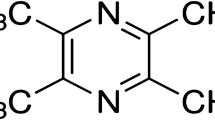
Abstract
Diabetes is associated with behavioural and neurochemical alterations. In this manuscript, we are reporting the beneficial effects of parthenolide, an NF-κB inhibitor on behavioural and neurochemical deficits in type 2 diabetic rat model. Diabetes was induced by high-fat diet followed by low dose of streptozotocin (35 mg/kg). Elevated plus maze, open-field, MWM and passive avoidance test paradigm were used to assess behavioural and cognitive deficits. Three-week treatment of parthenolide (0.25 and 0.50 mg/kg; i.p.) attenuated diabetes-induced alteration in cognitive function in Morris water maze and passive avoidance test. Anxiety-like behaviour was also reduced by parthenolide treatment. Moreover, TNF-α and IL-6 levels were significantly decreased in cortex and hippocampus of parthenolide-treated rats. Three-week parthenolide treatment also toned down the alteration of GABA and glutamate homoeostasis. Results of this study corroborate the involvement of neuroinflammation in the development of behavioural and neurochemical deficits in diabetic animals and point towards the therapeutic potential of parthenolide in diabetes-induced alteration of learning, memory and anxiety behaviour.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akrivos, J., Ravona-Springer, R., Schmeidler, J., LeRoith, D., Heymann, A., Preiss, R., et al. (2015). Glycemic control, inflammation, and cognitive function in older patients with type 2 diabetes. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, 30(10), 1093–1100.
Bak, L. K., Schousboe, A., & Waagepetersen, H. S. (2006). The glutamate/GABA-glutamine cycle: Aspects of transport, neurotransmitter homeostasis and ammonia transfer. Journal of Neurochemistry, 98, 641–653.
Barry, C., Heys, J. G., & Hasselmo, M. E. (2012). Possible role of acetylcholine in regulating spatial novelty effects on theta rhythm and grid cells. Frontiers in Neural Circuits, 6, 5. doi:10.3389/fncir.2012.00005.
Carola, V., D’Olimpio, F., Brunamonti, E., Mangia, F., & Renzi, P. (2002). Evaluation of the elevated plus-maze and open-field tests for the assessment of anxiety-related behaviour in inbred mice. Behavioural Brain Research, 134, 49–57.
Christoffel, D. J., Golden, S. A., Heshmati, M., Graham, A., Birnbaum, S., Neve, R. L., et al. (2012). Effects of inhibitor of κB kinase activity in the nucleus accumbens on emotional behavior. Neuropsychopharmacology, 37(12), 2615–2623.
Curry, E. A., 3rd, Murry, D. J., Yoder, C., Fife, K., Armstrong, V., Nakshatri, H., et al. (2004). Phase I dose escalation trial of feverfew with standardized doses of parthenolide in patients with cancer. Investigational New Drugs, 22(3), 299–305. doi:10.1023/B:DRUG.0000026256.38560.be.
Datusalia, A. K., & Sharma, S. S. (2014). Amelioration of diabetes-induced cognitive deficits by GSK-3beta inhibition is attributed to modulation of neurotransmitters and neuroinflammation. Molecular Neurobiology, 50(2), 390–405. doi:10.1007/s12035-014-8632-x.
Datusalia, A. K., & Sharma, S. S. (2016). NF-kappaB inhibition resolves cognitive deficits in experimental type 2 diabetes mellitus through CREB and Glutamate/GABA neurotransmitters pathway. Current Neurovascular Research, 13(1), 22–32.
D’Hooge, R., & De Deyn, P. P. (2001). Applications of the Morris water maze in the study of learning and memory. Brain Research Reviews, 36(1), 60–90.
Dong, L., Qiao, H., Zhang, X., Zhang, X., Wang, C., Wang, L., et al. (2013). Parthenolide is neuroprotective in rat experimental stroke model: Downregulating NF-kappaB, phospho-p38MAPK, and caspase-1 and ameliorating BBB permeability. Mediators of Inflammation, 2013, 370804. doi:10.1155/2013/370804.
