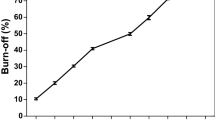
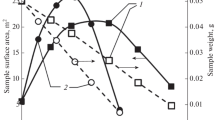
Abstract
The thermodynamic methods of the Arrhenius and Achar-Brindley-Sharp-Wendworth are employed to investigate the influence of the heating rate on oxidation characteristics of three carbon samples. High resolution transmission electron microscopy, Raman spectroscopy, and specific surface area measurements using Brunauer–Emmett–Teller theory are applied to evaluate the influence of the graphitization degree, the microcrystalline length, and the microstructure on the oxidation of carbon black. The results show that with the increase in heating rate, the reaction rate of carbon black increases and the oxidation activation energy gradually decreases; the fitted values of the activation energy range from 136.4 to 221.3 kJ mol−1 with the heating rate is <100 K min−1. Besides, the evaporation and oxidation of simulating soluble organic fractions absorbed on carbon samples can change its internal microstructure, which could influence carbon oxidation. All experimental results indicate that carbon black would sequentially take those steps during oxidation: volatile substance evaporation or oxidation, amorphous carbon oxidation, graphitization, and combustion finally.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhou LB, Liu XJ, Gao ZY. Internal combustion engine fundamentals. 3rd ed. Beijing: Machinery Industry Press; 2005.
Maricq MM. Chemical characterization of particulate emissions from diesel engines: a review. J Aerosol Sci. 2009;38:1079–188.
Bensaid S, Marchisio DL, Russo N, Fino D. Experimental investigation of soot deposition in diesel particulate filters. Catal Today. 2009;147:S295–300.
Bokova MN, Decarne C, Abi-Aad E, Pryakhin AN, Lunin VV, Aboukaïs A. Kinetics of catalytic carbon black oxidation. Thermochim Acta. 2005;428:165–71.
Zouaoui N, Brilhac JF, Mechati F, Jeguirim M, Djellouli B, Gilot P. Study of experimental and theoretical procedures when using thermogravimetric analysis to determine kinetic parameters of carbon black oxidation. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2010;102:837–49.
Sharma HN, Pahalagedara L, Joshi A, Suib SL, Mhadeshwar AB. Experimental study of carbon black and diesel engine soot oxidation kinetics using thermogravimetric analysis. Energy Fuels. 2012;26:5613–25.
Rodríguez-Fernández J, Oliva F, Vázquez RA. Characterization of the diesel soot oxidation process through an optimized thermogravimetric method. Energy Fuels. 2011;25:2040–6.
Chong HS, Aggarwal SK, Lee KO, Yang SY, Seong H. Experimental investigation on the oxidation characteristics of diesel particulates relevant to DPF regeneration. Combust Sci Technol. 2013;185:95–121.
Kalogirou M, Samaras Z. A thermogravimetric kinetic study of uncatalyzed diesel soot oxidation. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2009;98:215–24.
Ledesma B, Román S, Álvarez-Murillo A, Sabio E, González-García CM. Fundamental study on the thermal regeneration stages of exhausted activated carbons: kinetics. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;115:537–43.
Sima-Ella E, Mays TJ. Analysis of the oxidation reactivation of carbonaceous materials using thermogravimetric analysis. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2005;80:109–13.
Zheng M, Banerjee S. Diesel oxidation catalyst and particulate filter modeling in active flow configurations. Appl Therm Eng. 2009;29:3021–35.
Vander Wal RL, Yezertes A, Currier NW, Kim DH, Wang CM. HRTEM study of diesel soot collected from diesel particulate filters. Carbon. 2007;45:70–7.
Vander Wal RL, Tomasek AJ. Soot oxidation: dependence upon initial nanostructure. Combust Flame. 2003;134:1–9.
Vander Wal RL, Tomasek AJ. Soot nanostructure: dependence upon synthesis conditions. Combust Flame. 2004;136:129–40.
Stasio SD. Electron microscopy evidence of aggregation under three different size scales for soot nanoparticles in flame. Carbon. 2001;39:109–18.
Eichholz S, Lerch M, Heck M, Walter D. Various carbon dust particles-studies on thermal behavior. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012;110:437–41.
