Abstract
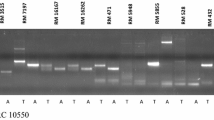
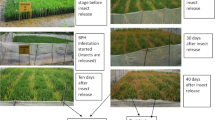
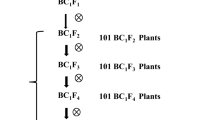
The brown planthopper (BPH) is a potent pest of rice in Asia and Southeast Asia. Host resistance has been found to be the most suitable alternative to manage the insect. But varietal resistance has been found to be short-lived. There has been a constant search for alternate resistance genes. We developed an F8 recombinant inbred population for the BPH resistance gene in Salkathi, an indica landrace from Odisha, India. Phenotyping of RILs against the BPH population at Cuttack, Odisha showed continuous skewed variation with four peaks at 2.1–3.0, 4.1–5.0, 6.1–7.0 and 8.1–9.0 SES score, suggesting the involvement of quantitative loci for resistance to BPH in Salkathi. Mapping showed the presence of two QTLs on the short arm of chromosome 4. One QTL, with phenotype variance of 37.02% is located between the markers RM551 and RM335. The other QTL, with phenotype variance of 7.1% is located between markers RM335 and RM5633. The two QTLs have been designated as qBph4.3 and qBph4.4. QBph4.3 seems to be a novel QTL associated with BPH resistance. We have successfully transferred qBph4.3 and qBph4.4 into two elite rice cultivars, Pusa 44 and Samba Mahsuri. Fine mapping of the identified QTLs may lead to a successful transfer of QTLs into other elite germplasm backgrounds.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam SN, Cohen MB (1998) Detection and analysis of QTLs for resistance to the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens, in a doubled haploid rice population. Theor Appl Genet 97:1370–1379
Ali MP, Alghamdi SS, Begum MA, Anwar Uddin ABM, Alam MZ, Huang D (2012) Screening of rice genotypes for resistance to the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens stal. Cereal Res Commun 40(4):502–508
Annual Report (2011) Multiple resistance screening trial. In: Directorate of Rice Research (ed), Hyderabad, pp 2.12–2.13
Annual Report (2012–2013) Host plant resistance. In: Directorate of rice research (ed), Hyderabad, p 14
Anonymous (2007) Proceedings of 42nd Annual All India Rice Group Meeting. In: Directorate of Rice Research (ed), Hyderabad, 9–11th April, p 34
Basanth YS, Sannaveerappanavar VT, Siddegowda DK (2013) Susceptibility of different populations of Nilaparvata lugens from major rice growing areas of Karnataka, India to different groups of insecticides. Rice Sci 20(5):371–378
Bosque-Perez NA, Buddenhagen IW (1992) The development of host-plant resistance to insects pests: outlook for the topics. In: Menken SBJ, Visser JH, Harrewijn P (eds) Proceedings 8th international symposium insect plant relationships. Springer-Science+Business Media, Dordrecht, pp 235–249
Chatterjee PB (1978) Occurrence of brown planthopper on rice in West Bengal, India. Int Rice Res Newsl 3:12
Chen JW, Wang L, Pang XF, Pan QH (2006) Genetic analysis and fine mapping of a rice brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stal) resistance gene bph19(t). Mol Genet Genomics 275:321–329
Cheng XY, Zhu LL, He CC (2013) Towards understanding of molecular interactions between rice and the brown planthopper. Mol Plant 6:621–634
Das NM, Mammen KV, Christudas SP (1973) Occurrence of Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) (Delphacidae: Homoptera) as a serious pest of paddy in Kerala. Agric Res J Kerala 10:191–192
Dhaliwal GS, Singh J (1983) Outbreaks of white backed planthopper and brown planthopper in Punjab, India. Int Rice Res Newsl 32:26–28
Du B, Zhang WL, Liu BF, Hu J, Wei Z, Shi ZY, He RF, Zhu LL, Chen RZ, Han B (2009) Identification and characterization of Bph14, a gene conferring resistance to brown planthopper in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 52:22163–22168
