Abstract
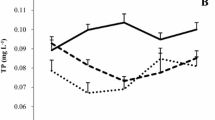
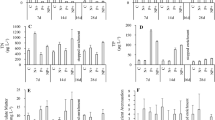
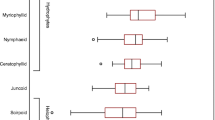
The global climate change may lead to more extreme climate events such as severe flooding creating excessive pulse-loading of nutrients, including nitrogen (N), to freshwaters. We conducted a 3-month mesocosm study to investigate the responses of phytoplankton, zooplankton and Vallisneria spinulosa to different N loading patterns using weekly and monthly additions of in total 14 g N m−2 month−1 during the first 2 months. The monthly additions led to higher phytoplankton chlorophyll a and total phytoplankton biomass than at ambient conditions as well as lower leaf biomass and a smaller ramet number of V. spinulosa. Moreover, the biomass of cyanobacteria was higher during summer (August) in the monthly treatments than those with weekly or no additions. However, the biomass of plankton and macrophytes did not differ among the N treatments at the end of the experiment, 1 month after the termination of N addition. We conclude that by stimulating the growth of phytoplankton (cyanobacteria) and reducing the growth of submerged macrophytes, short-term extreme N loading may have significant effects on shallow nutrient-rich lakes and that the lakes may show fast recovery if they are not close to the threshold of a regime shift from a clear to a turbid state.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biggs, B. J. F. & H. A. Thomsen, 1995. Disturbance of stream periphyton by perturbations in shear stress: time to structural failure and differences in community resistance. Journal of Phycology 31: 233–241.
Cao, T., L. Ni & P. Xie, 2004. Acute biochemical responses of a submersed macrophyte, Potamogeton crispus L., to high ammonium in an aquarium experiment. Journal of Freshwater Ecology 19: 279–284.
Elser, J. J., E. R. Marzolf & C. R. Goldman, 1990. Phosphorus and nitrogen limitation of phytoplankton growth in the freshwaters of North America: a review and critique of experimental enrichments. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 47: 1468–1477.
Field, C. B., V. R. Barros, K. Mach, & M. Mastrandrea, 2014. Climate change 2014: impacts, adaptation, and vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, New York.
González Sagrario, M. A., E. Jeppesen, J. Gomà, M. Søndergaard, J. P. Jensen, T. Lauridsen & F. Landkildehus, 2005. Does high nitrogen loading prevent clear-water conditions in shallow lakes at moderately high phosphorus concentrations? Freshwater Biology 50: 27–41.
Hein, T., G. Heiler, D. Pennetzdorfer, P. Riedler, M. Schagerl & F. Schiemer, 1999. The Danube restoration project: functional aspects and planktonic productivity in the floodplain system. Regulated River Research & Management 15: 259–270.
Higashino, M. & H. G. Stefan, 2014. Modeling the effect of rainfall intensity on soil-water nutrient exchange in flooded rice paddies and implications for nitrate fertilizer runoff to the Oita River in Japan. Water Resources Research 50: 8611–8624.
Huang, X. F., W. M. Chen & Q. M. Cai, 1999. Survey, observation and analysis of lake ecology. Standard methods for observation and analysis in Chinese Ecosystem Research Network, Series V. Standards Press of China, Beijing. (in Chinese).
Jackson, L. J., M. Søndergaard, T. L. Lauridsen & E. Jeppesen, 2007. Patterns, processes, and contrast of macrophyte-dominated and turbid Danish and Canadian shallow lakes, and implications of climate change. Freshwater Biology 52: 1782–1792.
James, C., J. Fisher, V. Russell, S. Collings & B. Moss, 2005. Nitrate availability and hydrophyte species richness in shallow lakes. Freshwater Biology 50: 1049–1063.
Jeppesen, E., J. P. Jensen, C. Jensen, B. Faafeng, D. O. Hessen, M. Søndergaard, T. Lauridsen, P. Brettum & K. Christoffersen, 2003. The impact of nutrient state and lake depth on top-down control in the pelagic zone of lakes: a study of 466 lakes from the temperate zone to the arctic. Ecosystems 6: 313–325.
Jeppesen, E., B. Kronvang, M. Meerhoff, M. Søndergaard, K. M. Hansen, H. E. Andersen, T. L. Lauridsen, L. Liboriussen, M. Beklioglu & A. Özen, 2009. Climate change effects on runoff, catchment phosphorus loading and lake ecological state, and potential adaptations. Journal of Environmental Quality American Society of Agronomy 38: 1930–1941.
