Abstract
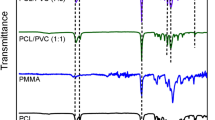
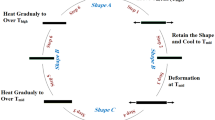
PCL based hybrid films exhibiting heat-responsive shape memory properties had been obtained by using Heptaphenyltricycloheptasiloxane Trihydroxy Silanol (T7-OH) as a cross-linker. The crystallization behaviors of the materials were studied in detail by DSC and XRD. The thermal properties of the materials were detected through TGA. The static mechanical properties, in vitro degradation and shape memory properties were also studied systematically. There was no remarkable T7-OH crystal plane diffraction peak according to XRD which indicated that T7-OH was well dispersed in the matrix. Meanwhile, according to the TGA, thermal degradation temperatures were increased significantly when T7-OH were added. It was worth noting that the materials possessed excellent shape memory properties with Rf > 97 % and Rr > 97 %.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garle A, Kong S, Ojha U, Budhlall BM (2012) Thermoresponsive Semicrystalline poly (ε-caprolactone) networks: exploiting cross-linking with Cinnamoyl moieties to design polymers with tunable shape memory. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4(2):645–657
Zhang D, Petersen KM, Grunlan MA (2012) Inorganic-organic shape memory polymer (SMP) foams with highly tunable properties. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5(1):186–191
Ahn S, Deshmukh P, Gopinadhan M, Osuji CO, Kasi RM (2011) Side-chain liquid crystalline polymer networks: exploiting nanoscale Smectic polymorphism to design shape-memory polymers. ACS Nano 5(4):3085–3095
Luo H, Liu Y, Yu Z, Zhang S, Li B (2008) Novel biodegradable shape memory material based on partial inclusion complex formation between α-Cyclodextrin and poly (ε-caprolactone). Biomacromolecules 9(10):2573–2577
Rochette JM, Ashby VS (2013) Photoresponsive polyesters for tailorable shape memory biomaterials. Macromolecules 46(6):2134–2140
Kumpfer JR, Rowan SJ (2011) Thermo-, photo-, and chemo-responsive shape-memory properties from photo-cross-linked Metallo-supramolecular polymers. J Am Chem Soc 133(32):12866–12874
Rogers N, Khan F (2013) Characterization of deformation induced changes to conductivity in an electrically triggered shape memory polymer. Polym Test 32(1):71–77
Silva JM, Videira M, Gaspar R, Préat V, Florindo HF (2013) Immune system targeting by biodegradable nanoparticles for cancer vaccines. J Control Release 168(2):179–199
Huang Y, Zhang S, Niu B, Wang D, Wang Z, Feng S, Xu H, Kong D, Qiao M (2013) Poly (ɛ-caprolactone) modified with fusion protein containing self-assembled hydrophobin and functional peptide for selective capture of human blood outgrowth endothelial cells. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 101(0):361–369
Wang F, Bronich TK, Kabanov AV, Rauh RD, Roovers J (2005) Synthesis and evaluation of a star amphiphilic block copolymer from poly(ε-caprolactone) and poly(ethylene glycol) as a potential drug delivery carrier. Bioconjug Chem 16(2):397–405
Suksiriworapong J, Sripha K, Kreuter J, Junyaprasert VB (2011) Investigation of polymer and nanoparticle properties with nicotinic acid and p-Aminobenzoic acid grafted on poly (ε-caprolactone)-poly (ethylene glycol)-poly (ε-caprolactone) via click chemistry. Bioconjug Chem 22(4):582–594
Ware T, Hearon K, Lonnecker A, Wooley KL, Maitland DJ, Voit W (2012) Triple-shape memory polymers based on self-complementary hydrogen bonding. Macromolecules 45(2):1062–1069
Meng H, Li G (2013) A review of stimuli-responsive shape memory polymer composites. Polymer 54(9):2199–2221
Huitron-Rattinger E, Ishida K, Romo-Uribe A, Mather PT (2013) Thermally modulated nanostructure of poly (ε-caprolactone)-POSS multiblock thermoplastic polyurethanes. Polymer 54(13):3350–3362
Filion TM, Xu J, Prasad ML, Song J (2011) In vivo tissue responses to thermal-responsive shape memory polymer nanocomposites. Biomaterials 32(4):985–991
Wu J, Ge Q, Mather PT (2010) PEG-POSS multiblock polyurethanes: synthesis, characterization, and hydrogel formation. Macromolecules 43(18):7637–7649
