndromes: a Japanese co-operative study. The Refractory Anemia Study Group of The Ministry of Health and Welfare, Japan. Leuk Res. 1997;21:241–7.
Dayyani F, Conley AP, Strom SS, Stevenson W, Cortes JE, Borthakur G, et al. Cause of death in patients with lower-risk myelodysplastic syndrome. Cancer. 2010;116:2174–9.
Kantarjian H, O’Brien S, Ravandi F, Cortes J, Shan J, Bennett JM, et al. Proposal for a new risk model in myelodysplastic syndrome that accounts for events not considered in the original International Prognostic Scoring System. Cancer. 2008;113:1351–61.
Nösslinger T, Tüchler H, Germing U, Sperr WR, Krieger O, Haase D, et al. Prognostic impact of age and gender in 897 untreated patients with primary myelodysplastic syndromes. Ann Oncol. 2010;21:120–5.
Germing U, Gattermann N, Strupp C, Aivado M, Aul C. Validation of the WHO proposals for a new classification of primary myelodysplastic syndromes: a retrospective analysis of 1600 patients. Leuk Res. 2000;24:983–92.
Pomeroy C, Oken MM, Rydell RE, Filice GA. Infection in the myelodysplastic syndromes. Am J Med. 1991;90:338–44.
Lee JH, Lee KH, Lee JH, Kim DY, Kim SH, Lim SN, et al. Decreased incidence of febrile episodes with antibiotic prophylaxis in the treatment of decitabine for myelodysplastic syndrome. Leuk Res. 2011;35:499–503.
Horiike S, Yokota S, Nakao M, Iwai T, Sasai Y, Kaneko H, et al. Tandem duplications of the FLT3 receptor gene are associated with leukemic transformation of myelodysplasia. Leukemia. 1997;11:1442–6.
Kita-Sasai Y, Horiike S, Misawa S, Kaneko H, Kobayashi M, Nakao M, et al. International prognostic scoring system and TP53 mutations are independent prognostic indicators for patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. Br J Haematol. 2001;115:309–12.
Van den Berghe H, Cassiman JJ, David G, Fryns JP, Michaux JL, Sokal G. Distinct haematological disorder with deletion of long arm of no. 5 chromosome. Nature. 1974;251:437–8.
Park MJ, Kim HJ, Kim SH, Kim DH, Kim SJ, Jang JH, et al. Is International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS) still standard in predicting prognosis in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome? External validation of the WHO Classification-Based Prognostic Scoring System (WPSS) and comparison with IPSS. Eur J Haematol. 2008;81:364–73.
Leitch HA. Improving clinical outcome in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome and iron overload using iron chelation therapy. Leuk Res. 2007;31(Suppl 3):S7–9.
Rose C, Brechignac S, Vassilief D, Pascal L, Stamatoullas A, Guerci A, et al. Does iron chelation therapy improve survival in regularly transfused lower risk MDS patients? A multicenter study by the GFM (Groupe Francophone des Myélodysplasies). Leuk Res. 2010;34:864–70.
Della Porta MG, Malcovati L, Boveri E, Travaglino E, Pietra D, Pascutto C, et al. Clinical relevance of bone marrow fibrosis and CD34-positive cell clusters in primary myelodysplastic syndromes. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:754–62.
Breccia M, Federico V, Latagliata R, Mercanti C, D’Elia GM, Cannella L, et al. Evaluation of comorbidities at diagnosis predicts outcome in myelodysplastic syndrome patients. Leuk Res. 2011;35:159–62.
Alessandrino EP, Amadori S, Barosi G, Cazzola M, Grossi A, Liberato LN, et al. Evidence- and consensus-based practice guidelines for the therapy of primary myelodysplastic syndromes. A statement from the Italian Society of Hematology. Haematologica. 2002;87:1286–306.
Bowen D, Culligan D, Jowitt S, Kelsey S, Mufti G, Oscier D, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and therapy of adult myelodysplastic syndromes. Br J Haematol. 2003;120:187–200.
List A, Dewald G, Bennett J, Giagounidis A, Raza A, Feldman E, et al. Lenalidomide in the myelodysplastic syndrome with chromosome 5q deletion. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:1456–65.
Raza A, Reeves JA, Feldman EJ, Dewald GW, Bennett JM, Deeg HJ, et al. Phase 2 study of lenalidomide in transfusion-dependent, low-risk, and intermediate-1 risk myelodysplastic syndromes with karyotypes other than deletion 5q. Blood. 2008;111:86–93.
Fenaux P, Mufti GJ, Hellstrom-Lindberg E, Santini V, Finelli C, Giagounidis A, et al. Efficacy of azacitidine compared with that of conventional care regimens in the treatment of higher-risk myelodysplastic syndromes: a randomised, open-label, phase III study. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:223–32.
Acknowledgments
We greatly appreciate the assistance of Masae Honma of the Clinical Laboratory of Sado Sogo Hospital for her management of clinical samples and data.
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Yagisawa, K., Okazuka, K., Toba, K. et al. Features of Japanese patients with myelodysplastic syndrome in an aging population of Sado Island. Int J Hematol 95, 420–427 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-012-1031-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-012-1031-z