Dyck VA, Thomas B (1979) The brown planthopper problem. In: International Rice Research Institute (ed) Brown planthopper-threat to rice production in Asia. International Rice Research Institute, Philippines, pp 3–17
Fujita D, Kohli A, Horgan FG (2013) Rice resistance to planthoppers and leafhoppers. Crit Rev Plant Sci 32(3):162–191
Gallagher KD, Kenmore PE, Sogawa K (1994) Judicial use of insecticides deter planthopper outbreaks and extend the life of resistant varieties in southeast Asian rice. In: Denno RF, Perfect JT (eds) Planthoppers: their ecology and management. Chapman and Hall, Boca Raton, pp 599–614
Gangrade GA, Kaushik UK, Patidar GL, Shukla BC, Shrivastava SK, Deshmukh PD, Pophaly DJ (1978) Insect pest of summer paddy in MP. Int Rice Res Newsl 3:16
Gunathilagaraj K, Ganesh Kumar M (1997) Rice insect outbreaks: an analysis. Madras Agric J 84:298–311
Heinrichs EA (1986) Perspectives and directions for the continued development of insect-resistant rice varieties. Agric Ecosyst Environ 18:9–36
Heinrichs EA, Medrano FG, Rapusas HR (1985) Genetic evaluation for insect resistance in rice. International Rice Research Institute, Manila, p 365
Heong KL (2010) Assessing BPH outbreak risks of commonly used insecticides. Available: http://ricehoppers.net/2010/09/farmers-in-central-thailand-remain-trapped-by-the-bph-problem/
Hibino H (1989) Insect-borne viruses in rice. In: Harris KF (ed) Advances in disease vector research. Springer-Verlag, New York, pp 209–241
Hibino H (1996) Biology and epidemiology of rice viruses. Annu Rev Phytopathol 34:249–274
Hirabayashi H, Ogawa T (1995) RFLP mapping of Bph-1 (Brown planthopper resistance gene) in rice. Breed Sci 45:369–371
Hirabayashi H, Angeles ER, Kaji R, Ogawa T, Brar DS, Khush GS (1998) Identification of brown planthopper resistance gene derived from O. officinalis using molecular markers in rice. Breed Sci 48:82
Holland JB, Moser HS, O’Donoughue LS, Lee M (1997) QTLs and epistasis associated with vernalization responses in oat. Crop Sci 37:1309–1414
Holt J, Chancellor TCB, Reynolds DR, Tiongco ER (1996) Risk assessment for rice planthopper and tungro disease outbreaks. Crop Prot 15(4):359–368
Hou L, Yu P, Xu Q, Yuan X, Yu H, Wang Y, Wang C, Wan G, Tang S, Peng S, Wei X (2011) Genetic analysis and preliminary mapping of two recessive resistance genes to brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens Stal in rice. Rice Sci 18:238–242
Hu J, Yang CJ, Zhang QL et al (2011) Resistance of pyramided rice hybrids to brown planthoppers. Chin J Appl Entom 48:1341–1347
Hu J, Li X, Wu C, Yang C, Hua H, Gao G, Xiao J, He Y (2012) Pyramiding and evaluation of the brown planthopper resistance genes Bph14 and Bph15 in hybrid rice. Mol Breed 29:61–69
Hu J, Cheng MX, Gao GJ et al (2013) Pyramiding and evaluation of three dominant brown planthopper resistance genes in the elite indica rice 9311 and its hybrids. Pest Manag Sci 69:802–808
Hu J, Xiao C, Cheng M, Gao G, Zhang Q, He Y (2015a) A new finely mapped Oryza autraliensis- derived QTL in rice confers resistance to brown planthopper. Gene 561:132–137
Hu J, Xiao C, Cheng M, Gao G, Zhang Q, He Y (2015b) Fine mapping and pyramiding of brown planthopper resistance genes QBph3 and QBph4 in an introgression line from wild rice O. officinalis. Mol Breed 35:3. doi:10.1007/s11032-015-0228-2
Hu J, Xiao C, He Y (2016) Recent progress on the genetics and molecular breeding of brown planthopper resistance in rice. Rice 9:30. doi:10.1186/s12284-016-0099-0
Huang Z, He G, Shu L, Li X, Zhang Q (2001) Identification and mapping of two brown planthopper resistance genes in rice. Theor Appl Genet 102:929–934
