Abstract
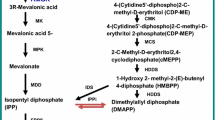
Artemisinin, isolated from an annual herbaceous plant Artemisia annua L., is an effective antimalarial compound. However, artemisinin is accumulated in small amounts (0.01–0.1% leaf dry weight) in A. annua, resulting in constant high artemisinin price. Although metabolic engineering of partial artemisinin metabolic pathway in yeast achieved great success, artemisinin from A. annua is still the important business resource. Here, we report on the generation of transgenic plants with simultaneously overexpressing four artemisinin biosynthetic pathway genes, amorpha-4,11-diene synthase gene (ADS), amorpha-4,11-diene 12-monooxygenase gene (CYP71AV1), cytochrome P450 reductase gene (CPR), and aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 gene (ALDH1) via Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. The qRT-PCR analysis demonstrated that the introduced four genes of the transgenic lines were all highly expressed. Through high-performance liquid chromatography analysis, the artemisinin contents were increased markedly in transformants, with the highest being 3.4-fold higher compared with non-converter. These results indicate that overexpression of multiple artemisinin biosynthetic pathway genes is a promising approach to improve artemisinin yield in A. annua.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ADS:
-
Amorpha-4,11-diene synthase
- CYP71AV1:
-
Cytochrome P450 monooxygenase
- CPR:
-
Cytochrome P450 reductase
- ALDH1:
-
Aldehyde dehydrogenase1
- HPLC:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
References
Abdin MZ, Israr M, Rehman RU, Jain SK (2003) Artemisinin, a novel antimalarial drug: biochemical and molecular approaches for enhanced production. Planta Med 69(04):289–299. doi:10.1055/s-2003-38871
Aquil S, Husaini AM, Abdin MZ, Rather GM (2009) Overexpression of the HMG-CoA reductase gene leads to enhanced artemisinin biosynthesis in transgenic Artemisia annua plants. Planta Med 75(13):1453–1458. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1185775
Banyai W, Kirdmanee C, Mii M, Supaibulwatana K (2010) Overexpression of farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase (FPS) gene affected artemisinin content and growth of Artemisia annua L. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 103(2):255–265. doi:10.1007/s11240-010-9775-8
Brisibe EA, Chukwurah PN (2014) Production of Artemisinin in planta and in microbial systems need not be mutually exclusive. Artemisia annua-pharmacology and biotechnology. Springer, Berlin, pp 269–292
Brown GD, Sy L-K (2004) In vivo transformations of dihydroartemisinic acid in Artemisia annua plants. Tetrahedron 60(5):1139–1159. doi:10.1016/j.tet.2003.11.070
Brown GD, Sy L-K (2007) In vivo transformations of artemisinic acid in Artemisia annua plants. Tetrahedron 63(38):9548–9566. doi:10.1016/j.tet2007.06.062
Corsello MA, Garg NK (2015) Synthetic chemistry fuels interdisciplinary approaches to the production of artemisinin. Nat Prod Rep 32(3):359–366. doi:10.1039/c4np00113c
Doyle JJ (1990) Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12:13–15
Efferth T (2006) Molecular pharmacology and pharmacogenomics of artemisinin and its derivatives in cancer cells. Curr Drug Target 7(4):407–421. doi:10.2174/138945006776359412
Fu X, Shi P, Shen Q, Jiang W, Tang Y, Lv Z, Yan T, Li L, Wang G, Sun X, Tang K (2015) T-shaped trichome-specific expression of monoterpene synthase ADH2 using promoter-beta-GUS fusion in transgenic Artemisia annua L. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. doi:10.1002/bab.1440
Fujisawa M, Takita E, Harada H, Sakurai N, Suzuki H, Ohyama K, Shibata D, Misawa N (2009) Pathway engineering of Brassica napus seeds using multiple key enzyme genes involved in ketocarotenoid formation. J Exp Bot 60(4):1319–1332. doi:10.1093/jxb/erp006
Jiang W, Fu X, Pan Q, Tang Y, Shen Q, Lv Z, Yan T, Shi P, Li L, Zhang L, Wang G, Sun X, Tang K (2016) Overexpression of AaWRKY1 leads to an enhanced content of artemisinin in Artemisia annua. Biomed Res Int 2016:7314971. doi:10.1155/2016/7314971
Kim S-H, Heo K, Chang Y-J, Park S-H, Rhee S-K, Kim S-U (2006) Cyclization mechanism of amorpha-4,11-diene synthase, a key enzyme in artemisinin biosynthesis. J Nat Prod 69(5):758–762