Donzis, E. J., & Tronson, N. C. (2014). Modulation of learning and memory by cytokines: Signaling mechanisms and long term consequences. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, 115, 68–77. doi:10.1016/j.nlm.2014.08.008.
Duncan, B. B., Schmidt, M. I., Pankow, J. S., Ballantyne, C. M., Couper, D., Vigo, A., et al. (2003). Low-grade systemic inflammation and the development of type 2 diabetes: The atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Diabetes, 52(7), 1799–1805.
Eysenck, M. W., Derakshan, N., Santos, R., & Calvo, M. G. (2007). Anxiety and cognitive performance: Attentional control theory. Emotion, 7, 336–353.
Ganesh Yerra, V., Negi, G., Sharma, S. S., & Kumar, A. (2013). Potential therapeutic effects of the simultaneous targeting of the Nrf2 and NF-κB pathways in diabetic neuropathy. Redox Biology, 1, 394–397. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2013.07.005.
Ghantous, A., Gali-Muhtasib, H., Vuorela, H., Saliba, N. A., & Darwiche, N. (2010). What made sesquiterpene lactones reach cancer clinical trials? Drug Discovery Today, 15(15–16), 668–678. doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2010.06.002.
Ghantous, A., Sinjab, A., Herceg, Z., & Darwiche, N. (2013). Parthenolide: From plant shoots to cancer roots. Drug Discovery Today, 18(17–18), 894–905. doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2013.05.005.
Gorelick, P. B. (2010). Role of inflammation in cognitive impairment: Results of observational epidemiological studies and clinical trials. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1207, 155–162. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05726.x.
Gould, T. D., Dao, D. T., & Kovacsics, C. E. (2009). The open field test. In T.D. Gould (Ed.), Mood and Anxiety Related Phenotypes in Mice (pp. 1–20): Springer.
Hasselmo, M. E. (2006). The role of acetylcholine in learning and memory. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 16, 710–715. doi:10.1016/j.conb.2006.09.002.
Hensley, K. (2010). Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease: Mechanisms, pathologic consequences, and potential for therapeutic manipulation. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 21, 1–14.
Hicks, D., John, D., Makova, N. Z., Henderson, Z., Nalivaeva, N. N., & Turner, A. J. (2011). Membrane targeting, shedding and protein interactions of brain acetylcholinesterase. Journal of Neurochemistry, 116(5), 742–746. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.07032.x.
Hwang, T., & Masterman, D. (2004). Mild cognitive impairment is associated with characteristic neuropsychiatric symptoms. Alzheimer Disease and Associated Disorders, 18, 17–21.
IDF Diabetes Atlas Group. (2015). Update of mortality attributable to diabetes for the IDF Diabetes Atlas: Estimates for the year 2013. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, 109(3), 461–465.
Jaworski, T., Lechat, B., Demedts, D., Gielis, L., Devijver, H., Borghgraef, P., et al. (2011). Dendritic degeneration, neurovascular defects, and inflammation precede neuronal loss in a mouse model for tau-mediated neurodegeneration. American Journal of Pathology, 179(4), 2001–2015. doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.06.025.
Juliana, C., Fernandes-Alnemri, T., Wu, J., Datta, P., Solorzano, L., Yu, J. W., et al. (2010). Anti-inflammatory compounds parthenolide and Bay 11-7082 are direct inhibitors of the inflammasome. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 285(13), 9792–9802. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.082305.
Kaltschmidt, B., Ndiaye, D., Korte, M., Pothion, S., Arbibe, L., Prullage, M., et al. (2006). NF-kappaB regulates spatial memory formation and synaptic plasticity through protein kinase A/CREB signaling. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 26(8), 2936–2946. doi:10.1128/MCB.26.8.2936-2946.2006.
Kodl, C. T., & Seaquist, E. R. (2008). Cognitive dysfunction and diabetes mellitus. Endocrine Reviews, 29, 494–511.