Huang D, Qiu Y, Zhang Y, Huang F, Meng J, Wei S, Li R, Chen B (2013) Fine mapping and characterization of Bph27, a brown planthopper resistance gene from wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff). Theor Appl Genet 126:219–229
Jena KK, Kim SM (2010) Current status of brown planthopper (BPH) resistance and genetics. Rice 3:161–171
Jena M, Sahu RK, Marndi BC (2006a) Screening of rice varieties for resistance against brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stal.). Oryza 43(4):334–335
Jena KK, Jeung JU, Lee JH, Cho HC, Brar DS (2006b) High-resolution mapping of a new brown planthopper (BPH) resistance gene, Bph18(t) and marker-assisted selection for BPH resistance in rice (Oryza Sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 112:288–297
Ji H, Kim SR, Kim YH et al (2016) Map-based cloning and characterization of the BPH18 gene from wild rice conferring resistance to brown plant hopper (BPH). Insect Pest Sci Rep 6:34376. doi:10.1038/srep34376
Khush GS (1979) Genetics of and breeding for resistance to the brown planthopper. In: International Rice Research Institute (ed) The brown planthopper threat to rice production. International Rice Research Institute, Los Banos, pp 321–332
Khush GS (1984) Breeding rice for resistance to insects. Prot Ecol 7:147–165
Khush GS (1989) Progress in irrigated rice research. International Rice Research Institute, Los Banos, pp 79–92
Khush GS, Brar DS (1991) Genetics of resistance to insects in crop plants. Adv Agron 45:223–274
Khush GS, Virk PS (2005) IR varieties and their impact. International Rice Research Institute, Los Banos
Kim SM, Sohn JK (2005) Identification of a rice gene Bph1 conferring resistance to brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stal.) using STS markers. Mol Cells 20(1):30–34
Lark KG, Chase K, Adler FR, Mansur LM, Orf JJ (1995) Interactions between quantitative trait loci in soybean in which trait variation at one locus is conditional upon a specific allele at another. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:4656–4660
Li H, Hearne S, Banziger M, Li Z, Wang J (2010) Statistical properties of QTL linkage mapping in biparental genetic populations. Heredity 105:257–267
Li H, Zhang L, Wang J (2012) Estimation of statistical power and false discovery rate of QTL mapping methods through computer simulation. Chin Sci Bull 57:2701–2710
Ling KC, Tiongco ER, Aguiero VM (1978) Rice ragged stunt, a new virus disease. Plant Dis Rep 62:701–705
Liu YQ, Su CC, Jiang L, He J, Wu H, Peng C, Wan JM (2009) The distribution and identification of brown planthopper resistance genes in rice. Hereditas 146:67–73
Liu Y et al (2014) A gene cluster encoding lectin receptor kinases confers broad-spectrum and durable insect resistance in rice. Nat Biotechnol 33:301–305
Liu Y, Wu H, Chen H, Liu Y, He J, Kang H et al (2015) A gene cluster encoding lectin receptor kinases confers broad-spectrum and durable insect resistance in rice. Nat Biotechnol 33(3):301–305
Luo X, Fu Y, Zhang P, Wu S, Tian F (2009) Additive and over-dominant effects resulting from epistatic loci are the primary genetic basis of heterosis in rice. J Integr Plant Biol 51:393–408
Meng L, Li H, Zhang L, Wang J (2015) QTL IciMapping: integrated software for genetic linkage map construction and quantitative trait locus mapping in biparental populations. Crop J 3:269–283
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular- weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4432
Myint K, Fujita D, Matsumura M et al (2012) Mapping and pyramiding of two major genes for resistance to the brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål) in the rice cultivar ADR52. Theor Appl Genet 124:495–504
Nguyen TL, Bui CB (2003) Genetic and physical maps of gene Bphl0 controlling brown planthopper resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Omonrice 11:35–41