Knight PT, Lee KM, Qin H, Mather PT (2008) Biodegradable thermoplastic polyurethanes incorporating polyhedral Oligosilsesquioxane. Biomacromolecules 9(9):2458–2467
Alvarado-Tenorio B, Romo-Uribe A, Mather PT (2011) Microstructure and phase behavior of POSS/PCL shape memory nanocomposites. Macromolecules 44(14):5682–5692
Li WB, Gong T, Chen HM, Wang L, Li JR, Zhou SB (2013) Tuning surface micropattern features using a shape memory functional polymer. RSC Adv 3:9865–9874
Chen HM, Liu Y, Gong T, Wang L, Zhao KQ, Zhou SQ (2013) Use intermolecular hydrogen bonding synthesize triple-shape memory supermolecular composites. RSC Adv 3:7048–7056
Gu X, Mather PT (2013) Water-triggered shape memory of multiblock thermoplastic polyurethanes (TPUs). RSC Adv 3(36):15783–15791
Masser KA, Yuan H, Karim A, Snyder CR (2013) Polymer chain dynamics in intercalated poly (ε-caprolactone) / Nanoplatelet blends. Macromolecules 46(6):2235–2240
Ni Y, Zheng SX (2007) Supramolecular inclusion complexation of polyhedral oligomeric Silsesquioxane capped poly (ε-caprolactone) with α-Cyclodextrin. J Polym Sci Part A Polym Chem 45:1247–1259
Bai H, Xiu H, Gao J, Deng H, Zhang Q, Yang MB, Fu Q (2012) Tailoring impact toughness of poly (L-lactide) / poly (ε-caprolactone) (PLLA/PCL) blends by controlling crystallization of PLLA matrix. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:897–905
Ghavimi SAA, Ebrahimzadeh MH, Shokrgozarc MA, Solati-Hashjin M, Osman NAA (2015) Effect of starch content on the biodegradation of polycaprolactone/starch composite for fabricating in situ pore-forming scaffolds. Polym Test 43:94–102
Luo X, Mather PT (2009) Preparation and characterization of shape memory elastomeric composites. Macromolecules 42(19):7251–7253
Zhang H, Chen Z, Zheng Z, Zhu X, Wang H (2013) Shape memory polymer hybrids of SBS/dl-PLA and their shape memory effects. Mater Chem Phys 137:750–755
Rodriguez ED, Luo X, Mather PT (2011) Linear/network poly (ε-caprolactone) blends exhibiting shape memory assisted self-healing (SMASH). ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 3(2):152–161
Yang LQ, Li JX, Jin Y, Li M, Gu ZW (2015) In vitro enzymatic degradation of the cross-linked poly (ε-caprolactone) implants. Polym Degrad Stab 112:10–19
Tsou CH, Lee HT, Tsai HA, Cheng HJ, Suen MC (2013) Synthesis and properties of biodegradable polycaprolactone/polyurethanes by using 2,6-pyridinedimethanol as a chain extender. Polym Degrad Stab 98:643–650
Yin GZ, Chen GX, Zhou Z, Li QF (2015) Modification of PEG-b-PCL block copolymer with high melting temperature by the enhancement of POSS crystal and ordered phase structure. RSC Adv 5:33356–33363
Fonseca MA, Abreu B, Gonçalves FAMM, Ferreira AGM, Moreira RAS, Oliveira MSA (2013) Shape memory polyurethanes reinforced with carbon nanotubes. Compos Struct 99 (0): 105–111
Nerantzaki M, Papageorgiou GZ, Bikiaris DN (2014) Effect of nanofiller’s type on the thermal properties and enzymatic degradation of poly (ε-caprolactone). Polym Degrad Stab 108:257–268
Yin GZ, Zhao DL, Wang X, Ren Y, Zhang LW, Wu XX, Nie SP, Li QF (2015) Bio-compatible poly(ester-urethane)s based on PEG–PCL–PLLA copolymer with tunable crystallization and bio-degradation properties. RSC Adv 5:79070–79080
García AV, Santonja MR, Sanahuja AB, Selva MDCG (2014) Characterization and degradation characteristics of poly (ε-caprolactone)-based composites reinforced with almond skin residues. Polym Degrad Stab 108:269–279
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51273017). The authors also thank the anonymous referees for their valuable suggestions which improve the presentation of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(MOV 20 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, G., Zhang, L. & Li, Q. Preparation and characterization of POSS-crosslinked PCL based hybrid materials. J Polym Res 23, 138 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-016-1028-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-016-1028-z