Abstract
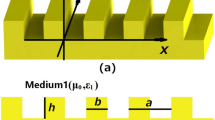
The propagation characteristics of symmetric surface plasmon polariton mode in a glass–metal–glass waveguide are presented. Gallium lanthanum sulfide has been taken as the glass and silver (Ag) has been used as the metal. The analysis has been done both numerically and analytically. A two-dimensional finite-difference time-domain-based simulation model has been developed in order to analyze the propagation characteristics numerically. The obtained results using numerical and analytical methods have been compared and a very good agreement has been found.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes WL, Dereux A, Ebbesen TW (2003) Surface plasmon subwavelength optics. Nature 424(6950):824–830
Dionne J, Lezec H, Atwater HA (2006) Highly confined photon transport in subwavelength metallic slot waveguides. Nano Lett 6(9):1928–1932
Gramotnev DK, Bozhevolnyi SI (2010) Plasmonics beyond the diffraction limit. Nat Photonics 4(2):83–91
Haes AJ, Van Duyne RP (2002) A nanoscale optical biosensor: sensitivity and selectivity of an approach based on the localized surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy of triangular silver nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 124(35):10596–10604
Blaikie RJ, Melville DO (2005) Imaging through planar silver lenses in the optical near field. J Opt A Pure Appl Opt 7(2):S176
Melville DO, Blaikie RJ (2005) Super-resolution imaging through a planar silver layer. Opt Express 13(6):2127–2134
Hosseini A, Massoud Y (2006) A low-loss metal–insulator–metal plasmonic Bragg reflector. Opt Express 14(23):11318–11323
Henzie J, Lee MH, Odom TW (2007) Multiscale patterning of plasmonic metamaterials. Nat Nanotechnol 2(9):549–554
Ferry VE, Sweatlock LA, Pacifici D, Atwater HA (2008) Plasmonic nanostructure design for efficient light coupling into solar cells. Nano Lett 8(12):4391–4397
Chou SY, Ding W (2013) Ultrathin, high-efficiency, broad-band, omni-acceptance, organic solar cells enhanced by plasmonic cavity with subwavelength hole array. Opt Express 21(101):A60–A76
Asobe M (1997) Nonlinear optical properties of chalcogenide glass fibers and their application to all-optical switching. Opt Fiber Technol 3(2):142–148
Des Francs GC, Grandidier J, Massenot S, Bouhelier A, Weeber J-C, Dereux A (2009) Integrated plasmonic waveguides: a mode solver based on density of states formulation. Phys Rev B 80(11):115419
Sámson ZL, Yen SC, MacDonald KF, Knight K, Li S, Hewak DW, Tsai DP, Zheludev NI (2010) Chalcogenide glasses in active plasmonics. Physica Status Solidi (RRL)-Rapid Res Lett 4(10):274–276
Rakic AD, Djurišic AB, Elazar JM, Majewski ML (1998) Optical properties of metallic films for vertical-cavity optoelectronic devices. Appl Opt 37(22):5271–5283
Sagor RH (2012) Plasmon enhanced symmetric mode generation in metal–insulator–metal structure with Kerr nonlinear effect. Int J Comput Appl 50(18):24–28
Yee K (1966) Numerical solution of initial boundary value problems involving Maxwell’s equations in isotropic media. IEEE Trans Antenn Propag 14(3):302–307
Berenger JP (1994) A perfectly matched layer for the absorption of electromagnetic waves. J Comput Phys 114(2):185–200
Taflove A, Hagness SC (2000) Computational electrodynamics: the finite-difference time-domain method, 2nd edn. Artech House, Norwood
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saber, M.G., Sagor, R.H. Characteristics of Symmetric Surface Plasmon Polariton Mode in Glass–Metal–Glass Waveguide. Plasmonics 8, 1621–1625 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-013-9579-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-013-9579-x