Abstract
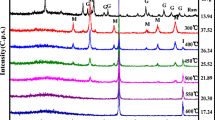
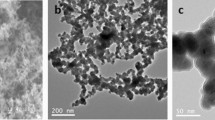
Mechanism of zinc iron removal by zero-valent iron was discussed through zinc removal responses to several operational conditions of a packed column reactor with zero-valent iron powder. The adsorption isotherm observed implied that a kind of chemisorption was responsible for zinc removal. Zinc removal by zero-valent iron was enhanced by dissolved oxygen and ferric ion addition. However, it was deteriorated under acidic pH. In addition, zinc adsorbed on zero-valent iron was eluted by a reducing agent such as citric acid, whereas the zinc was not eluted by diluted sulfuric acid. Consequently, the zinc removal mechanism by zero-valent iron was inferred to be as follows: Zero-valent iron was firstly corroded and oxidized into ferric ion by dissolved oxygen. The ferric ion was precipitated as iron hydroxide onto the surface of the zero-valent iron powder. Zinc ion was adsorbed on and/or coprecipitated with the iron hydroxide. The iron hydroxide was finally oxidized and transformed into iron oxides.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bard, A. J., Parsons, R., & Jordan, J. (1985). Standard potentials in aqueous solution. New York: Marcel Dekker.
Charerntanyarak, L. (1999). Heavy metals removal by chemical coagulation and precipitation. Water Science and Technology, 39(10–11), 135–138.
Clements, W. H., & Kiffney, P. M. (1995). The influence of elevation on benthic community responses to heavy metals in Rocky Mountain streams. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 52, 1966–1977.
Dries, J., Bastiaens, L., Springael, D., Kuypers, S., Agathos, S. N., & Diels, L. (2005). Effect of humic acids on heavy metal removal by zero-valent iron in batch and continuous flow column systems. Water Research, 39, 3531–3540.
Furukawa, Y., Kim, J., Watkins, J., & Wilken, R. T. (2002). Formation of ferrihydrite and associated iron corrosion products in permeable reactive barriers of zero-valent iron. Environmental Science & Technology, 36, 5469–5475.
Gordon, R. B., Bertram, M., & Graedel, T. E. (2006). Metal stocks and sustainability. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103, 1209–1214.
Hatakeyama, S. (1989). Effect of copper and zinc on the growth and emergence of epeorus latifolium (ephemeroptera) in an indoor model stream. Hydrobiologia, 174, 17–27.
Inamoto, J. (2006). Waste water treatment for plating. Journal of the Surface Finishing Society of Japan, 57, 889–894 (in Japanese).
Iwasaki, Y., Kagaya, T., Miyamoto, K., & Matsuda, H. (2009). Effects of heavy metals on riverine benthic macroinvertebrate assemblages with reference to potential food availability for drift-feeding fiches. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 28, 354–363.
Jones, D. V., Darrah, P. R., & Kochian, L. V. (1996). Critical evaluation of organic acid mediated iron dissolution in the rhizosphere and its potential role in root iron uptake. Plant and Soil, 180, 57–66.
Lee, T., Park, J., & Lee, J. (2004). Waste green sands as reactive media for the removal of zinc from water. Chemosphere, 56, 571–581.
Nakanishi, J., Naito, W., & Kamo, M. (2008). Zinc. Tokyo: Maruzen (in Japanese).
Nishiyama, T. (2009). Rare metal resource. Tokyo: Maruzen (in Japanese).
Oh, B., Lee, J., & Yoon, J. (2007). Removal of contaminants in leachate from landfill by waste steel scrap to converter slag. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 29, 331–336.
Rangsivek, R., & Jekel, M. R. (2005). Removal of dissolved metals by zero-valent iron (ZVI): kinetics, equilibria, processes and implications for stormwater runoff treatment. Water Research, 39, 4153–4163.
Roh, Y., Lee, S. Y., & Elless, M. P. (2000). Caracterization of corrosion products in the permeable reactive barriers. Environmental Geology, 40, 184–194.
Schwertmann, U. (1991). Solubility and dissolution of iron oxides. Plant and Soil, 130, 1–25.
Shokes, T. E., & Möller, G. (1999). Removal of dissolved heavy metals from acid rock drainage using iron metal. Environmental Science & Technology, 33, 282–287.
Stauber, J. L., & Florence, T. M. (1990). Mechanism of toxicity of zinc to the marine diatom Nitzschia closterium. Marine Biology, 105, 519–524.
World Health Organization. (2001). Zinc, Environmental Health Criteria 221. Geneva: World Health Organization.
Zouboulis, A. I., Lazaridis, N. K., & Grohmann, A. (2002). Toxic metals removal from waste waters by upflow filtration with floating filter medium. I. The case of zinc. Separation Science and Technology, 37, 403–416.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kishimoto, N., Iwano, S. & Narazaki, Y. Mechanistic Consideration of Zinc Ion Removal by Zero-Valent Iron. Water Air Soil Pollut 221, 183–189 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-011-0781-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-011-0781-1