López-Fonseca R, Landa I, Elizundia U, Gutiérrez-Ortiz MA, González-Velasco JR. Thermokinetic modeling of the combustion of carbonaceous particulate matter. Combust Flame. 2006;144:398–406.
Yezerets A, Currier NW, Kim DH, Eadler HA, Epling WS, Peden CHF. Differential kinetic analysis of diesel particulate matter (soot) oxidation by oxygen using a step-response technique. Appl Catal B. 2005;61:120–9.
Stratakis GA, Konstantas SG, Stamatelos MA. Experimental investigation of the role of soot volatile organic fraction in regeneration of diesel filters. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part D. 2003;217:307–17.
Stanmore RB, Brilhac FJ, Gilot P. The oxidation of soot: a review of experiments, mechanisms and models. Carbon. 2001;39:2247–68.
Song Q, He BL, Yao Q, Meng ZW, Chen CH. Influence of diffusion on thermogravimetric analysis of carbon black oxidation. Energy Fuels. 2006;20:1895–900.
Neeft JPA, Hoornaert F, Makkee M, Moulijn JA. The effects of heat and mass transfer in thermogravimetrical analysis. A case study towards the catalytic oxidation of soot. Thermochim Acta. 1996;287:261–78.
Gilot P, Bonnefoy F, Marcuccilli F, Prado G. Determination of kinetic data for soot oxidation. Modeling of competition between oxygen diffusion and reaction during thermogravimetric analysis. Combust Flame. 1993;95:87–100.
Neeft JPA, Nijhuis TX, Smakman E, Makkee M, Moulijn JA. Kinetics of oxidation of diesel soot. Fuel. 1997;76:1129–36.
He BL. Investigations on LaMnO3 catalysts for diesel particle trap regeneration. Beijing: Tsinghua University; 2006.
Cheng HKF, Chong MF, Liu E, Zhou K, Li L. Thermal decomposition kinetics of multiwalled carbon nanotube/polypropylene nanocomposites. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;117:63–71.
Kalogirou M, Pistikopoulos P, Ntziachristos L, Samaras Z. Isothermal soot oxidation experiments with intermediate gas change in a Perkin-Elmer TG6. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2009;95:141–7.
Chang SY, Wu QW, Yang DX, Duan CK, Zhao YK. Combustion characteristics and dynamic analysis of diesel soot. Trans CSICE. 2009;27:256–8.
Meng ZW, Yang D, Yan Y. The comparison of analysis method of diesel particulate oxidation kinetics. J Xihua Univ (Natural Science Edition). 2013;32:51–5.
Zhang W. Study on the microstructure, surface functional groups and oxidation reactivity of diesel in-cylinder particles. Tianjin: Tianjin University; 2011.
Yehliu K, Vander Wal RL, Armas O, Boehman AL. Impact of fuel formulation on the nanostructure and reactivity of diesel soot. Combust Flame. 2012;159:3597–606.
Fang HL, Lance MJ. Influence of soot surface changes on DPF regeneration. SAE technical paper, 2004, 2004-01-3043.
Zhu JY, Lee KO, Yozgatligil A. Effects of engine operating conditions on morphology, microstructure, and fractal geometry of light-duty diesel engine particulates. Proc Combust Inst. 2005;30:2781–9.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by (1) The National Natural Science Foundation of China (51106130); (2) The Sichuan Provincial Scientific Research Innovation Team Program (KYTD201003); (3) The Youth Foundation of Sichuan Provincial Education Department (10ZB078, 12ZB138); (4) The Open Research Fund of Vehicle Measurement, Control and Safety Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Xihua University (SZJJ2011-001); (5) The Cultivation Fund of the Key Laboratory of Fluid and Power Machinery (Xihua University), Ministry of Education of China (SBZDPY-11-18); (6) The Key Research Fund of Xihua University (Z1120320, Z1120319); (7) The Key Science and Technology Project of Sichuan Province (2011JYZ014); and (8) The innovation foundation of Xihua University (ycjj2014096).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, Z., Yang, D. & Yan, Y. Study of carbon black oxidation behavior under different heating rates. J Therm Anal Calorim 118, 551–559 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-014-4020-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-014-4020-z