Normile D (2008) Reinventing rice to feed the world. Science 321:330–337
Pathak MD (1972) Resistance to insect pests in rice varieties. In: International Rice Research Institute (ed) Rice breeding. IRRI, Los Banos, pp 325–341
Qiao Y, Jiang W, Rahman ML, Chu SH, Piao R, Han L, Koh HJ (2008) Comparison of molecular linkage maps and QTLs for morphological traits in two reciprocal backcross populations of rice. Mol Cells 25(3):417–427
Qiu Y, Guo J, Jing S, Zhu L, He G (2010) High-resolution mapping of the brown planthopper resistance gene Bph6 in rice and characterizing its resistance in the 9311 and Nipponbare near isogenic backgrounds. Theor Appl Genet 121:1601–1611
Qiu Y, Guo J, Jing S et al (2012) Development and characterization of japonica rice lines carrying the brown planthopper-resistance genes BPH12 and BPH6. Theor Appl Genet 124:485–494
Rahman ML, Jiang W, Chu SH, Qiao Y, Ham Th, Mo Woo, Lee J, Khanam MS, Chin JH, Jeung JU (2009) High resolution mapping of two rice brown planthopper resistance genes, Bph20 (t) and Bph21(t), originating from Oryza minuta. Theor Appl Genet 119(7):1237–1246
Ramalingam J, Vera Cruz C, Kukreja K, Chittoorr JM, Wu JL, Lee SW (2003) Candidate defense genes from rice, barley and maize and their association with qualitative and quantitative resistance in rice. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 16:14–24
Ren X, Wang X, Yuan H, Weng Q, Zhu L, He G (2004) Mapping quantitative trait loci and expressed sequence tags related to brown planthopper resistance in rice. Plant Breed 123:342–348
Rivera CT, Ou SH, Lida TT (1996) Grassy stunt disease of rice and its transmission by Nilaparvata lugens(stal.). Plant Dis Rep 50:453–456
Rizvi SMA, Singh HM (1983) Brown planthopper in Eastern Uttar Pradesh, India. Int Rice Res Newsl 8:16
Santhanalakshmi S, Saikumar S, Rao S, Saiharini A, Khera P, Shashidhar HE, Kadirvel P (2010) Mapping genetic locus linked to brown planthopper resistance in rice Oryza sativa. Int J Plant Breed Genet 4(1):13–22
Sharma PN, Torii A, Takumi S, Mori N, Nakamura C (2004) Marker-assisted pyramiding of brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stal) resistance genes Bph1 and Bph2 on rice chromosome 12. Hereditas 140:61–69
Sidde Gowda DK, Gubbaiah (2011) Insect pests of rice and their management in Karnataka state of India: a review. Agric Rev 32:55–62
Sogawa K (1982) The rice brown planthopper: feeding physiology and host plant interactions. Annu Rev Entomol 27:49–73
Sogawa K, Liu GJ, Shen JH (2003) A review on the hyper-susceptibility of Chinese hybrid rice to insect pests. Chin J Rice Sci 17:23–30
Soundararajan RP, Kadirvel P, Gunathilagaraj K, Maheswaran M (2004) Mapping of quantitative trait loci associated with resistance to brown planthopper in rice by means of a doubled haploid population. J Agron Crop Sci 44:2214–2220
Su CC, Cheng XN, Zhai HQ, Wan JM (2002) Detection and analysis QTL for resistance to brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål), in rice (Oryza sativa L) using backcross inbred lines. Acta Genet Sin 29:332–338
Su CC, Zhai HQ, Wang CM, Sun LH, Wan JM (2006) SSR mapping of brown planthopper resistance gene Bph9 in Kaharamana, an indica rice (Oryza sativa L.). Acta Genet Sin 33:262–268
Sun L, Su C, Wang C, Zhai H, Wan J (2005) Mapping of a major resistance gene to the brown planthopper in the rice cultivar Rathu Heenati. Breed Sci 55:391–396
Sun LH, Wang CM, Su CC, Liu YQ, Zhai HQ, Wan J (2006) Mapping and marker-assisted selection of a brown planthopper resistance gene bph2 in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Acta Genet Sin 33:171–723
Sun LH, Liu YQ, Jiang L, Su CC, Wang CM, Zhai HQ, Wan JM (2007) Identification of quantitative trait loci associated with resistance to brown planthopper in the indica cultivar Col. 5 Thailand. Hereditas 144:48–52
