Abstract
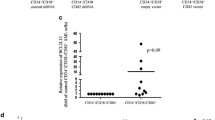
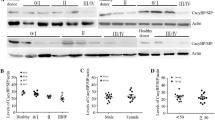
To detect the expression of cancerous inhibitor of phosphatase 2A (CIP2A) in chronic myelocytic leukemia (CML) and investigate the mechanism underlying CIP2A knockdown-mediated cell proliferation and apoptosis as well as the interaction of CIP2A with breakpoint cluster region-Abelson leukemia virus (BCR-ABL). CIP2A mRNA and protein expression in chronic myelocytic leukemia-chronic (CML-CP) patients and healthy controls were determined by RT-PCR and Western blot. In vivo, c-Myc expression, PP2A activity, cell proliferation, and apoptosis of CML cells were detected with CIP2A depletion. In addition, the relationship among CIP2A, BCR-ABL, and tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 was explored by depleting/overexpressing CIP2A or inhibiting BCR-ABL. The level of CIP2A mRNA was higher in CML-CP patients than healthy controls (56/74, 75.7 % vs. 1/35, 2.9 %, P < 0.001), and CIP2A protein was overexpressed in corresponding specimens. CIP2A knockdown by siRNA reduced the level of c-Myc protein and clonogenic formation, inhibited the activity of PP2A, K562 cell proliferation, and promoted cell apoptosis. Suppressing BCR-ABL by imatinib mesylate (IM) significantly decreased CIP2A expression. CIP2A knockdown decreased BCR-ABL but increased SHP-1 expression, and CIP2A overexpression had the reverse effect. CIP2A is overexpressed in CML-CP patients, and its expression may promote CML pathogenesis. CIP2A and BCR-ABL can regulate each other in a positive feedback loop. CIP2A may be a useful therapeutic target in CML-CP, particularly in patients with IM resistance. However, further studies are needed to validate the interaction between CIP2A and BCR-ABL using other tyrosine kinase inhibitors than IM.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CIP2A:
-
Cancerous inhibitor of PP2A
- PP2A:
-
Protein phosphatase 2A
- S62:
-
Serine 62
- CML:
-
Chronic myelocytic leukemia
- CP:
-
Chronic phase
- IM:
-
Imatinib mesylate
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- AML:
-
Acute myeloid leukemia
References
Heisterkamp N, Stephenson JR, Groffen J, Hansen PF, de Klein A, Bartram CR et al. Localization of the c-abl oncogene adjacent to a translocation break point in chronic myelocytic leukaemia. Nature. 1983;306(5940):239–42.
Shtivelman E, Lifshitz B, Gale RP, Canaani E. Fused transcript of abl and bcr genes in chronic myelogenous leukaemia. Nature. 1985;315(6020):550–4.
Lucas C, Wang L, Austin G, Knight K, Watmough S, Shwe K, et al. A population study of imatinib in chronic myeloid leukaemia demonstrates lower efficacy than in clinical trials. Leukemia. 2008;22(10):1963–6.
de Lavallade H, Apperley JF, Khorashad JS, Milojkovic D, Reid AG, Bua M, et al. Imatinib for newly diagnosed patients with chronic myeloid leukemia: incidence of sustained responses in an intention-to-treat analysis. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(20):3358–63.
Barnes DJ, Schultheis B, Adedeji S, Melo JV. Dose-dependent effects of Bcr-Abl in cell line models of different stages of chronic myeloid leukemia. Oncogene. 2005;24(42):6432–40.
Schultheis B, Szydlo R, Mahon FX, Apperley JF, Melo JV. Analysis of total phosphotyrosine levels in CD34+ cells from CML patients to predict the response to imatinib mesylate treatment. Blood. 2005;105(12):4893–4.
Sablina AA, Chen W, Arroyo JD, Corral L, Hector M, Bulmer SE, et al. The tumor suppressor PP2A Aβ regulates the RalA GTPase. Cell. 2007;129(5):969–82.
Schönthal AH. Role of serine/threonine protein phosphatase 2A in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2001;170(1):1–13.
Sontag E. Protein phosphatase 2A: the Trojan Horse of cellular signaling. Cell Signal. 2001;13(1):7–16.
Blume-Jensen P, Hunter T. Oncogenic kinase signalling. Nature. 2001;411(6835):355–65.
Neviani P, Santhanam R, Trotta R, Notari M, Blaser BW, Liu S, et al. The tumor suppressor PP2A is functionally inactivated in blast crisis CML through the inhibitory activity of the BCR/ABL-regulated SET protein. Cancer Cell. 2005;8(5):355–68.
Perrotti D, Neviani P. ReSETting PP2A tumour suppressor activity in blast crisis and imatinib-resistant chronic myelogenous leukaemia. Br J Cancer. 2006;95(7):775–81.
Côme C, Laine A, Chanrion M, Edgren H, Mattila E, Liu X, et al. CIP2A is associated with human breast cancer aggressivity. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15(16):5092–100.