Jeppesen, E., P. Nõges, T. A. Davidson, J. Haberman, T. Nõges, K. Blank, T. L. Lauridsen, M. Søndergaard, C. Sayer & R. Laugaste, 2011. Zooplankton as indicators in lakes: a scientific-based plea for including zooplankton in the ecological quality assessment of lakes according to the European Water Framework Directive (WFD). Hydrobiologia 676: 279–297.
Leigh, C., A. Bush, E. T. Harrison, S. S. Ho, L. Luke, R. J. Rolls & M. E. Ledger, 2014. Ecological effects of extreme climatic events on riverine ecosystems: insights from Australia. Freshwater Biology. doi:10.1111/fwb.12515.
Li, W., Z. Zhang & E. Jeppesen, 2008. The response of Vallisneria spinulosa (Hydrocharitaceae) to different loadings of ammonia and nitrate at moderate phosphorus concentration: a mesocosm approach. Freshwater Biology 53: 2321–2330.
Löfgren, S., U. Grandin & S. Stendera, 2014. Long-term effects on nitrogen and benthic fauna of extreme weather events: examples from two Swedish headwater streams. Ambio 43: 58–76.
Moss, B., E. Jeppesen, M. Søndergaard, T. Lauridsen & Z. Liu, 2013. Nitrogen, macrophytes, shallow lakes and nutrient limitation: resolution of a current controversy? Hydrobiologia 710: 3–21.
Olsen, S., F. Chan, W. Li, S. Zhao, M. Søndergaard & E. Jeppesen, 2015. Strong impact of nitrogen loading on submerged macrophytes and algae: a long-term mesocosm experiment in a shallow Chinese lake. Freshwater Biology 60: 1525–1536.
Özkan, K., E. Jeppesen, L. S. Johansson & M. Beklioglu, 2010. The response of periphyton and submerged macrophytes to nitrogen and phosphorus loading in shallow warm lakes: a mesocosm experiment. Freshwater Biology 55: 463–475.
Scheffer, M., S. H. Hosper, M.-L. Meijer, B. Moss & E. Jeppesen, 1993. Alternative equilibria in shallow lakes. Trends in Ecology and Evolution 8: 275–279.
Schindler, D. W., 1977. Evolution of phosphorus limitation in lakes. Science 195: 260–262.
Shivoga, W. A., 2001. The influence of hydrology on the structure of invertebrate communities in two streams flowing into Lake Nakuru, Kenya. Hydrobiologia 458: 121–130.
Strauss, E. A., W. K. Dodds & C. C. Edler, 1994. The impact of nutrient pulses on trophic interactions in a farm pond. Journal of Freshwater Ecology 9: 217–228.
Vollenweider, R. A., 1976. Advances in defining critical loading levels for phosphorus in lake eutrophication. Memorie dell’Istituto italiano di idrobiologia 33: 53–83.
Wang, X. H., C. Q. Yin & B. Q. Shan, 2005. The role of diversified landscape buffer structures for water quality improvement in an agricultural watershed, North China. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment 107: 381–396.
Wang, H. J., H. Z. Wang, X. M. Liang & S. K. Wu, 2014. Total phosphorus thresholds for regime shifts are nearly equal in subtropical and temperate shallow lakes with moderate depths and areas. Freshwater Biology 59: 1659–1671.
Zhao S., L. Yin, F. Chang, S. Olsen, M. Søndergaard, E. Jeppesen. & W. Li, 2015. Response of Vallisneria spinulosa (Hydrocharitaceae) to contrasting nitrogen loadings in controlled lake mesocosms. Hydrobiologia. doi: 10.1007/s10750-015-2456-1.
Zuur, A. F., E. N. Ieno, N. J. Walker, A. A. Saveliev & G. M. Smith, 2009. Mixed effects models and extensions in ecology with R. Statistics for biology and health. Springer, New York.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31170340), CRES (Danish Strategic Research Council), CLEAR (a Villum Kann Rasmussen Centre of Excellence project) and the MARS project (Managing Aquatic ecosystems and water Resources under multiple Stress) funded under the 7th EU Framework Programme, Theme 6 (Environment including Climate Change), Contract No.: 603378 (http://www.mars-project.eu). Mrs. Xie is greatly acknowledged for water sample analyses and Anne Mette Poulsen for valuable editing of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Sidinei M. Thomaz
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Cao, Y., Jeppesen, E. et al. The response of Vallisneria spinulosa (Hydrocharitaceae) and plankton to pulse addition of inorganic nitrogen with different loading patterns. Hydrobiologia 767, 175–184 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-015-2494-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-015-2494-8