Tamura Y, Hattori M, Yoshioka H, Yoshioka M, Takahashi A, Wu J, Sentoku N, Yasui H (2014) Map-based cloning and characterization of a brown planthopper resistance gene BPH26 from Oryza sativa L. ssp. indica cultivar ADR52. Sci Rep 4:5872
Visalakshmi V, Satyanarayna H, Jyothula DPB, Raju MRB, Murthy KVR (2014) Screening of rice germplasm for resistance to yellow stem borer Scirpophaga insertulas Walker. Int J Plant Animal Environ Sci 4(1):129–133
Wang Y, Cao L, Zhang Y, Cao C, Liu F, Huang F et al (2015) Map-based cloning and characterization of BPH29, a B3 domain-containing recessive gene conferring brown planthopper resistance in rice. J Exp Bot 66:6035–6045
Wang H, Ye S, Mou T (2016) Molecular breeding of rice restorer lines and hybrids for brown planthopper (BPH) resistance using the Bph14 and Bph15 genes. Rice 9:53. doi:10.1186/s12284-016-0126-1
Watanabe T, Kitagawa H (2000) Photosynthesis and translocation of assimilates in rice plants following phloem feeding by the planthopper Nilaparvata lugens (Homoptera: Delphacidae). J Econ Entomol 93:1192–1198
Wu CJ, Jiang GH, Li X, Liu T, Xu CG, He YQ (2005) Dynamic detection and analysis of QTL for resistance to the brown planthopper using a double haploid rice population. Mol Plant Breed 3(4):456–462
Wu H, Liu Y, He J, Yanling Liu, Jiang L, Liu L, Wang C, Cheng X, Wan J (2014) Fine mapping of brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stàl) resistance gene Bph28(t) in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Breed 33:909–918
Xu XF, Mei HW, Luo LJ, Cheng XN, Li ZK (2002) RFLP facilitated investigation of the quantitative resistance of rice to brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens). Theor Appl Genet 104:248–253
Yang H, Ren X, Weng Q, Zhu L, He G (2002) Molecular mapping and genetics of a rice brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stal) resistance gene. Hereditas 136:39–43
Yang HY, You AQ, Yang ZF, Zhang FT, He RF, Zhu LL, He GC (2004) High-resolution genetic mapping at the Bph15 locus for brown planthopper resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 110:182–191
Yara A, Phi CN, Matsumura M, Yoshimura A, Yasui H (2010) Development of near isogenic lines for Bph25(t) and Bph26(t), which confers resistance to the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stàl) in indica rice ‘ADR52’. Breed Sci 60:639–647
Zhiyong X, Guangxuan TAN, Aiqing YOU, Guangyuan HE, Chaowen SHE, Lijia LI, Yunchun SONG (2004) Comparative physical mapping of rice BAC clones linked to resistance genes Glh, Bph-3 and xa-5 in Oryza sativa L. and O. granulate Nees et Arn ex Watt. Chin Sci Bull 49:591–596
Acknowledgements
We express our gratitude to the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Ministry of Science and Technology, Govt. of India for financial support to carry out this research. We also thank the Director, NRRI, Odisha for providing all necessary infrastructure facility to carry out this research.
Author contribution statement
SKM, RSP, SLM, AN conducted phenotyping and genotyping of RIL mapping population experiment, RKS, SCS and LB developed RIL mapping population, SCS and MJ which contributed to phenotyping of RIL mapping population, LB and SKM carried out QTL analysis, LB, SKM and RSP prepared manuscript, TM helped in preparation and critical review of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohanty, S.K., Panda, R.S., Mohapatra, S.L. et al. Identification of novel quantitative trait loci associated with brown planthopper resistance in the rice landrace Salkathi. Euphytica 213, 38 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-017-1835-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-017-1835-2