Li W, Ge Z, Liu C, Liu Z, Björkholm M, Jia J, et al. CIP2A is overexpressed in gastric cancer and its depletion leads to impaired clonogenicity, senescence, or differentiation of tumor cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14(12):3722–8.
Junttila MR, Puustinen P, Niemelä M, Ahola R, Arnold H, Böttzauw T, et al. CIP2A inhibits PP2A in human malignancies. Cell. 2007;130(1):51–62.
Yi F, Ni W, Liu W, Bai J, Li W. Expression and biological role of CIP2A in human astrocytoma. Mol Med Rep. 2013;7(5):1376–80.
Xu P, Huang Q, Xie F, Xu X-L, Shao F. Increased expression of CIP2A in cholangiocarcinoma and correlation with poor prognosis. Hepatogastroenterology. 2013;60(124):669–72.
Laine A. The role of an oncoprotein CIP2A in breast cancer. Turku: University of Turku; 2013.
Basile JR, Czerninski R. The role of CIP2A in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther. 2010;10(7):700–2.
Qu W, Li W, Wei L, Xing L, Wang X, Yu J. CIP2A is overexpressed in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Med Oncol. 2012;29(1):113–8.
Wiegering A, Pfann C, Uthe FW, Otto C, Rycak L, Mäder U, et al. CIP2A influences survival in colon cancer and is critical for maintaining Myc expression. PLoS One. 2013;8(10):e75292.
Wang L, Gu F, Ma N, Zhang L, Bian J-M, Cao H-Y. CIP2A expression is associated with altered expression of epithelial–mesenchymal transition markers and predictive of poor prognosis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Tumor Biol. 2013:1–5.
Shi F, Ding Y, Ju S, Wu X, Cao S. Expression and prognostic significance of CIP2A in cutaneous malignant melanoma. Biomarkers. 2013;19(1):70–6.
Böckelman C, Hagström J, Mäkinen L, Keski-Säntti H, Häyry V, Lundin J, et al. High CIP2A immunoreactivity is an independent prognostic indicator in early-stage tongue cancer. Br J Cancer. 2011;104(12):1890–5.
Dong QZ, Wang Y, Dong XJ, Li ZX, Tang Z-P, Cui Q-Z, Wang E-H. CIP2A is overexpressed in non-small cell lung cancer and correlates with poor prognosis. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011;18(3):857–65.
Ma L, Wen Z-S, Liu Z, Hu Z, Ma J, Chen X-Q, et al. Overexpression and small molecule-triggered downregulation of CIP2A in lung cancer. PLoS One. 2011;6(5):e20159.
Zhai M, Cong L, Han Y, Tu G. CIP2A is overexpressed in osteosarcoma and regulates cell proliferation and invasion. Tumor Biol. 2013;35(2):1123–8.
Liu J, Wang X, Zhou G, Wang H, Xiang L, Cheng Y, et al. Cancerous inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2A is overexpressed in cervical cancer and upregulated by human papillomavirus 16 E7 oncoprotein. Gynecol Oncol. 2011;122(2):430–6.
Wang J, Li W, Li L, Yu X, Jia J, Chen C. CIP2A is over-expressed in acute myeloid leukaemia and associated with HL60 cells proliferation and differentiation. Int J Lab Hematol. 2011;33(3):290–8.
Lucas CM, Harris RJ, Giannoudis A, Copland M, Slupsky JR, Clark RE. Cancerous inhibitor of PP2A (CIP2A) at diagnosis of chronic myeloid leukemia is a critical determinant of disease progression. Blood. 2011;117(24):6660–8.
Zhao D, Liu Z, Ding J, Li W, Sun Y, Yu H, et al. Helicobacter pylori CagA upregulation of CIP2A is dependent on the Src and MEK/ERK pathways. Int J Med Microbiol. 2010;59(3):259–65.
Khanna A, Böckelman C, Hemmes A, Junttila MR, Wiksten J-P, Lundin M, et al. MYC-dependent regulation and prognostic role of CIP2A in gastric cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2009;101(11):793–805.
Liedtke M, Pandey P, Kumar S, Kharbanda S, Kufe D. Regulation of Bcr-Abl-induced SAP kinase activity and transformation by the SHPTP1 protein tyrosine phosphatase. Oncogene. 1998;17(15):1889.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81170514 and 30971151), the Project Sponsored by the Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars, State Education Ministry (The Project sponsored by SRF for ROCS, SEM), Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation, China (Nos. ZR2009CM002 and ZR2012HQ003), Traditional Chinese Medicine Science and Technology Development Program of Shandong Province (No. 2011-211), Colleges Science and Technology Project of Shandong Province (No. J10LF74) and the Independent Innovation Foundation of Shandong University (IIFSDU, No. 2012TS128).
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Huang, T., Sun, J. et al. CIP2A is overexpressed and involved in the pathogenesis of chronic myelocytic leukemia by interacting with breakpoint cluster region-Abelson leukemia virus. Med Oncol 31, 112 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0112-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0112-7