Kuhad, A., Bishnoi, M., Tiwari, V., & Chopra, K. (2009). Suppression of NF-kappabeta signaling pathway by tocotrienol can prevent diabetes associated cognitive deficits. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior, 92(2), 251–259. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2008.12.012.
Kwok, B. H., Koh, B., Ndubuisi, M. I., Elofsson, M., & Crews, C. M. (2001). The anti-inflammatory natural product parthenolide from the medicinal herb Feverfew directly binds to and inhibits IkappaB kinase. Chemistry and Biology, 8(8), 759–766.
Li, J., Tang, Y., & Cai, D. (2012). IKKbeta/NF-kappaB disrupts adult hypothalamic neural stem cells to mediate a neurodegenerative mechanism of dietary obesity and pre-diabetes. Nature Cell Biology, 14(10), 999–1012. doi:10.1038/ncb2562.
Llansola, M., Montoliu, C., Agusti, A., Hernandez-Rabaza, V., Cabrera-Pastor, A., Gomez-Gimenez, B., et al. (2015). Interplay between glutamatergic and GABAergic neurotransmission alterations in cognitive and motor impairment in minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Neurochemistry International, 88, 15–19. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2014.10.011.
Manschot, S. M., Biessels, G. J., Cameron, N. E., Cotter, M. A., Kamal, A., Kappelle, L. J., et al. (2003). Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition partially prevents deficits in water maze performance, hippocampal synaptic plasticity and cerebral blood flow in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Brain Research, 966(2), 274–282. doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(02)04211-7.
Materazzi, S., Benemei, S., Fusi, C., Gualdani, R., De Siena, G., Vastani, N., et al. (2013). Parthenolide inhibits nociception and neurogenic vasodilatation in the trigeminovascular system by targeting the TRPA1 channel. Pain, 154(12), 2750–2758. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2013.08.002.
Meffert, M. K., Chang, J. M., Wiltgen, B. J., Fanselow, M. S., & Baltimore, D. (2003). NF-kappa B functions in synaptic signaling and behavior. Nature Neuroscience, 6(10), 1072–1078. doi:10.1038/nn1110.
Mijnhout, G. S., Scheltens, P., Diamant, M., Biessels, G. J., Wessels, A. M., Simsek, S., et al. (2006). Diabetic encephalopathy: A concept in need of a definition. Diabetologia, 49, 1447–1448. doi:10.1007/s00125-006-0221-8.
Mittra, S., Datta, A., Singh, S. K., & Singh, A. (2000). 5-Hydroxytryptamine-inhibiting property of Feverfew: Role of parthenolide content. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica, 21, 1106–1114.
Moosavi, M., Zarifkar, A. H., Farbood, Y., Dianat, M., Sarkaki, A., & Ghasemi, R. (2014). Agmatine protects against intracerebroventricular streptozotocin-induced water maze memory deficit, hippocampal apoptosis and Akt/GSK3beta signaling disruption. European Journal of Pharmacology, 736, 107–114. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.03.041.
Morris, R. (1984). Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 11, 47–60.
Muriach, M., Flores-Bellver, M., Romero, F. J., & Barcia, J. M. (2014). Diabetes and the brain: Oxidative stress, inflammation, and autophagy. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2014, 102158. doi:10.1155/2014/102158.
Myhrer, T. (2003). Neurotransmitter systems involved in learning and memory in the rat: A meta-analysis based on studies of four behavioral tasks. Brain Research Reviews, 41, 268–287. doi:10.1016/S0165-0173(02)00268-0.
Ohta, Y., Tremblay, C., Schneider, J. A., Bennett, D. A., Calon, F., & Julien, J. P. (2014). Interaction of transactive response DNA binding protein 43 with nuclear factor kappaB in mild cognitive impairment with episodic memory deficits. Acta Neuropathology Communications, 2, 37. doi:10.1186/2051-5960-2-37.
