Abstract
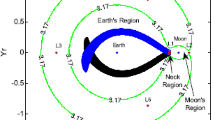
As one of the vital steps in the 3rd phase of China’s lunar exploration program (CLEP), the circumlunar return and reentry spacecraft, developed by China Academy of Space Technology (CAST), is used to demonstrate the key technologies of hyper-speed return and reentry spacecraft. The system configuration and flight process are presented in this paper, as well as the analysis of mission characteristics, the key technologies and the technical advancement during the R&D progress. The significance of circumlunar return and reentry spacecraft is given at the end.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ye P J, Peng J. Deep space exploration and its prospect in China. Eng Sci, 2006, 8: 13–18
Zhao B, Huang F, Cheng X L. Utilization of engineering calculation method for transitional regime aerodynamics. Spacecraft Recovery Remote Sens, 2014, 1: 6–13
Lv J M, Pan H L, Miao W B, et al. Impact of chemical non-equilibrium effect on aerodynamic characteristics of reentry capsules. Spacecraft Recovery Remote Sens, 2014, 3: 11–19
Chen S Y, Miao W B, Cheng X L. Study on radiative heating calculation method for reentry vehicles. Acta Aerodyn Sin, 2013, 31: 36–41
Chaudhuri S K, Nandi P K. Transfer alignment for space vehicles launched form a moving base. Defense Sci J, 2005, 55: 245–252
Dai S W, Li J, Dai H D, et al. Study of rapid transfer alignment error model. J Astronautics, 2009, 30: 261–266
Zhang L, Yu D Y, Zhang H. Design and analysis of circumlunar free-return orbits. Spacecraft Eng, 2010, 19: 128–135
Hou Y Z, Zuo G, Wang P, et al. Entry/reentry corridor design for human deep space exploration. Spacecraft Recovery Remote Sens, 2014, 3: 1–10
Du X, Li H Y, Shen H X. Skip entry corridor design for lunar module considering multiple constraints. Manned Spaceflight, 2014, 5: 21–33
Fan H L, Huang J R, Liu Q Z. Scheme of fluid loop system on manned spacecraft for transport. Chin Space Sci Technol, 2007, 27: 38–43
Peng Q B, Shen H X, Li H Y. Free return orbit design and characteristics analysis for manned lunar mission. Sci China Tech Sci, 2011, 54: 3243–3250
Liu M X, Xue T, Zhao Y N, et al. Composite thermal protection coating on woven silica fiber fabrics. Sci China Tech Sci, 2014, 57: 1121–1126
Wang Y P, Zhen X, Wu J, et al. Hybrid CFD/FEM-BEM simulation of cabin aerodynamic noise for vehicles traveling at high speed. Sci China Tech Sci, 2013, 56: 1697–1708
Wu W R, Liu W W, Qiao D, et al. Investigation on the development of deep space exploration. Sci China Tech Sci, 2012, 55: 1086–1091
Wang S, Shang H B, Wu W R. Interplanetary transfers employing invariant manifolds and gravity assist between periodic orbits. Sci China Tech Sci, 2013, 56: 786–794
Sun Z Z, Jia Y, Zhang H. Technological advancements and promotion roles of Chang’e-3 lunar probe mission. Sci China Tech Sci, 2013, 56: 2702–2708
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, M., Zhang, W., Peng, J. et al. Technical advancements and significance of circumlunar return and reentry spacecraft. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 58, 738–745 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-015-5792-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-015-5792-5