Liu B, Wang H, Du Z, Li G, Ye H (2011) Metabolic engineering of artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua L. Plant Cell Rep 30(5):689–694. doi:10.1007/s00299-010-0967-9
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25(4):402–408. doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Lu X, Shen Q, Zhang L, Zhang F, Jiang W, Lv Z, Yan T, Fu X, Wang G, Tang K (2013a) Promotion of artemisinin biosynthesis in transgenic Artemisia annua by overexpressing ADS, CYP71AV1 and CPR genes. Ind Crop Prod 49:380–385. doi:10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.04.045
Lu X, Zhang L, Zhang F, Jiang W, Shen Q, Zhang L, Lv Z, Wang G, Tang K (2013b) AaORA, a trichome-specific AP2/ERF transcription factor of Artemisia annua, is a positive regulator in the artemisinin biosynthetic pathway and in disease resistance to Botrytis cinerea. New Phytol 198(4):1191–1202
Lv Z, Zhang F, Pan Q, Fu X, Jiang W, Shen Q, Yan T, Shi P, Lu X, Sun X, Tang K (2016) Branch pathway blocking in Artemisia annua is a useful method for obtaining high yield artemisinin. Plant Cell Physiol 57(3):588–602. doi:10.1093/pcp/pcw014
Ma C, Wang H, Lu X, Wang H, Xu G, Liu B (2009) Terpenoid metabolic profiling analysis of transgenic Artemisia annua L. by comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Metabolomics 5(4):497–506. doi:10.1007/s11306-009-0170-6
Ma DM, Wang Z, Wang L, Alejos-Gonzales F, Sun MA, Xie DY (2015) A Genome-wide scenario of terpene pathways in self-pollinated Artemisia annua. Mol Plant 8(11):1580–1598 doi:10.1016/j.molp.2015.07.004
McCormick S, Niedermeyer J, Fry J, Barnason A, Horsch R, Fraley R (1986) Leaf disc transformation of cultivated tomato (L. esculentum) using Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plant Cell Rep 5(2):81–84. doi:10.1007/bf00269239
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15(3):473–497. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.1962.tb08052.x
Mutabingwa TK (2005) Artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs): best hope for malaria treatment but inaccessible to the needy! Acta Trop 95(3):305–315. doi:10.1016/j.actatropica.2005.06.009
Paddon CJ, Westfall PJ, Pitera DJ, Benjamin K, Fisher K, McPhee D, Leavell MD, Tai A, Main A, Eng D, Polichuk DR, Teoh KH, Reed DW, Treynor T, Lenihan J, Jiang H, Fleck M, Bajad S, Dang G, Dengrove D, Diola D, Dorin G, Ellens KW, Fickes S, Galazzo J, Gaucher SP, Geistlinger T, Henry R, Hepp M, Horning T, Iqbal T, Kizer L, Lieu B, Melis D, Moss N, Regentin R, Secrest S, Tsuruta H, Vazquez R, Westblade LF, Xu L, Yu M, Zhang Y, Zhao L, Lievense J, Covello PS, Keasling JD, Reiling KK, Renninger NS, Newman JD (2013) High-level semi-synthetic production of the potent antimalarial artemisinin. Nature 496(7446):528–532. doi:10.1038/nature12051
Peplow M (2016) Synthetic biology’s first malaria drug meets market resistance. Nature 530(7591):389–390. doi:10.1038/530390a
Ro D-K, Paradise EM, Ouellet M, Fisher KJ, Newman KL, Ndungu JM, Ho KA, Eachus RA, Ham TS, Kirby J, Chang MCY, Withers ST, Shiba Y, Sarpong R, Keasling JD (2006) Production of the antimalarial drug precursor artemisinic acid in engineered yeast. Nature 440(7086):940–943
Romero MR, Serrano MA, Vallejo M, Efferth T, Alvarez M, Marin J (2006) Antiviral effect of artemisinin from Artemisia annua against a model member of the Flaviviridae family, the bovine viral diarrhoea virus (BVDV). Planta Med 72(13):1169–1174
Schramek N, Wang H, Römisch-Margl W, Keil B, Radykewicz T, Winzenhörlein B, Beerhues L, Bacher A, Rohdich F, Gershenzon J (2010) Artemisinin biosynthesis in growing plants of Artemisia annua. A 13CO2 study. Phytochemistry 71(2):179–187
Shen Q, Chen YF, Wang T, Wu SY, Lu X, Zhang L, Zhang FY, Jiang WM, Wang GF, Tang KX (2012) Overexpression of the cytochrome P450 monooxygenase (cyp71av1) and cytochrome P450 reductase (cpr) genes increased artemisinin content in Artemisia annua (Asteraceae). Genet Mol Res 11(3):3298–3309. doi:10.4238/2012.September.12.13
Shen Q, Lu X, Yan T, Fu X, Lv Z, Zhang F, Pan Q, Wang G, Sun X, Tang K (2016) The jasmonate-responsive AaMYC2 transcription factor positively regulates artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua. New Phytol 210(4):1269–1281. doi:10.1111/nph.13874
Tang K, Shen Q, Yan T, Fu X (2014) Transgenic approach to increase artemisinin content in Artemisia annua L. Plant Cell Rep 33(4):605–615. doi:10.1007/s00299-014-1566-y