Ownby, R. L. (2010). Neuroinflammation and cognitive aging. Current Psychiatry Reports, 12(1), 39–45. doi:10.1007/s11920-009-0082-1.
Pandey, D. K., Rajkumar, R., Mahesh, R., & Radha, R. (2008). Depressant-like effects of parthenolide in a rodent behavioural antidepressant test battery. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 60(12), 1643–1650. doi:10.1211/jpp/60.12.0010.
Patel, S., & Santani, D. (2009). Role of NF-kappa B in the pathogenesis of diabetes and its associated complications. Pharmacological Reports, 61, 595–603.
Phillips, E. C., Croft, C. L., Kurbatskaya, K., O’Neill, M. J., Hutton, M. L., Hanger, D. P., et al. (2014). Astrocytes and neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Biochemical Society Transactions, 42(5), 1321–1325. doi:10.1042/BST20140155.
Reske-Nielsen, E., Lundbæk, K., & Rafaelsen, O. J. (1966). Pathological changes in the central and peripheral nervous system of young long-term diabetics I. diabetic encephalopathy. Diabetologia, 1, 233–241. doi:10.1007/BF01257917.
Rummel, C., Gerstberger, R., Roth, J., & Hubschle, T. (2011). Parthenolide attenuates LPS-induced fever, circulating cytokines and markers of brain inflammation in rats. Cytokine, 56(3), 739–748. doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2011.09.022.
Saranitzky, E., White, C. M., Baker, E. L., Baker, W. L., & Coleman, C. I. (2009). Feverfew for migraine prophylaxis: A systematic review. Journal Dietary Supplements, 6(2), 91–103. doi:10.1080/19390210902861809.
Schmeisser, M. J., Baumann, B., Johannsen, S., Vindedal, G. F., Jensen, V., Hvalby, O. C., et al. (2012). IkappaB kinase/nuclear factor kappaB-dependent insulin-like growth factor 2 (Igf2) expression regulates synapse formation and spine maturation via Igf2 receptor signaling. Journal of Neuroscience, 32(16), 5688–5703. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0111-12.2012.
Schousboe, A., Bak, L. K., Sickmann, H. M., Sonnewald, U., & Waagepetersen, H. S. (2007). Energy substrates to support glutamatergic and GABAergic synaptic function: Role of glycogen, glucose and lactate. Neurotoxicity Research, 12(4), 263–268.
Shankaranarayana Rao, B. S., Raju, T. R., & Meti, B. L. (1998). Self-stimulation of lateral hypothalamus and ventral tegmentum increases the levels of noradrenaline, dopamine, glutamate, and AChE activity, but not 5-hydroxytryptamine and GABA levels in hippocampus and motor cortex. Neurochemical Research, 23(8), 1053–1059.
Sickmann, H. M., Waagepetersen, H. S., Schousboe, A., Benie, A. J., & Bouman, S. D. (2012). Brain glycogen and its role in supporting glutamate and GABA homeostasis in a type 2 diabetes rat model. Neurochemistry International, 60, 267–275. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2011.12.019.
Skovso, S. (2014). Modeling type 2 diabetes in rats using high fat diet and streptozotocin. Journal of Diabetes Investigation, 5(4), 349–358. doi:10.1111/jdi.12235.
Smith, K. J., Béland, M., Clyde, M., Gariépy, G., Pagé, V., Badawi, G., et al. (2013). Association of diabetes with anxiety: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Psychosomatic Research, 74, 89–99. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychores.2012.11.013.
Snow, W. M., Stoesz, B. M., Kelly, D. M., & Albensi, B. C. (2014). Roles for NF-kappaB and gene targets of NF-kappaB in synaptic plasticity, memory, and navigation. Molecular Neurobiology, 49(2), 757–770. doi:10.1007/s12035-013-8555-y.
Srikumar, B., Ramkumar, K., Raju, T., & Shankaranarayana, R. (2004). Assay of acetylcholinesterase activity in the brain (pp. 142–144). Bangalore, India: National Institute of Mental Health and Neuro Sciences.
Srinivasan, K., Viswanad, B., Asrat, L., Kaul, C. L., & Ramarao, P. (2005). Combination of high-fat diet-fed and low-dose streptozotocin-treated rat: A model for type 2 diabetes and pharmacological screening. Pharmacological Research, 52(4), 313–320.
Srodulski, S., Sharma, S., Bachstetter, A. B., Brelsfoard, J. M., Pascual, C., Xie, X. S., et al. (2014). Neuroinflammation and neurologic deficits in diabetes linked to brain accumulation of amylin. Molecular Neurodegeneration, 9, 30. doi:10.1186/1750-1326-9-30.
Sun, B., Halabisky, B., Zhou, Y., Palop, J. J., Yu, G., Mucke, L., et al. (2009). Imbalance between GABAergic and Glutamatergic Transmission Impairs Adult Neurogenesis in an Animal Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Cell Stem Cell, 5, 624–633. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2009.10.003.
Tassorelli, C., Greco, R., Morazzoni, P., Riva, A., Sandrini, G., & Nappi, G. (2005). Parthenolide is the component of tanacetum parthenium that inhibits nitroglycerin-induced Fos activation: Studies in an animal model of migraine. Cephalalgia, 25(8), 612–621. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2005.00915.x.
Tellez, R., Gómez-Víquez, L., & Meneses, A. (2012). GABA, glutamate, dopamine and serotonin transporters expression on memory formation and amnesia. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, 97, 189–201. doi:10.1016/j.nlm.2011.12.002.
Tilstra, J. S., Clauson, C. L., Niedernhofer, L. J., & Robbins, P. D. (2011). NF-kappaB in Aging and Disease. Aging and Disease, 2(6), 449–465.
von Bernhardi, R., Eugenin-von Bernhardi, L., & Eugenin, J. (2015). Microglial cell dysregulation in brain aging and neurodegeneration. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 7, 124. doi:10.3389/fnagi.2015.00124.
Walf, A. A., & Frye, C. A. (2007). The use of the elevated plus maze as an assay of anxiety-related behavior in rodents. Nature Protocols, 2(2), 322–328.
Wang, M., & Li, Q. (2015). Parthenolide could become a promising and stable drug with anti-inflammatory effects. Natural Product Research, 29(12), 1092–1101. doi:10.1080/14786419.2014.981541.
Weber, J. T., O’Connor, M. F., Hayataka, K., Colson, N., Medora, R., Russo, E. B., et al. (1997). Activity of Parthenolide at 5HT2A receptors. Journal of Natural Products, 60, 651–653. doi:10.1021/np960644d.
Yirmiya, R., & Goshen, I. (2011). Immune modulation of learning, memory, neural plasticity and neurogenesis. Brain Behavior and Immunity, 25(2), 181–213. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2010.10.015.
Zhao, Y., Krishnamurthy, B., Mollah, Z. U. A., Kay, T. W. H., & Thomas, H. E. (2011). NF-κB in type 1 diabetes. Inflammation and Allergy Drug Targets, 10, 208–217.
Zou, J., & Crews, F. T. (2012). Inflammasome-IL-1beta signaling mediates ethanol inhibition of hippocampal neurogenesis. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 6, 77. doi:10.3389/fnins.2012.00077.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by an institutional funding from National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research (NIPER), S.A.S. Nagar and Department of Pharmaceuticals, Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers, Government of India. We thank University Grant Commission, New Delhi, India, for providing research fellowship to Mr. Ashok Kumar Datusalia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khare, P., Datusalia, A.K. & Sharma, S.S. Parthenolide, an NF-κB Inhibitor Ameliorates Diabetes-Induced Behavioural Deficit, Neurotransmitter Imbalance and Neuroinflammation in Type 2 Diabetes Rat Model. Neuromol Med 19, 101–112 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-016-8434-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-016-8434-6