Teoh KH, Polichuk DR, Reed DW, Nowak G, Covello PS (2006) Artemisia annua L. (Asteraceae) trichome-specific cDNAs reveal CYP71AV1, a cytochrome P450 with a key role in the biosynthesis of the antimalarial sesquiterpene lactone artemisinin. FEBS Lett 580(5):1411–1416
Teoh KH, Polichuk DR, Reed DW, Covello PS (2009) Molecular cloning of an aldehyde dehydrogenase implicated in artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua. Botany 87(6):635–642. doi:10.1139/b09-032
Towler MJ, Weathers PJ (2007) Evidence of artemisinin production from IPP stemming from both the mevalonate and the nonmevalonate pathways. Plant Cell Rep 26(12):2129–2136
Wallaart TE, Bouwmeester HJ, Hille J, Poppinga L, Maijers NC (2001) Amorpha-4,11-diene synthase: cloning and functional expression of a key enzyme in the biosynthetic pathway of the novel antimalarial drug artemisinin. Planta 212(3):460–465
Wang M, Park C, Wu Q, Simon JE (2005) Analysis of Artemisinin in Artemisia annua L. by LC-MS with selected ion monitoring. J Agric Food Chem 53(18):7010–7013. doi:10.1021/jf051061p
Wang S, Towler MJ, Weathers PJ (2016) Root regulation of artemisinin production in Artemisia annua: trichome and metabolite evidence. Planta 244(5):999–1010. doi:10.1007/s00425-016-2560-0
WHO Malaria Policy Advisory Committee and Secretariat (2016) Malaria Policy Advisory Committee to the WHO: conclusions and recommendations of eighth biannual meeting (September 2015). Malaria J 15(1). doi:10.1186/s12936-016-1169-x
Xiang L, Zeng L, Yuan Y, Chen M, Wang F, Liu X, Zeng L, Lan X, Liao Z (2012) Enhancement of artemisinin biosynthesis by overexpressing dxr, cyp71av1 and cpr in the plants of Artemisia annua L. Plant Omics 5(6):503
Zhang L, Ding R, Chai Y, Bonfill M, Moyano E, Oksman-Caldentey KM, Xu T, Pi Y, Wang Z, Zhang H, Kai G, Liao Z, Sun X, Tang K (2004) Engineering tropane biosynthetic pathway in Hyoscyamus niger hairy root cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(17):6786–6791. doi:10.1073/pnas.0401391101
Zhang Y, Teoh KH, Reed DW, Maes L, Goossens A, Olson DJ, Ross AR, Covello PS (2008) The molecular cloning of artemisinic aldehyde Delta11(13) reductase and its role in glandular trichome-dependent biosynthesis of artemisinin in Artemisia annua. J Biol Chem 283(31):21501–21508. doi:10.1074/jbc.M803090200
Zhang L, Jing F, Li F, Li M, Wang Y, Wang G, Sun X, Tang K (2009) Development of transgenic Artemisia annua (Chinese wormwood) plants with an enhanced content of artemisinin, an effective anti-malarial drug, by hairpin-RNA-mediated gene silencing. Appl Biochem Biotech 52(3):199–207
Zhang G, Zhang Y, Su Z (2012) CYPSI: a structure-based interface for cytochrome P450s and ligands in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Bioinform 13:332–332. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-13-332
Zhang F, Fu X, Lv Z, Lu X, Shen Q, Zhang L, Zhu M, Wang G, Sun X, Liao Z, Tang K (2015) A basic leucine zipper transcription factor, AabZIP1, connects abscisic acid signaling with artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua. Mol Plant 8(1):163–175. doi:10.1016/j.molp.2014.12.004
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by China National High-Tech “863” Program, Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China (Grant No. 2011AA100605), Shanghai Key Discipline Cultivation and Construction Project (Horticulture), and Shanghai Jiao Tong University Agri-Engineering Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11240_2017_1173_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Fig. S A) The mass spectrum of artemisinin standard by UPLC-MS. B) The standard curve (log-log) of artemisinin. C) The chromatographic plot of artemisinin standard. D) The chromatographic plot of representative transgenic Line 63. [M+Na]+=305.1358 (cal. 305.1365), [2M+Na]+=587.2824 (cal. 587.2832). (PDF 163 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, P., Fu, X., Liu, M. et al. Promotion of artemisinin content in Artemisia annua by overexpression of multiple artemisinin biosynthetic pathway genes. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 129, 251–259 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-017-1173-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-017-1173-z